Abstract
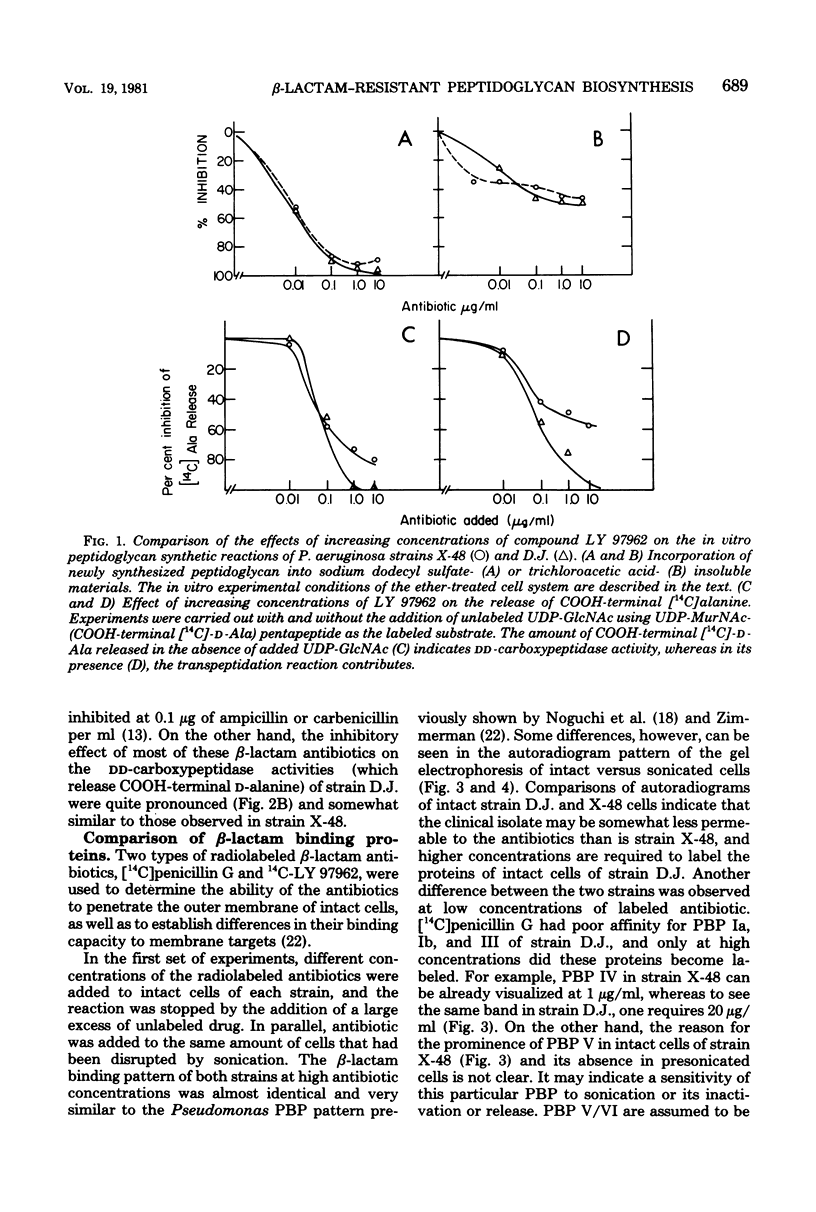
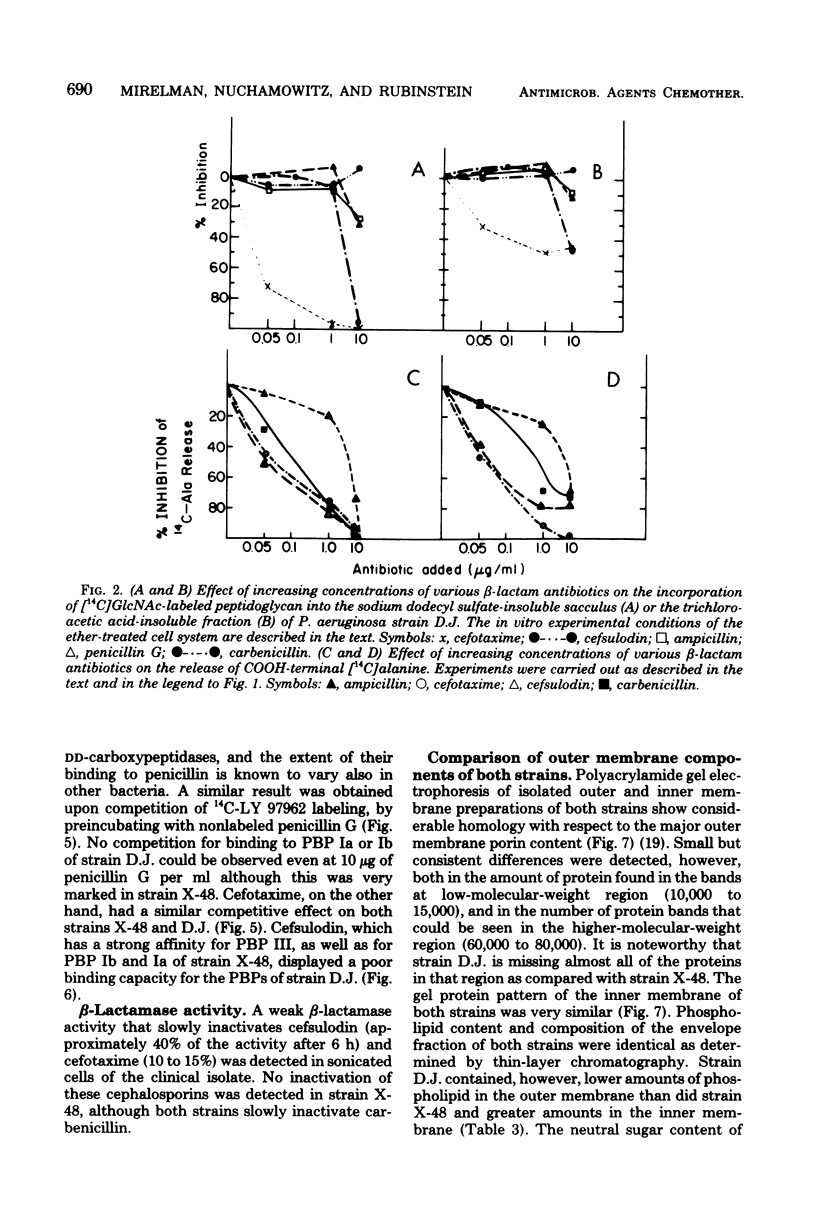
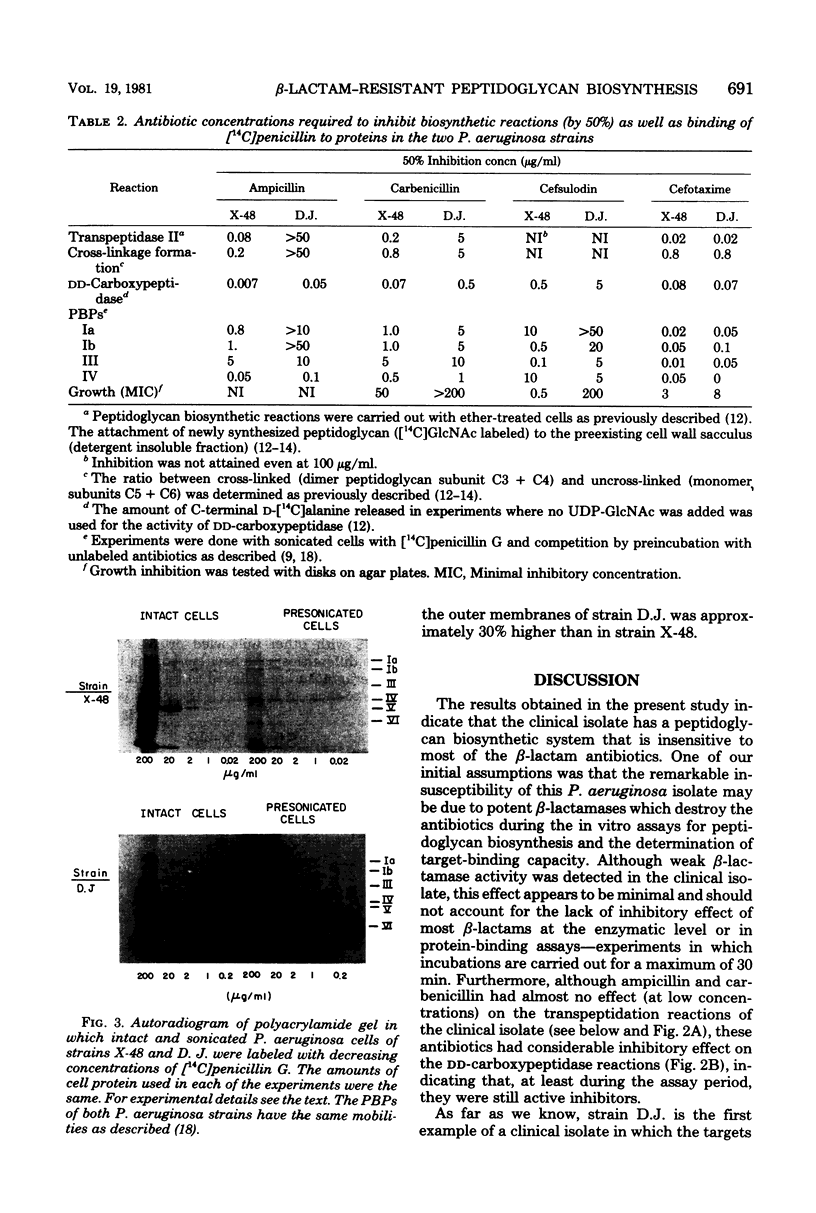
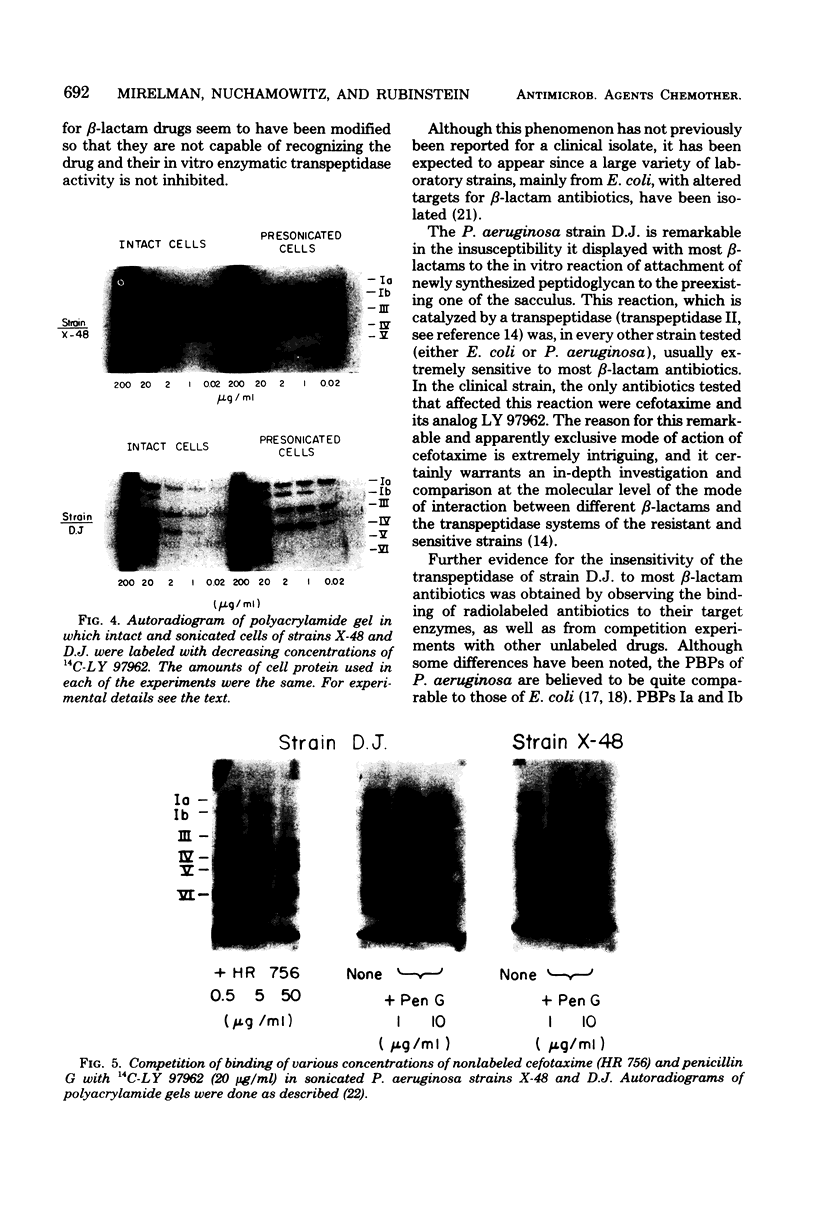
The enzymatic reactions (transpeptidases/ that catalyze the attachment of newly synthesized peptidoglycan to the preexisting cell wall sacculus of both Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa have been shown to be very sensitive to most beta-lactam antibiotics. Biosynthetic studies carried out with a clinical isolate of P. aeruginosa resistant to carbenicillin and cefsulodin showed that the in vitro reactions were also insensitive to most beta-lactam antibiotics (up to 50 micrograms/ml) and only cefotaxime or its tetrazolyl analog, compound LY 97962, had an inhibitory effect at 0.01 microgram/ml. The pattern of beta-lactam binding proteins obtained upon exposure of intact or presonicated cells to radioactively labeled compound LY 97962 or penicillin G indicates that: (i) intact cells of the clinical isolate are 10 to 50 times less permeable to the antibiotics than is the wild-type strain X-48; (ii) beta-lactam binding proteins Ia, Ib, and III of the clinical isolate showed poor affinity for penicillin G and cefsulodin, but were