Abstract
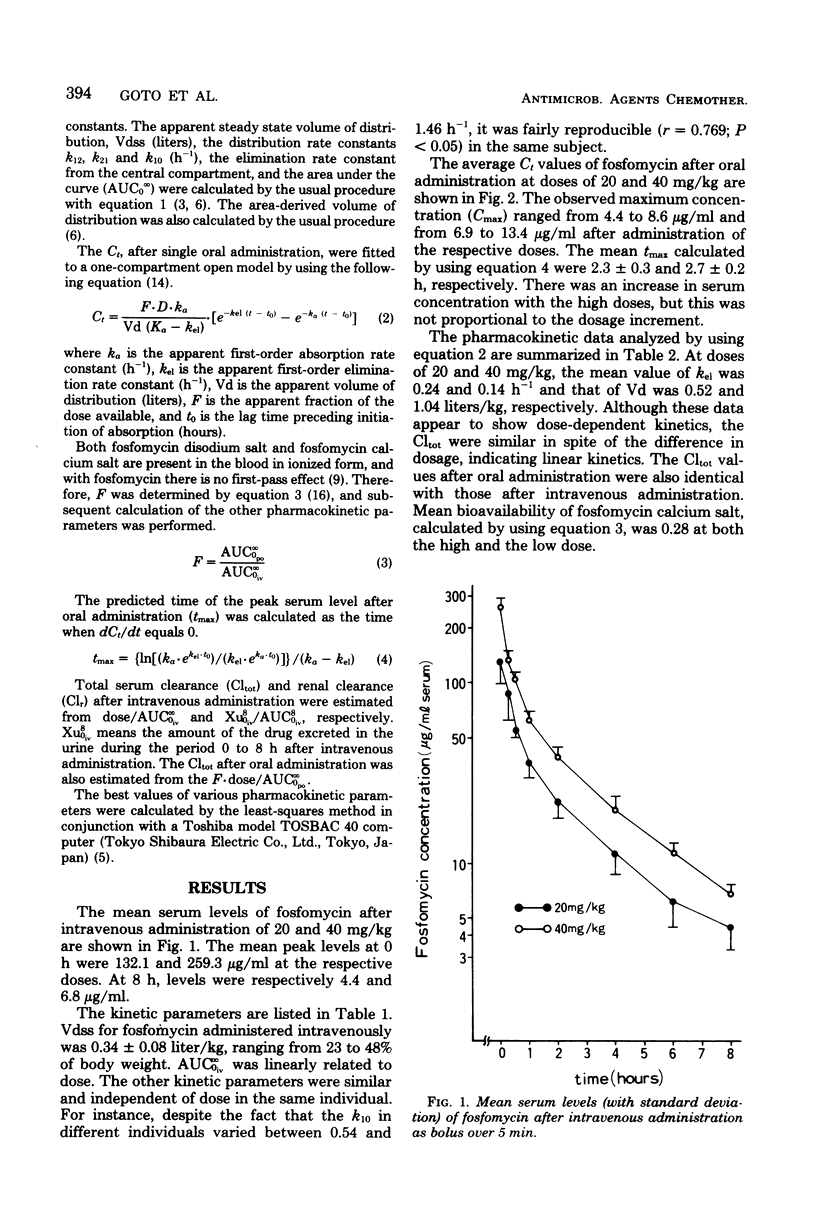
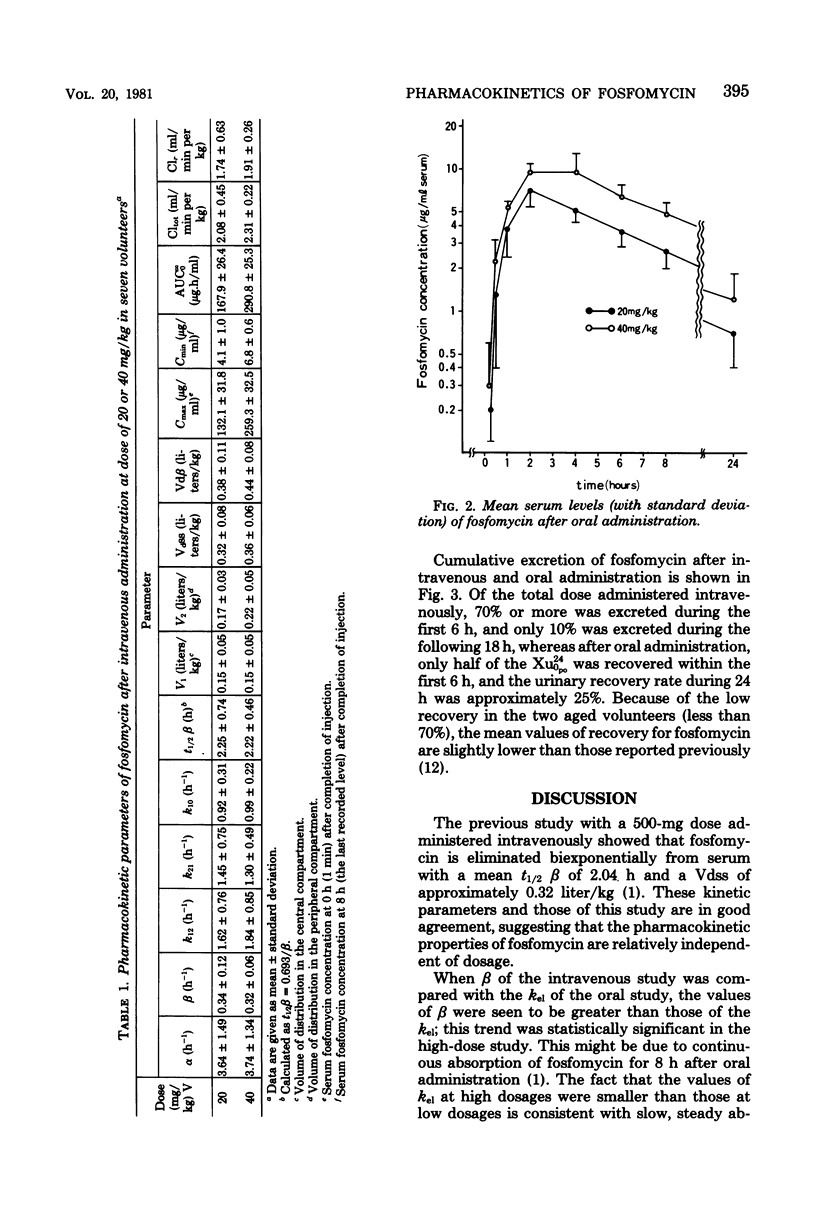
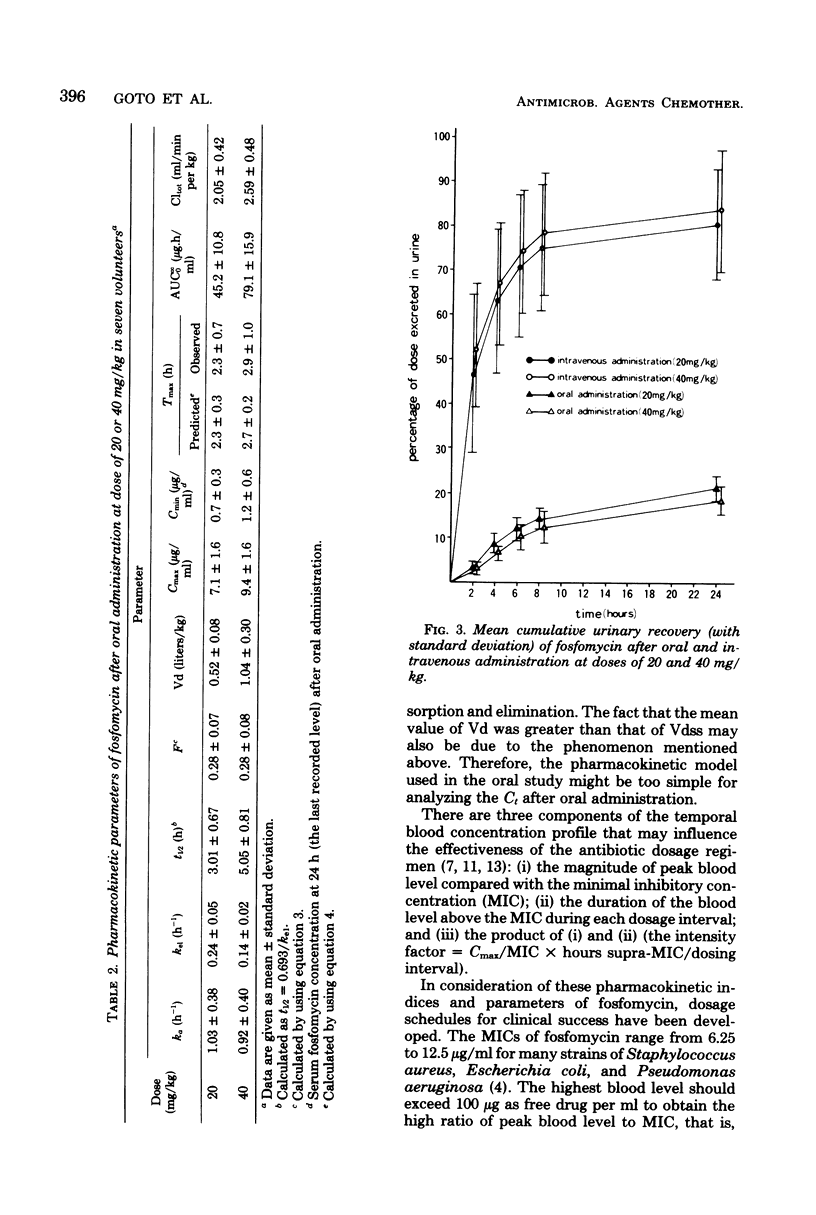
The pharmacokinetics of fosfomycin, administered intravenously and orally at two different doses (20 and 40 mg/kg of body weight), was studied in seven volunteers. The elimination profile of this antibiotic, when administered intravenously, followed a two-compartment kinetic model, independent of dosage, giving an elimination half-life of 2.23 +/- 0.62 h and an average total volume of distribution at steady state of 0.34 liter/kg. Peak serum levels after rapid intravenous administration of 20 and 40 mg/kg were 132.1 +/- 31.8 and 259.3 +/- 32.5 micrograms/ml, respectively. Peak serum levels after oral administration were 7.1 +/- 1.6 and 9.4 +/- 3.6 micrograms/ml for the 20 and 40 mg/kg doses, respectively. During the first 24 h after administration, an average of 80% of the intravenous doses and less than 25% of the oral doses were recovered in the urine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cadórniga R., Diaz Fierros M., Olay T. Pharmacokinetic study of fosfomycin and its bioavailability. Chemotherapy. 1977;23 (Suppl 1):159–174. doi: 10.1159/000222043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Sugiyama M., Ishizaki T. Pharmacokinetic studies with dibekacin, a new aminoglycoside, after intravenous and intramuscular administration to human volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):372–376. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto S. Fosfomycin, antimicrobial activity in vitro and in vivo. Chemotherapy. 1977;23 (Suppl 1):63–74. doi: 10.1159/000222028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Kock-Weser J. Drug therapy. Clinical Pharmacokinetics (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 2;293(14):702–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510022931406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henricks J. N., Schumacher G. E. Using pharmacokinetics in drug therapy. VIII: Pharmacokinetic evaluation of antibiotic dosage regimens. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1980 Oct;37(10):1356–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan F. M., Kahan J. S., Cassidy P. J., Kropp H. The mechanism of action of fosfomycin (phosphonomycin). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):364–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata N., Shiraha Y., Doi S., Umemura K., Yaginuma K. [A study on serum level and urinary excretion of fosfomycin-Na in man with special reference to pharmacokinetic analysis (author's transl)]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1978 Sep;31(9):549–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Daneau D., Swings G., Weerts D. Antibacterial activity in serum and urine as a therapeutic guide in bacterial infections. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):187–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan K. C., Wadke D. A., Foltz E. L. Pharmacokinetics of phosphonomycin in Man. I. Intravenous administration. J Pharm Sci. 1971 May;60(5):678–685. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600600504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrikin D., Rolinson G. N. Antibiotic levels in experimentally infected mice in relation to therapeutic effect and antibacterial activity in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Jul;5(4):423–429. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.4.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen D. D., Fixley M., Azarnoff D. L. Theophylline bioavailability following chronic dosing of an elixir and two solid dosage forms. J Pharm Sci. 1978 Jul;67(7):916–919. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600670711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff H. B., Mata J. M., Hernández S., Mochales S., Rodríguez A., Stapley E. O., Wallick H., Miller A. K., Hendlin D. Fosfomycin: Laboratory studies. Chemotherapy. 1977;23 (Suppl 1):1–22. doi: 10.1159/000222020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


