Abstract
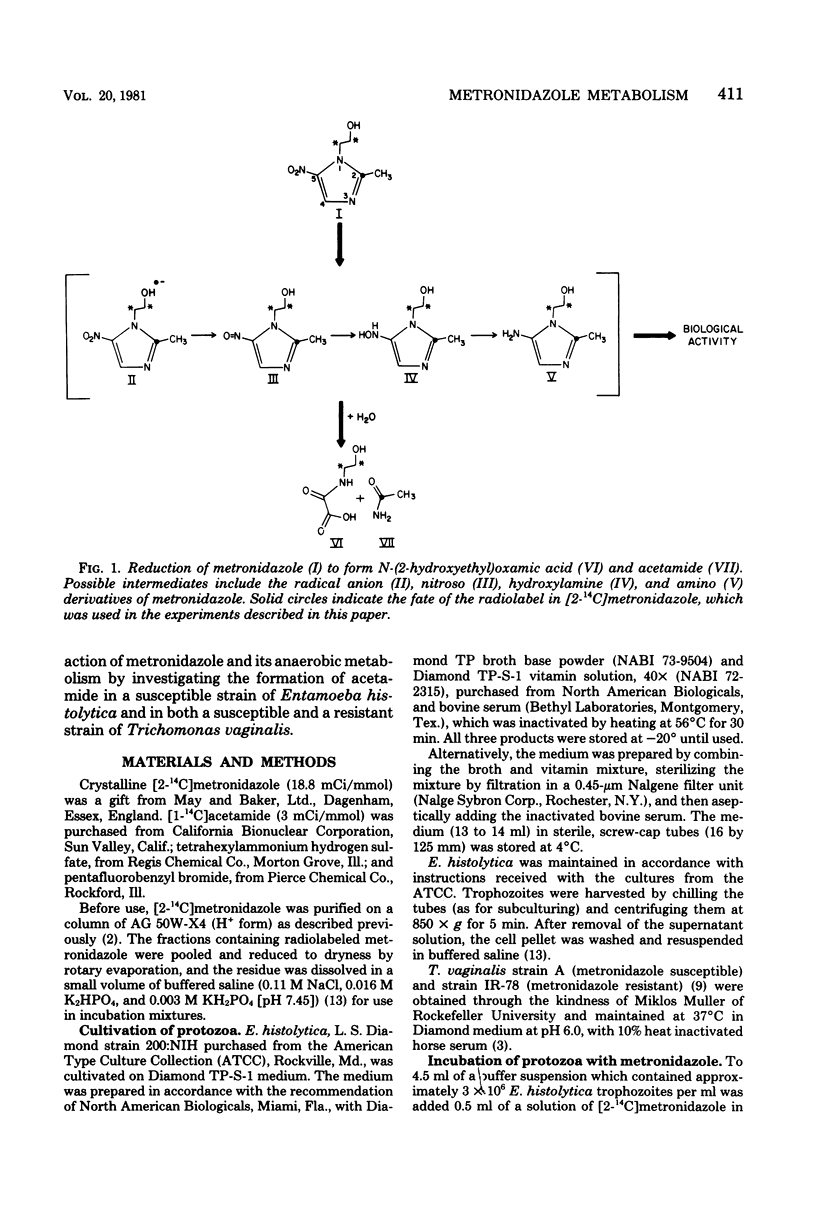
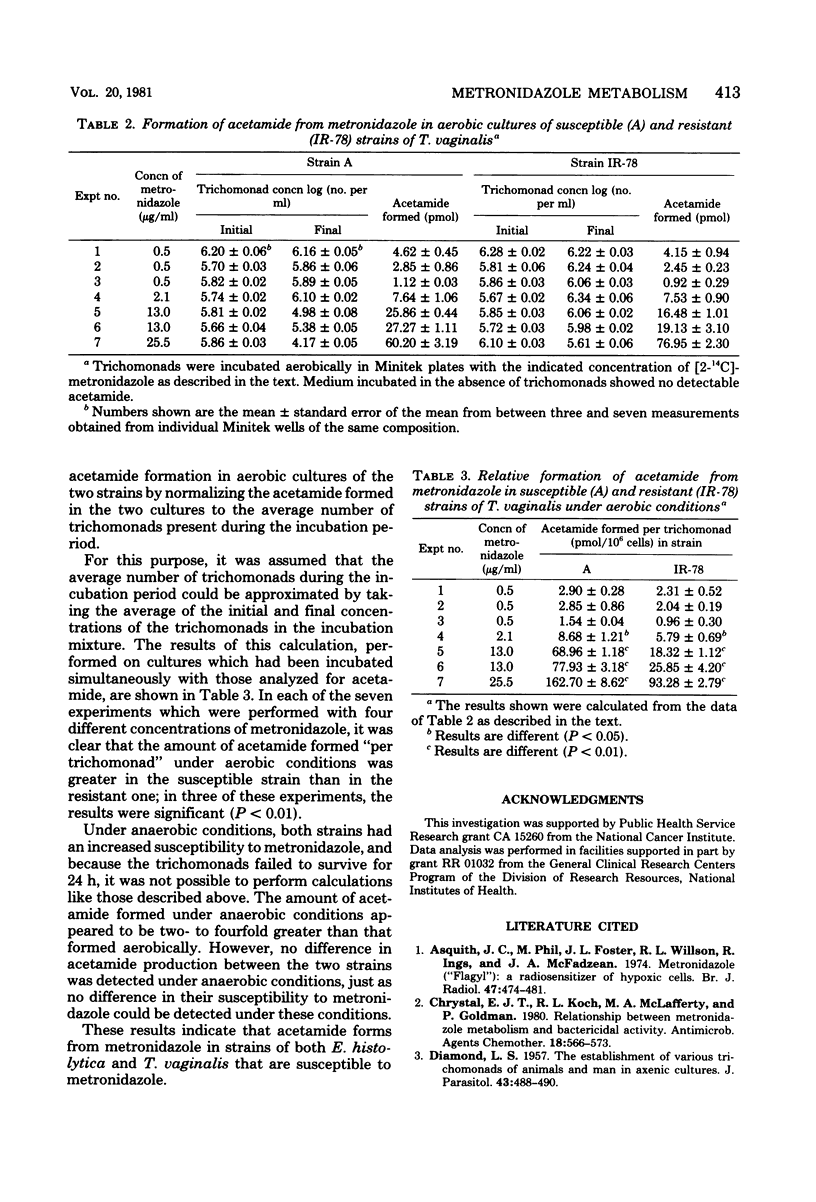
Acetamide forms from metronidazole in cultures of either Entamoeba histolytica or Trichomonas vaginalis as it does in cultures of bacteria which are susceptible to this drug. Under aerobic conditions, the formation of acetamide is more rapid in a strain of T. vaginalis which is more susceptible to metronidazole. Thus, it appears that the formation of acetamide may be associated with the microbiocidal action of metronidazole.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asquith J. C., Foster J. L., Willson R. L., Ings R., McFadzean J. A. Metronidazole ("Flagyl"). A radiosensitizer of hypoxic cells. Br J Radiol. 1974 Aug;47(560):474–481. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-47-560-474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrystal E. J., Koch R. L., McLafferty M. A., Goldman P. Relationship between metronidazole metabolism and bactericidal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):566–573. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND L. S. The establishment of various trichomonads of animals and man in axenic cultures. J Parasitol. 1957 Aug;43(4):488–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ings R. M., McFadzean J. A., Ormerod W. E. The mode of action of metronidazole in Trichomonas vaginalis and other micro-organisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 May 1;23(9):1421–1429. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight R. C., Skolimowski I. M., Edwards D. I. The interaction of reduced metronidazole with DNA. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(17):2089–2093. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90277-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch R. L., Chrystal E. J., Beaulieu B. B., Jr, Goldman P. Acetamide--a metabolite of metronidazole formed by the intestinal flora. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Dec 15;28(24):3611–3615. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90407-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch R. L., Goldman P. The anaerobic metabolism of metronidazole forms N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-oxamic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Mar;208(3):406–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Tomasz M., Müller M., Lipman R. Interaction of metronidazole with nucleic acids in vitro. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;13(5):872–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meingassner J. G., Thurner J. Strain of Trichomonas vaginalis resistant to metronidazole and other 5-nitroimidazoles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):254–257. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Lindmark D. G. Uptake of metronidazole and its effect on viability in trichomonads and Entamoeba invadens under anaerobic and aerobic conditions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):696–700. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Reyes E., Kalyanaraman B., Mason R. P. The reductive metabolism of metronidazole and ronidazole by aerobic liver microsomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;17(2):239–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Metronidazole versus anaerobes. In vitro data and initial clinical observations. Calif Med. 1972 Dec;117(6):22–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbach E. C., Diamond L. S. Entamoeba histolytica. I. Aerobic metabolism. Exp Parasitol. 1974 Apr;35(2):232–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(74)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