similar to the wild type in their affinity for cefotaxime and compound LY 979062. The two strains also differed in several of their outer membrane components. These results suggest that the insusceptibility of this clinical isolate is due to a combination of outer membrane impermeability and intrinsic insensitivity to most of the beta-lactams on the part of the enzymes which catalyze expansion and growth of peptidoglycan.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buckley R. H., Wray B. B., Belmaker E. Z. Extreme hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and undue susceptibility to infection. Pediatrics. 1972 Jan;49(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitler C. Use of ANS to detect phospholipids and apolar molecules in chromatograms. Anal Biochem. 1972 Nov;50(1):324–325. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90512-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. XIX. Isolation from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and use in reconstitution and definition of the permeability barrier. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.381-390.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANFER J., KENNEDY E. P. METABOLISM AND FUNCTION OF BACTERIAL LIPIDS. I. METABOLISM OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI B. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:2919–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Nuchamowitz Y. Biosynthesis of peptidoglycan in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 1. The incorporation of peptidoglycan into the cell wall. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar;94(2):541–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Nuchamowitz Y. Biosynthesis of peptidoglycan in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 2. Mode of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar;94(2):549–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Nuchamowitz Y. Biosynthesis of peptidoglycan in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of the inhibitory effects of cefotaxime, its anti isomer, and the syn S-oxide compound. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):115–119. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Yashouv-Gan Y., Schwarz U. Regulation of murein biosynthesis and septum formation in filamentous cells of Escherichia coli PAT 84. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1593–1600. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1593-1600.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. A., Jevons S., Brammer K. W. Peptidoglycan transpeptidase inhibition in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli by Penicillins and Cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):513–517. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Permeability of the outer membrane of bacteria. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1979 May;18(5):337–350. doi: 10.1002/anie.197903373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Matsuhashi M., Mitsuhashi S. Comparative studies of penicillin-binding proteins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Nakajima S., Matsuhashi M. Thermosensitive mutation in Escherichia coli simultaneously causing defects in penicillin-binding protein-1Bs and in enzyme activity for peptidoglycan synthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5472–5476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W. Penetration of beta-lactam antibiotics into their target enzymes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of a highly sensitive mutant with its parent strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








