Abstract
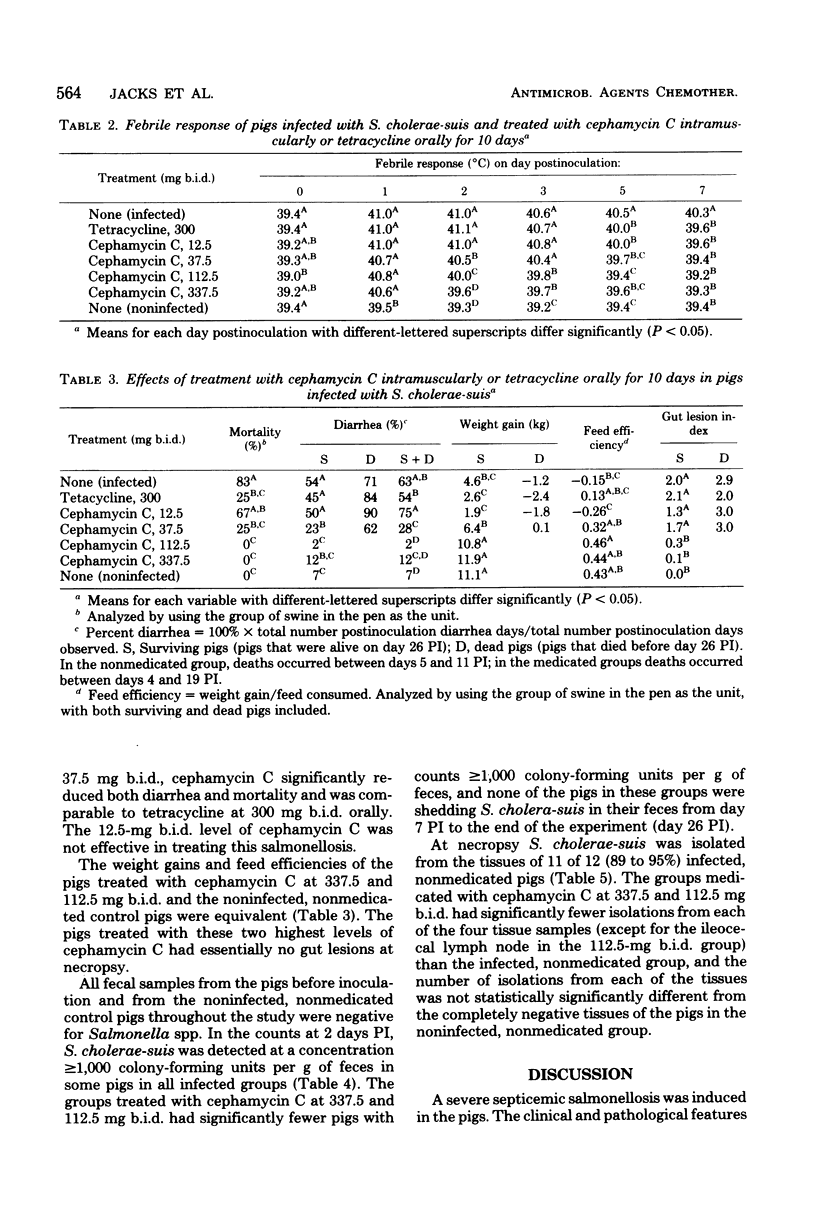
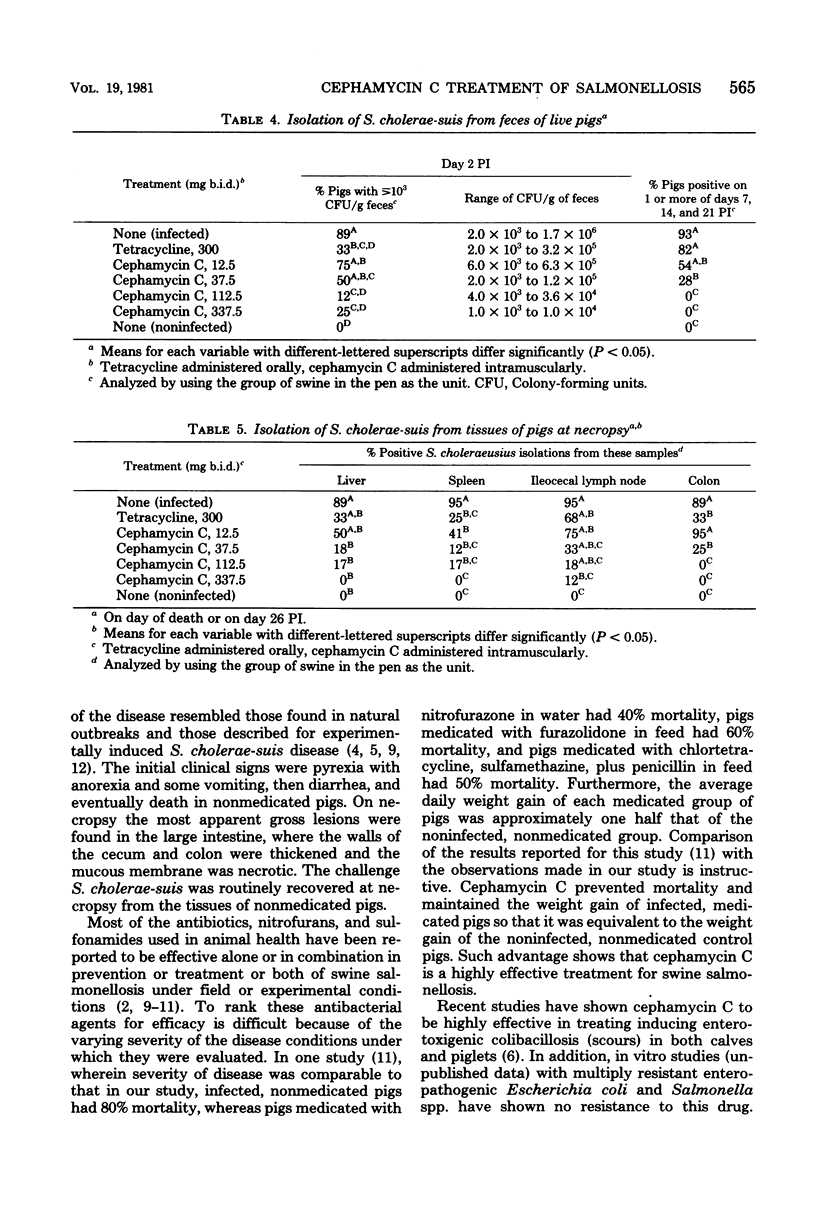
Weanling pigs in groups of 12 were infected orally with Salmonella choleraesuis and were treated intramuscularly with doses of cephamycin C ranging from 12.5 to 337.5 mg twice daily for 10 days beginning 1 day postinoculation. Pigs in two other infected groups either received 300 mg of tetracycline orally on a similar schedule or served as nonmedicated controls. Optimal responses to cephamycin C were achieved at a twice daily dose of 112.5 mg. With this regimen, the febrile response was significantly reduced on day 2 and eliminated by day 5 postinfection, and the shedding of Salmonella spp. in feces was eliminated by day 5 postinfection; essentially, no lesions were found in the gastrointestinal tract at necropsy (day 26 postinfection). There was no mortality among recipients of the 112.5-mg dose; diarrhea was present on only 2% of the observation days. In contrast, 83% of the infected, nonmedicated pigs and 25% of the tetracycline-medicated pigs died, and diarrhea was present in these groups on 63 and 54% of the observation days, respectively. The striking benefits of cephamycin C treatment was achieved without adverse reactions. The weight gain and feed efficiency of the infected pigs treated with the 112.5-mg dose of cephamycin C and the noninfected, nonmedicated control pigs were equivalent.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culbreth W., Simkins K. L., Gale G. O., Messersmith R. E., Alford B. T. Effect of chlortetracycline-sulfamethazine water medication against experimentally induced swine salmonellosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Feb 15;160(4):436–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daoust D. R., Onishi H. R., Wallick H., Hendlin D., Stapley E. O. Cephamycins, a new family of beta-lactam antibiotics: antibacterial activity and resistance to beta-lactamase degradation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):254–261. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson E. A. Salmonella infection in pigs. Br Vet J. 1969 Sep;125(9):431–436. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)48757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Schleim K. D., Judith F. R., Miller B. M. Cephamycin C treatment of induced enterotoxigenic colibacillosis (scours) in calves and piglets. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):397–402. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews J. I., Gibbons R. B. Embolization complicating radial artery puncture. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Jul;75(1):87–88. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. K., Celozzi E., Kong Y., Pelak B. A., Kropp H., Stapley E. O., Hendlin D. Cephamycins, a new family of beta-lactam antibiotics. IV. In vivo studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):287–290. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. K., Celozzi E., Pelak B. A., Stapley E. O., Hendlin D. Cephamycins, a new family of beta-lactam antibiotics. 3. In vitro studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):281–286. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morehouse L. G. Salmonellosis in swine and its control. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Feb 15;160(4):593–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L. D., Rodabaugh D. E., Morehouse L. G. Comparison of furazolidone and carbadox in the feed for treatment of Salmonella choleraesuis in swine. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Oct;38(10):1471–1477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Jones J. E. Observations on experimental oral infection with Salmonella dublin in calves and Salmonella choleraesuis in pigs. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):141–156. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


