Abstract
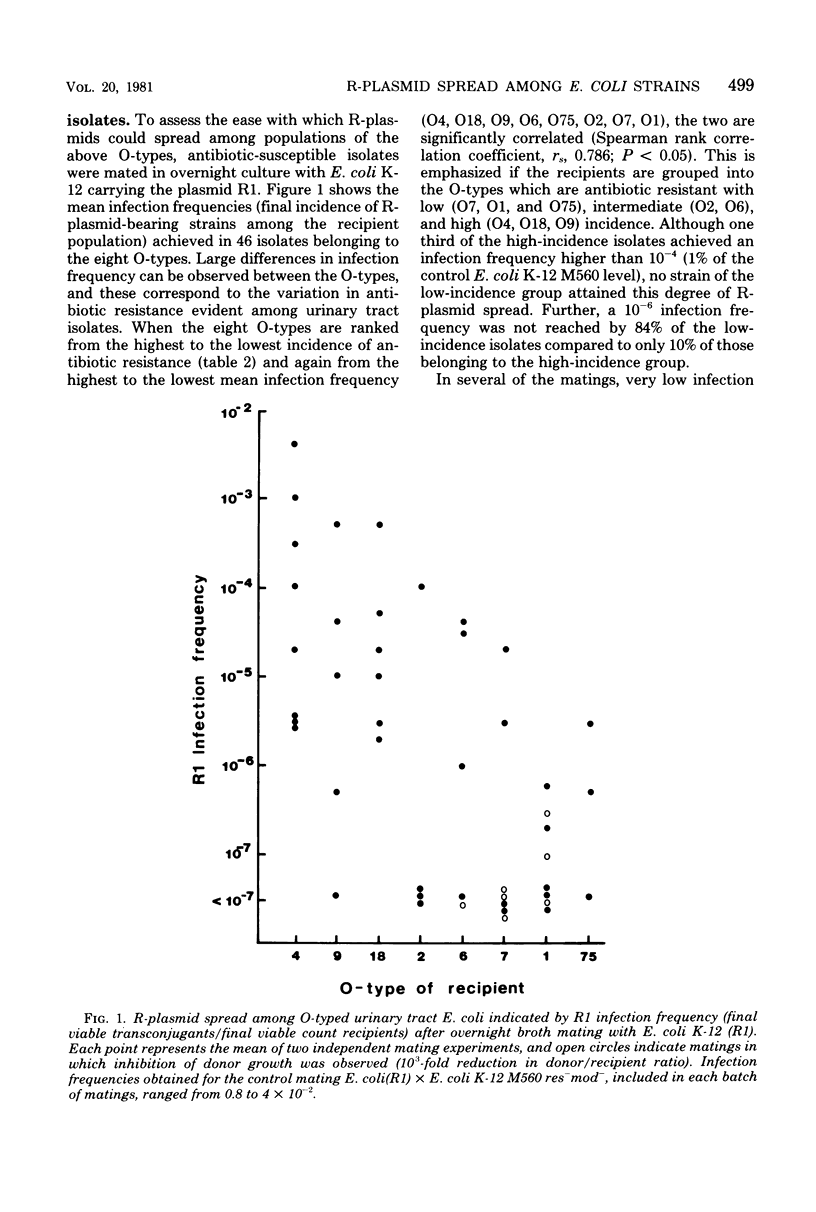
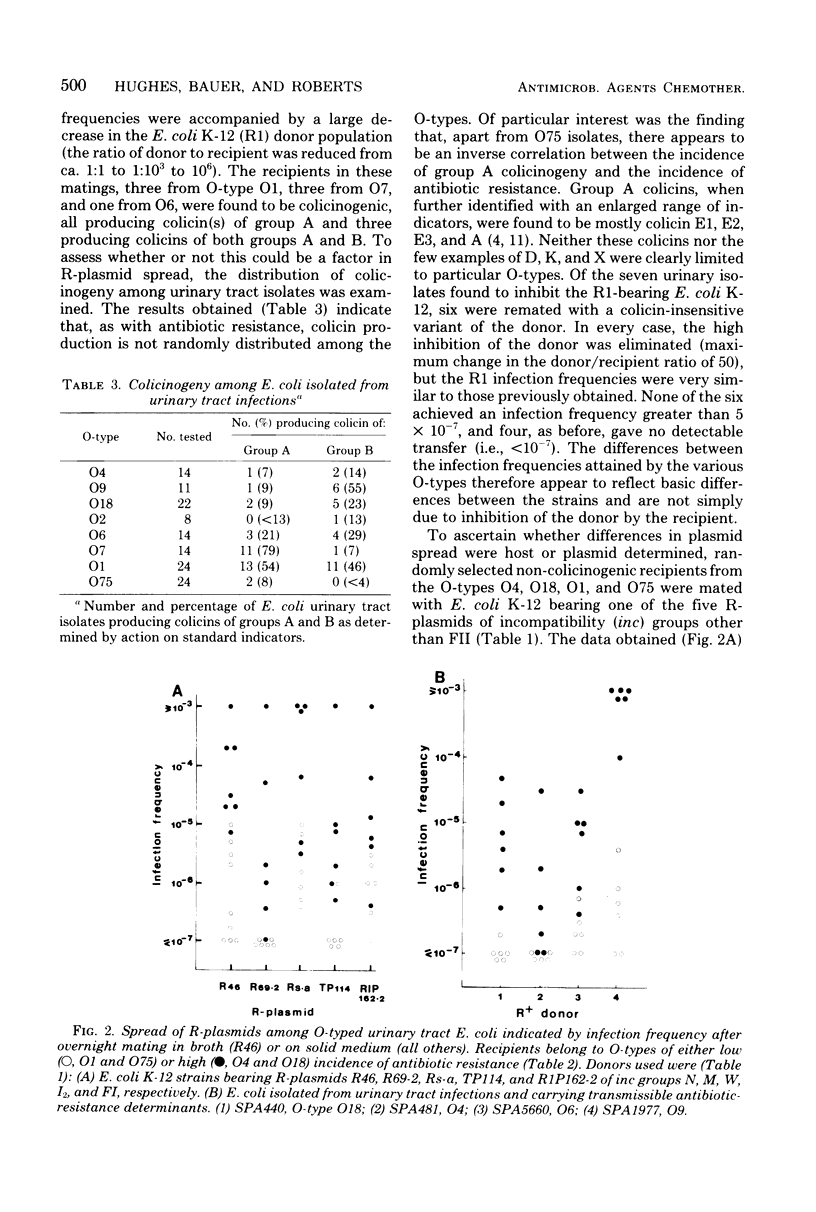
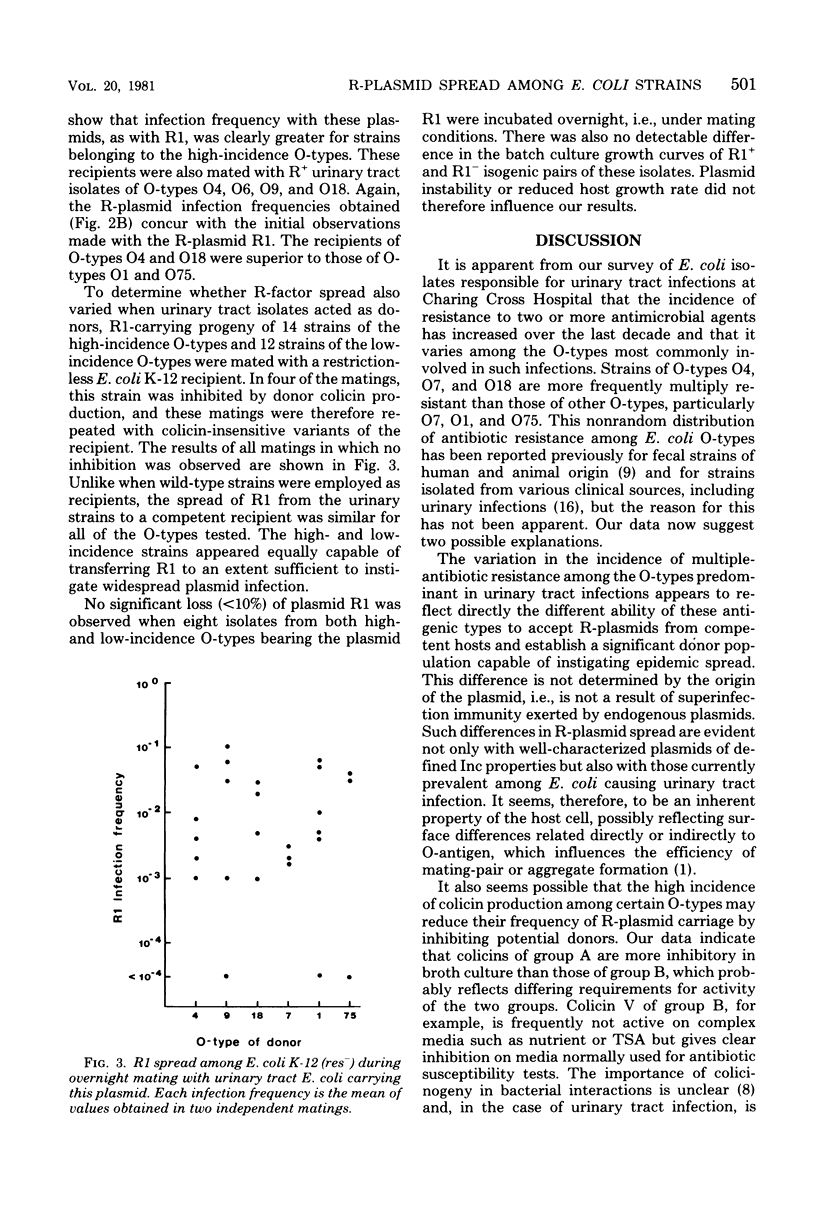
The incidence of multiple-antibiotic resistance among Escherichia coli isolated from urinary tract infections at Charing Cross Hospital, London, increased over the last 10 years, and its distribution was related to O-type. Among strains of the eight O-types most frequently causing such infections at this hospital, O4, O9, and O18 had a high incidence of multiple resistance (35, 22, and 19%, respectively); O2 and O6 had a intermediate incidence (14 and 11%, respectively); and O7, O1, and O75 had a low incidence (8, 6, and less than 3%, respectively). This nonrandom distribution appears to be a consequence of unequal plasmid recipient ability. After overnight mating with antibiotic-resistant donors, R-plasmid infection frequencies among antibiotic-sensitive urinary tract isolates differed by up to 10(5)-fold, and such differences were correlated with the variation in the incidence of antibiotic resistance among the O-types. The inherent differences in the ability to achieve significant R-plasmid spread, which appear to be determined by the host, not the plasmid, may be compounded in some cases by the inhibition of potential mating partners by colicin production.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley D. E., Taylor D. E., Cohen D. R. Specification of surface mating systems among conjugative drug resistance plasmids in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1466–1470. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1466-1470.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group A. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):102–117. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.102-117.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel W., Royer-Pokora B., Lindenmaier W., Bujard H. Plasmids controlling synthesis of hemolysin in Escherichia coli: molecular properties. