Abstract
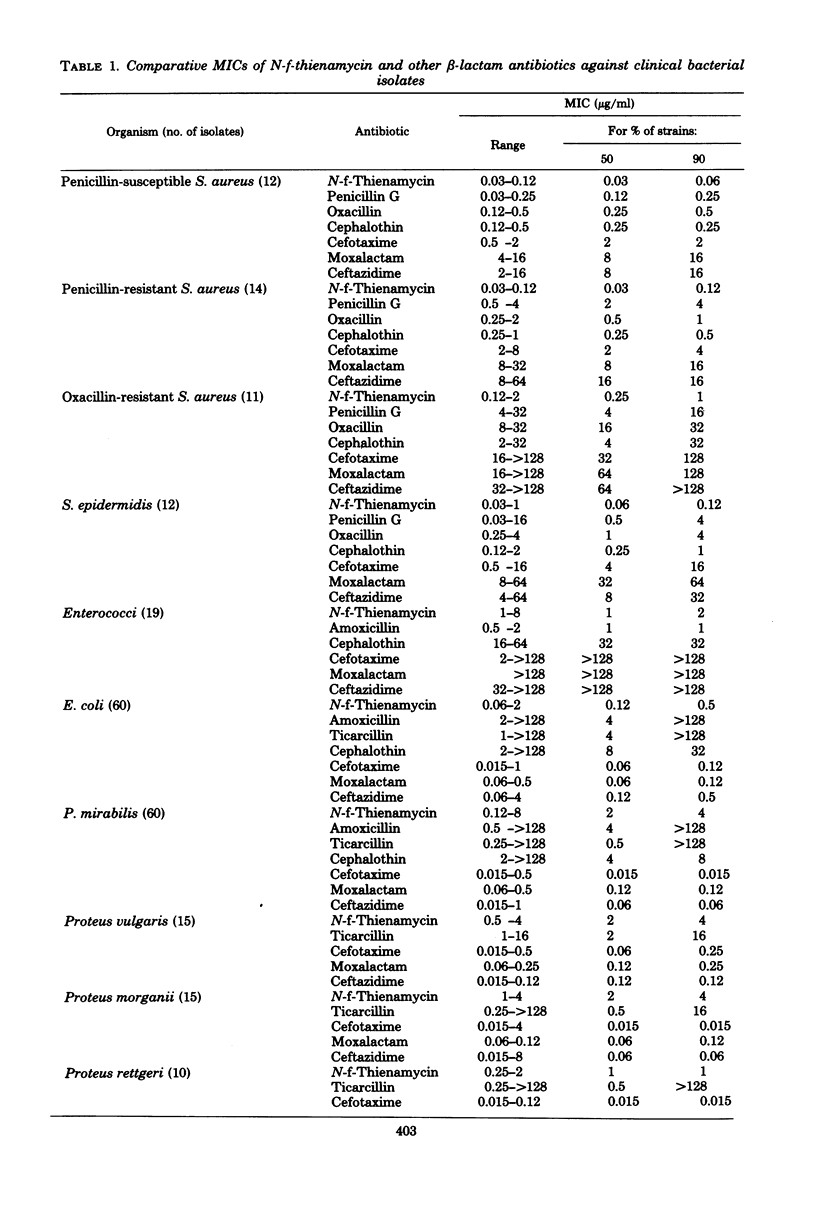
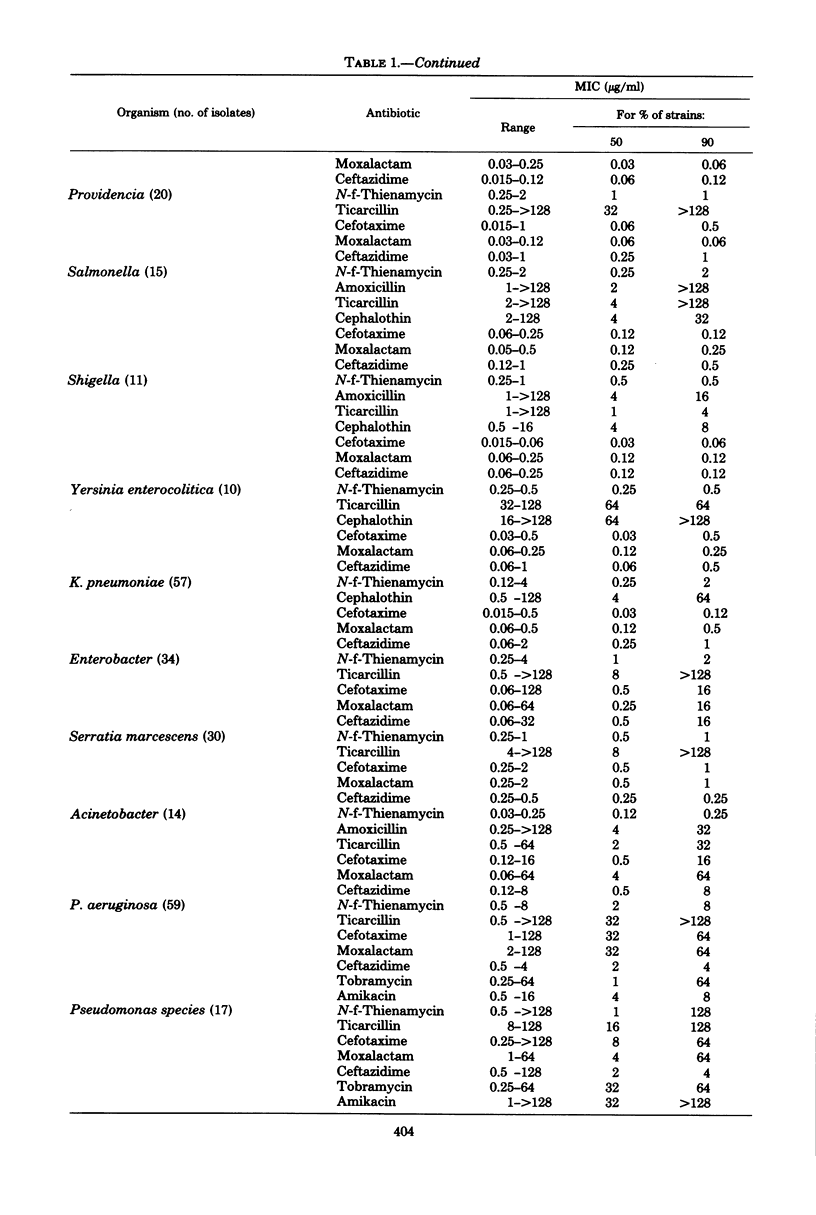
The in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (N-f-thienamycin) was compared with the activities of other B-lactam antibiotics, using over 500 clinical bacterial isolates. N-f-Thienamycin inhibited 90% of the isolates of the common Enterobacteriaceae between 0.006 and 2 microgram/ml, regardless of their resistance to amoxicillin, ticarcillin, or cephalothin. It was, however, fourfold less active than moxalactam and ceftazidime and eightfold less active than cefotaxime. N-f-Thienamycin was nearly as active as ceftazidime against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (mean minimal inhibitory concentration, 3.0 microgram/ml) and eightfold more active than cefotaxime and moxalactam. In contrast to cefotaxime, moxalactam, and ceftazidime, N-f-thienamycin was highly active against enterococci (mean minimal inhibitory concentration, 1.3 microgram/ml) and staphylococci. The oxacillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus were inhibited between 0.03 and 0.12 microgram/ml, and the oxacillin-resistant S. aureus were inhibited between 0.12 and 2 microgram/ml. The high activity of N-f-thienamycin against both of the most important gram-positive and gram-negative organisms makes it a very promising new antibiotic.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Horadam V. W., Smilack J. D., Montgomery C. L., Werringloer J. In vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787), a crystalline derivative of thienamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):557–561. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesado T., Hashizume T., Asahi Y. Antibacterial activities of a new stabilized thienamycin, N-formimidoyl thienamycin, in comparison with other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):912–917. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Kahan J. S., Kahan F. M., Birnbaum J. MK0787 (N-formimidoyl thienamycin): evaluation of in vitro and in vivo activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):993–1000. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. In vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):642–644. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L., Verhaegen J. GR-20263: a new aminothiazolyl cephalosporin with high activity against Pseudomonas and Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):807–812. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


