Abstract
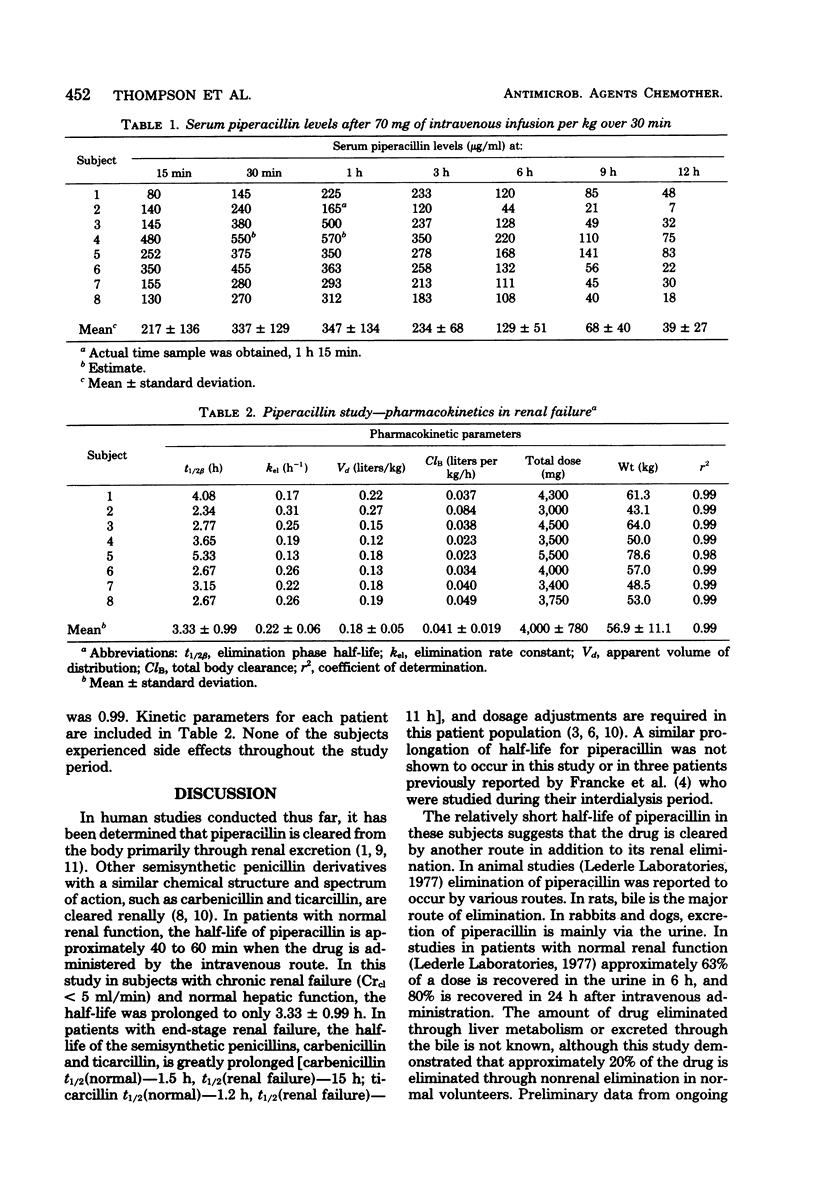
The pharmacokinetic parameters of piperacillin sodium were studied in eight volunteer subjects with chronic renal failure. Subjects were given a single 30-min intravenous infusion of 70 mg/kg (lean body weight) on their off-dialysis day. Blood was drawn from the contralateral arm at 15 and 30 min and 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 h from the start of the infusion. Kinetic parameters were determined during the elimination phase with a one-compartment open model for linear kinetics. The following pharmacokinetic parameters (mean +/- standard deviation) were determined for the eight subjects: elimination half-life = 3.33 +/- 0.99 h, elimination rate constant = 0.22 +/- 0.06 h-1, apparent volume of distribution = 0.18 +/- 0.05 liters per kg, and total body clearance = 0.041 +/- 0.019 liters per kg/h. The mean peak serum concentration was 372 +/- 125 microgram/ml, and mean trough at 12 h was 39 +/- 27 microgram/ml. A dose of 70 mg/kg (lean body weight) or a dose of 4 g appears to provide adequate serum concentrations against susceptible organisms for a 12-h interval. No adverse reactions were noted in any subject throughout the study.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batra V. K., Morrison J. A., Lasseter K. C., Joy V. A. Piperacillin kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Jul;26(1):41–53. doi: 10.1002/cpt197926141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood J. B., Curtis J. R. Carbenicillin administration in patients with severe renal failure. Br Med J. 1968 Feb 24;1(5590):486–487. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5590.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke E. L., Appel G. B., Neu H. C. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous piperacillin in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):788–791. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Lewis R. P., Meyer R. D. Susceptibility of cephalothin-resistant gram-negative bacilli to piperacillin, cefuroxime, and other selected antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):484–489. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Fuchs P. C., Gerlach E. H., Gavan T. L. Piperacillin and carbenicillin; a collaborative in vitro comparison against 10,838 clinical bacterial isolates. Cleve Clin Q. 1979 Summer;46(2):49–55. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.46.2.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latos D. L., Bryan C. S., Stone W. J. Carbenicillin therapy in patients with normal and impaired renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Jun;17(6):692–700. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975176692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers B. R., Hirschman S. Z., Strougo L., Srulevitch E. Comparative study of piperacillin, ticarcillin, and carbenicillin pharmacokinetics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):608–611. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry M. F., Neu H. C. Pharmacokinetics of ticarcillin in patients with abnormal renal function. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):46–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjandramaga T. B., Mullie A., Verbesselt R., De Schepper P. J., Verbist L. Piperacillin: human pharmacokinetics after intravenous and intramuscular administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):829–837. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L. In vitro activity of piperacillin, a new semisynthetic penicillin with an unusually broad spectrum of activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):349–357. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Murphy W., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Piperacillin therapy for serious bacterial infections. Am J Med. 1980 Aug;69(2):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Wang D., Young L. S., Martin W. J., Hewitt W. L. In vitro studies of piperacilin, a new semisynthetic penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):944–950. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