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):964–973. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.964-973.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gower P. E., Taylor P. W., Koutsaimanis K. G., Roberts A. P. Serum bactericidal activity in patients with upper and lower urinary tract infections. Clin Sci. 1972 Jul;43(1):13–22. doi: 10.1042/cs0430013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. G. Colicinogeny and related phenomena. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):464–515. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.464-515.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley C. L., Howe K., Linton A. H., Linton K. B., Richmond M. H. Distribution of R plasmids among the O-antigen types of Escherichia coli isolated from human and animal sources. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):122–131. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horák V., Lanc A. Colicins of Escherichia coli strains causing urinary tract infections, sensitivity of these strains towards colicins, and their O-serotypes. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1973;18(4):332–340. doi: 10.1007/BF02868052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes V., Le Grice S., Hughes C., Meynell G. G. Two major groups of colicin factors: their molecular weights. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Feb 16;159(2):219–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00270897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Kaijser B., Olling S., Uwaydah M., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli in bacteremia: K and O antigens and serum sensitivity of strains from adults and neonates. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):33–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olling S., Hanson L. A., Holmgren J., Jodal U., Lincoln K., Lindberg U. The bactericidal effect of normal human serum on E. coli strains from normals and from patients with urinary tract infections. Infection. 1973;1(1):24–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01638251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrocheilou V., Richmond M. H. Distribution of R plasmids among the Q-antigen types of Escherichia coli isolated from various clinical sources. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynard A. M., Beck M. E. Plasmid-mediated resistance to the bactericidal effects of normal rabbit serum. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):848–850. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.848-850.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. P., Linton J. D., Waterman A. M., Gower P. E., Koutsaimanis K. G. Urinary and faecal Escherichia coli O-sero-groups in symptomatic urinary-tract infection and asymptomatic bacteriuria. J Med Microbiol. 1975 May;8(2):311–318. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. P., Phillips R. Bacteria causing symptomatic urinary tract infection or asymptomatic bacteriuria. J Clin Pathol. 1979 May;32(5):492–496. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.5.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw E. J., Pursell R. E., Datta N., Brumfitt W. R factors in Enterobacteriaceae causing urinary-tract infection in general practice in 1962-63 and 1968-69. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Nov;6(4):451–454. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-4-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W., Hughes C. Plasmid carriage and the serum sensitivity of enterobacteria. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):10–17. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.10-17.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W., Koutsaimanis K. G. Experimental Escherichia coli urinary infection in the rat. Kidney Int. 1975 Oct;8(4):233–238. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



