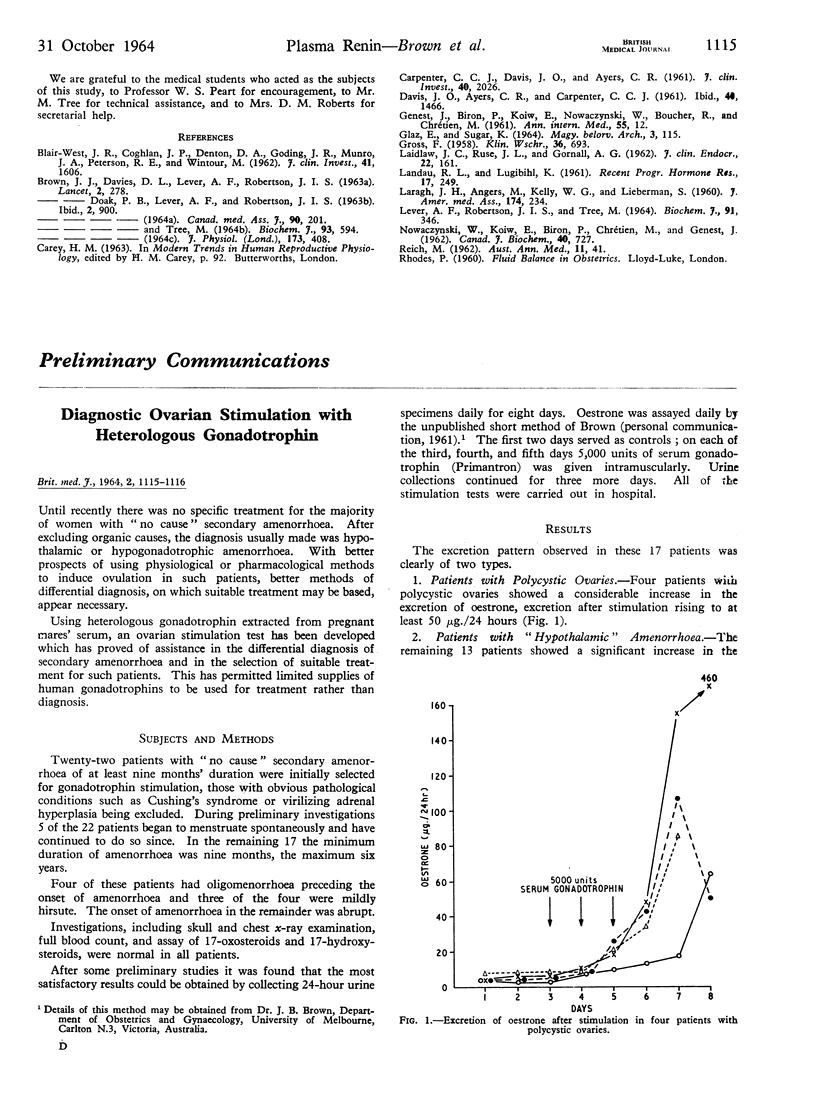
Full text
PDF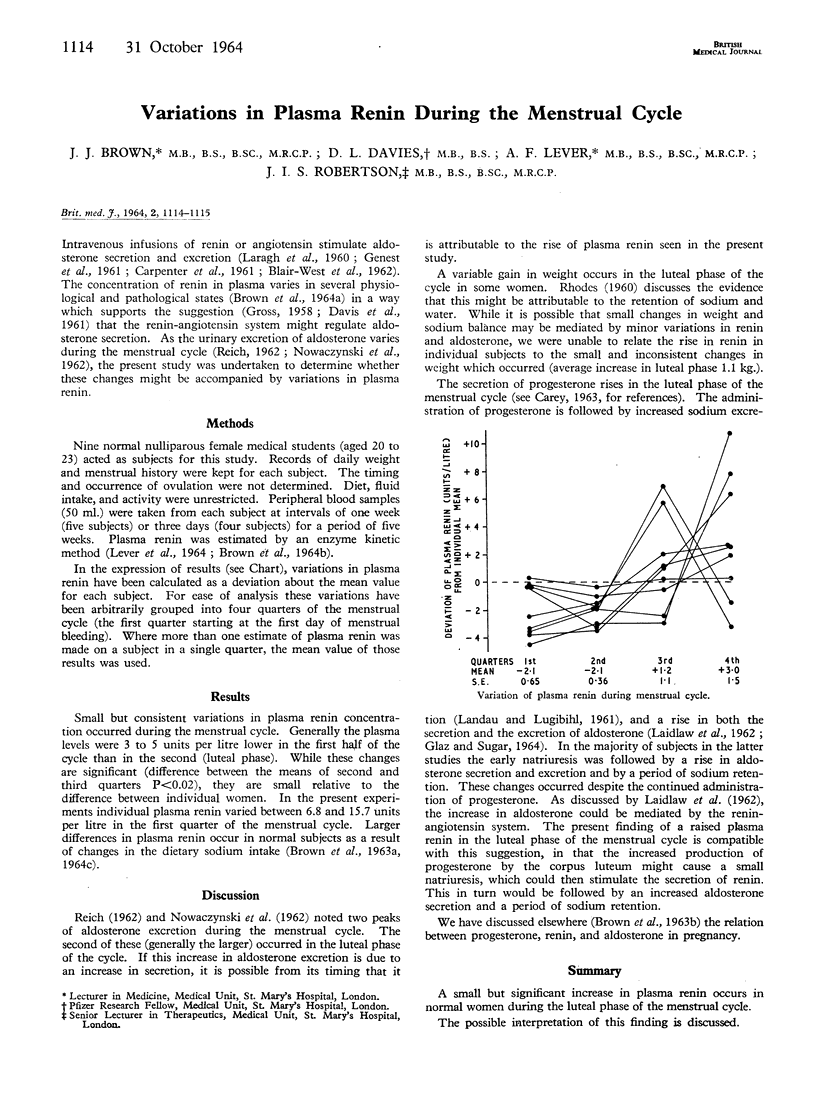
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAIR-WEST J. R., COGHLAN J. P., DENTON D. A., GODING J. R., MUNRO J. A., PETERSON R. E., WINTOUR M. Humoral stimulation of adrenal cortical secretion. J Clin Invest. 1962 Aug;41:1606–1627. doi: 10.1172/JCI104619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN J. J., DAVIES D. L., DOAK P. B., LEVER A. F., ROBERTSON J. I. PLASMA-RENIN IN NORMALPREGNANCY. Lancet. 1963 Nov 2;2(7314):900–901. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90614-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN J. J., DAVIES D. L., LEVER A. F., ROBERTSON J. I. Influence of sodium loading and sodium depletion on plasma-renin in man. Lancet. 1963 Aug 10;2(7302):278–279. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. J., Davies D. L., Lever A. F., Robertson J. I., Tree M. The estimation of renin in human plasma. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):594–600. doi: 10.1042/bj0930594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARPENTER C. C., DAVIS J. O., AYERS C. R. Relation of renin, angiotensin II, and experimental renal hypertension to aldosterone secretion. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:2026–2042. doi: 10.1172/JCI104429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. O., AYERS C. R., CARPENTER C. C. Renal origin of an aldosterone-stimulating hormone in dogs with thoracic caval constriction and in sodium-depleted dogs. J Clin Invest. 1961 Aug;40:1466–1474. doi: 10.1172/JCI104377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GENEST J., BIRON P., KOIW E., NOWACZYNSKI W., BOUCHER R., CHRETIEN M. Studies of the pathogenesis of human hypertension. The adrenal cortex and renal pressor mechanism. Ann Intern Med. 1961 Jul;55:12–28. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-55-1-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS F. Renin und Hypertensin, physiologische oder pathologische Wirkstoffe? Klin Wochenschr. 1958 Aug 1;36(15):693–706. doi: 10.1007/BF01493136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAIDLAW J. C., RUSE J. L., GORNALL A. G. The influence of estrogen and progesterone on aldosterone excretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Feb;22:161–171. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-2-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU R. L., LUGIBIHL K. The catabolic and natriuretic effects of progesterone in man. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1961;17:249–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARAGH J. H., ANGERS M., KELLY W. G., LIEBERMAN S. Hypotensive agents and pressor substances. The effect of epinephrine, norepinephrine, angiotensin II, and others on the secretory rate of aldosterone in man. JAMA. 1960 Sep 17;174:234–240. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03030030014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOWACZYNSKI W., KOIW E., BIRON P., CHRETIEN M., GENEST J. Effects of angiotensin infusions on urinary excretion of compound III and substances other than aldosterone. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1962 Jun;40:727–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH M. The variations in urinary aldosterone levels of normal females during their menstrual cycle. Australas Ann Med. 1962 Feb;11:41–49. doi: 10.1111/imj.1962.11.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



