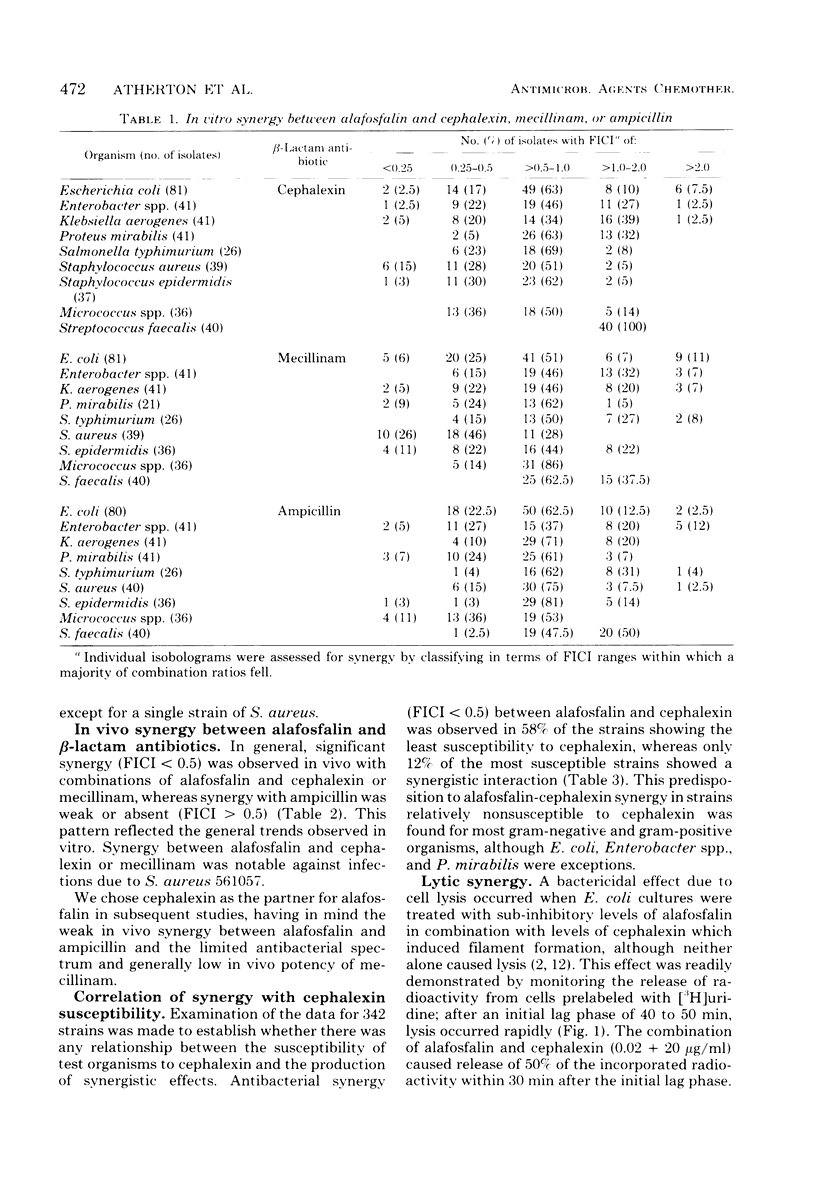
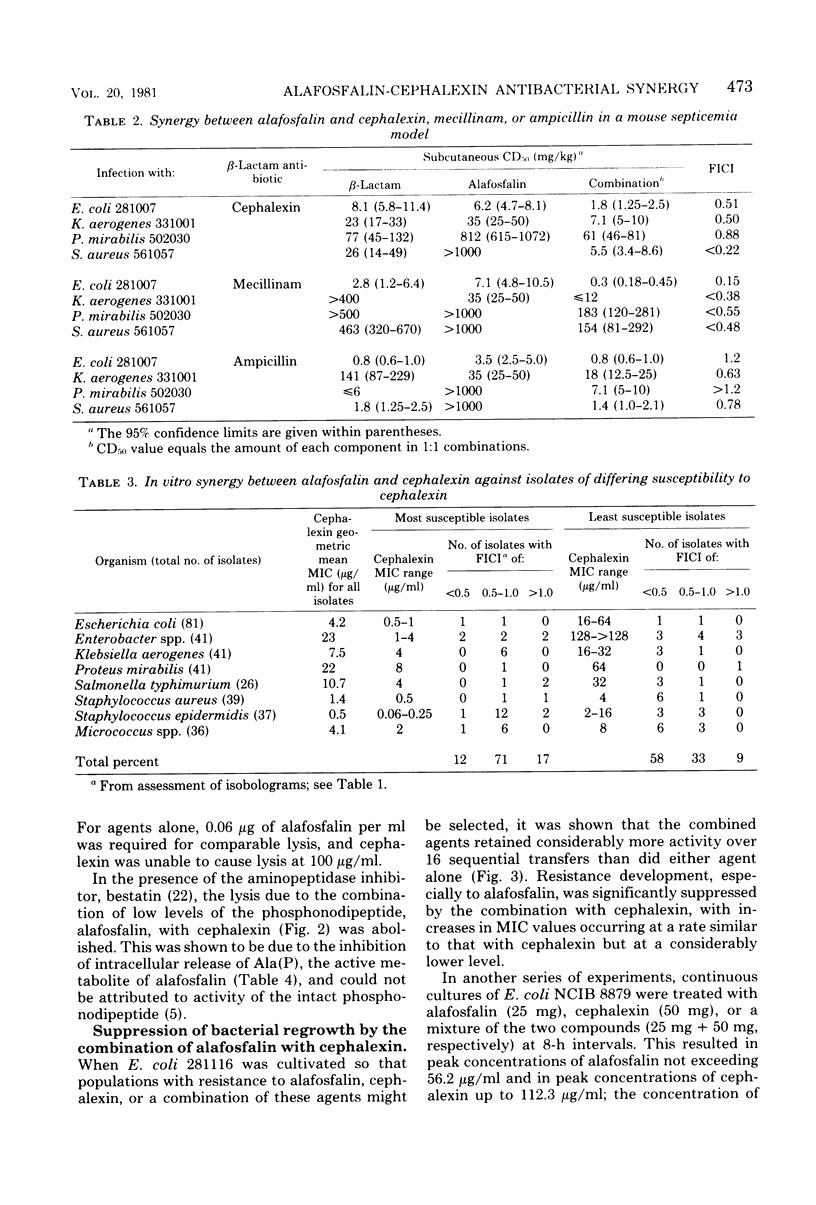
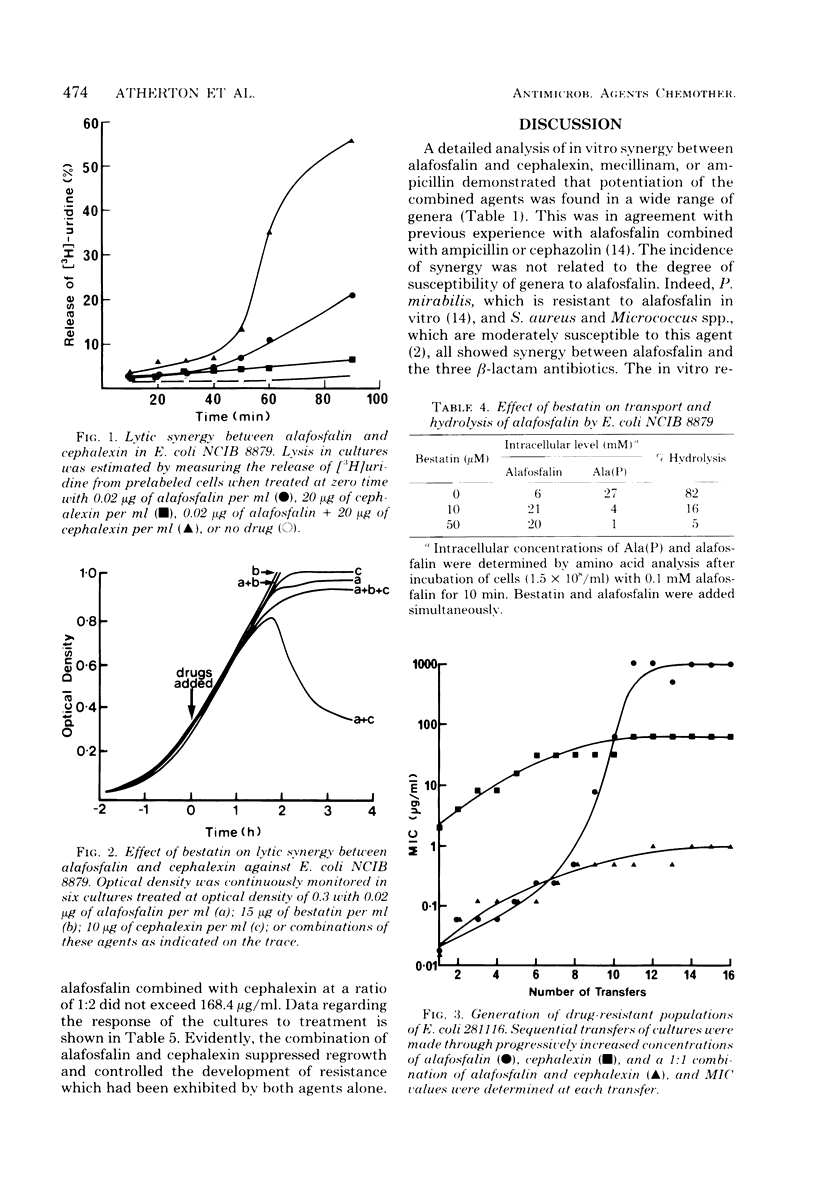
Abstract
The phosphonopeptide alafosfalin (L-alanyl-L-1-aminoethylphosphonic acid) exhibited synergy in vitro and in animal studies against a range of bacterial genera when combined with cephalexin. Alafosfalin also showed synergy with mecillinam and, to a much lesser extent, with ampicillin. Synergy with cephalexin was more pronounced when the bacteria were relatively insensitive to the beta-lactam component. The action of this combination involved both an inhibitory and a bacteriolytic mechanism which was abolished by concurrent treatment with the aminopeptidase inhibitor, bestatin. Regrowth of subpopulation resistant to either component was markedly reduced by the combination. The potential of alafosfalin combined with cephalexin for use in therapy is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. G., Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Nisbet L. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides as antibacterial agents: alaphosphin and related phosphonopeptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):684–695. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. G., Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Nisbet L. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides, a new class of synthetic antibacterial agents. Nature. 1978 Mar 2;272(5648):56–58. doi: 10.1038/272056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. G., Lees L. J. Pharmacokinetics of alafosfalin, alone and in combination with cephalexin, in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):973–979. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Lloyd W. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptide antibacterial agents related to alafosfalin: design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):897–905. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Lambert R. W., Lloyd W. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides as antibacterial agents: mechanism of action of alaphosphin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):696–705. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Lambert R. W., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides as antibacterial agents: rationale, chemistry, and structure-activity relationships. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):677–683. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELION G. B., SINGER S., HITCHINGS G. H. Antagonists of nucleic acid derivatives. VIII. Synergism in combinations of biochemically related antimetabolites. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillett A. P., Wise R., Geddes A. M. Use of antibiotics. Infection in the compromised host. Br Med J. 1978 Jul 29;2(6133):335–337. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6133.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., O'Grady F. Comparison of the responses of Escherichia coli and proteus mirabilis to seven beta-lactam antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):211–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., O'Grady F. FL 1060: a new beta-lactam antibiotic with novel properties. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Jan;26(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendlin D., Frost B. M., Thiele E., Kropp H., Valiant M. E., Pelak B., Weissberger B., Cornin C., Miller A. K. Phosphonomycin. 3. Evaluation in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1969;9:297–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama H. B., Arisawa M., Sawada T. Alafosfalin, a new inhibitor of cell wall biosynthesis: in vitro activity against urinary isolates in Japan and potentiation with beta-lactams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):444–451. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Medoff G., Leech I., Wennersten C., Kunz L. J. Antibiotic synergism against Listeria monocytogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jan;1(1):30–34. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUHAUS F. C., LYNCH J. L. THE ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF D-ALANYL-D-ALANINE. 3. ON THE INHIBITION OF D-ALANYL-D-ALANINE SYNTHETASE BY THE ANTIBIOTIC D-CYCLOSERINE. Biochemistry. 1964 Apr;3:471–480. doi: 10.1021/bi00892a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Wheeler N., Laverdiere M., Blazevic D., Wilkinson B. J. A new type of penicillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1977 Feb 26;1(8009):443–447. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91941-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt L. S., Botta G., Park J. T. Effects of furazlocillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic which binds selectively to penicillin-binding protein 3, on Escherichia coli mutants deficient in other penicillin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):632–637. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.632-637.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J. Mode of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Jan-Feb;1(1):39–54. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Kondo M., Nagatomo H. SCE-129, antipseudomonal cephalosporin: in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):137–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Aoyagi T., Suda H., Hamada M., Takeuchi T. Bestatin, an inhibitor of aminopeptidase B, produced by actinomycetes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Jan;29(1):97–99. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



