Abstract
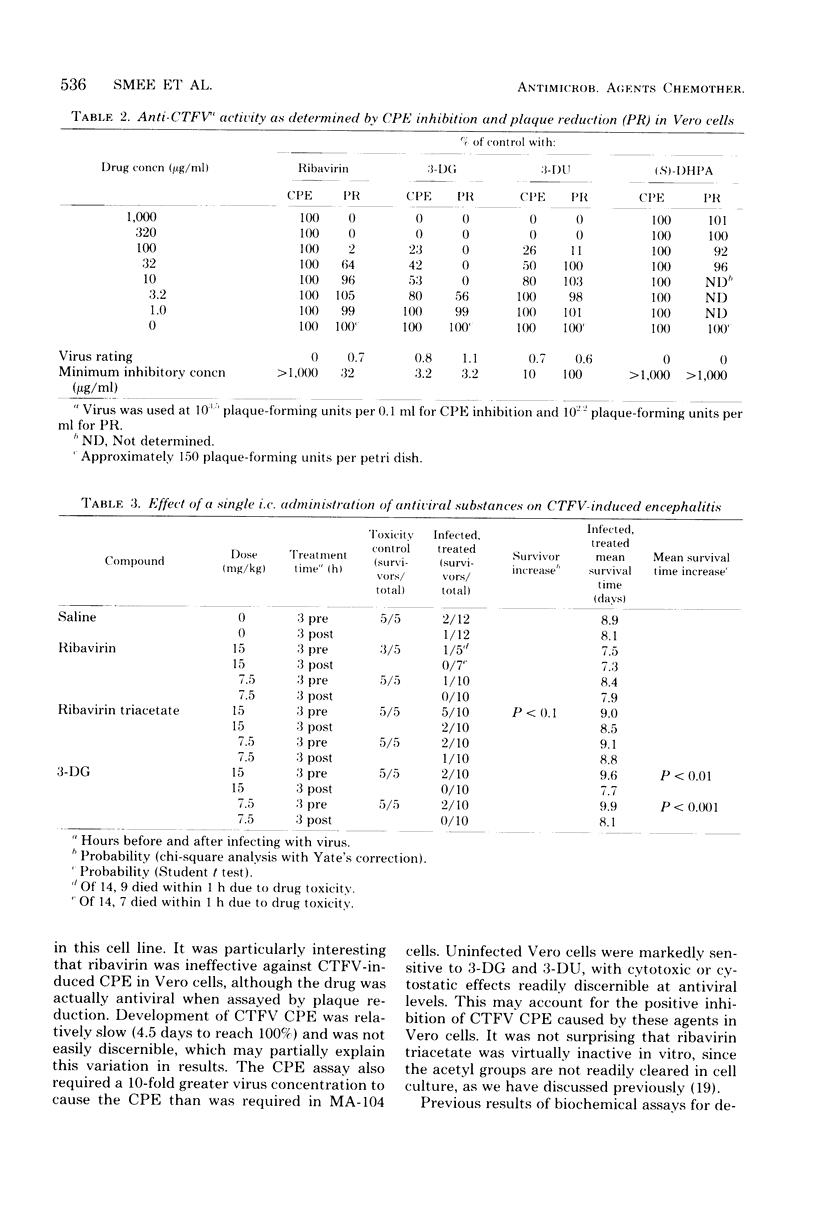
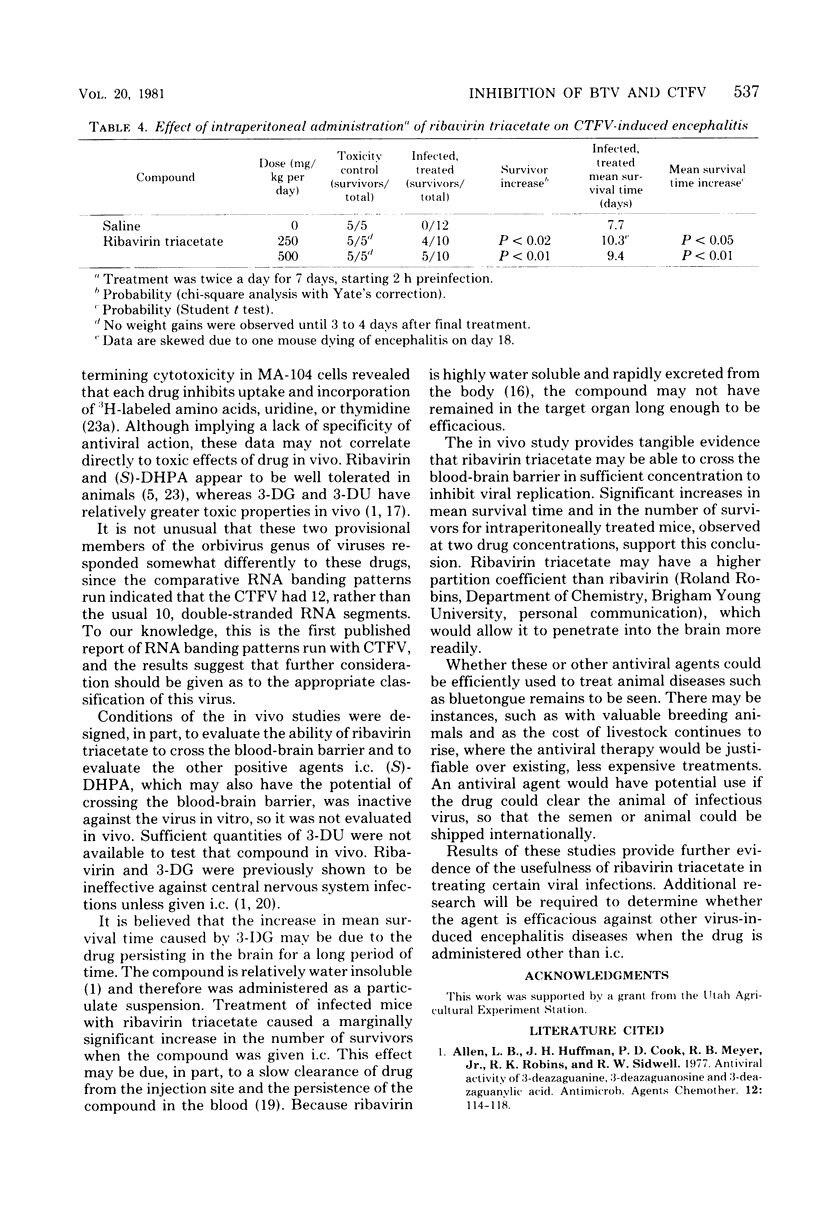
The effects of four ribonucleic acid virus inhibitors were evaluated in cell cultures and in mice to determine inhibitory effects against bluetongue virus and Colorado tick fever virus (CTFV). Test compounds included 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (ribavirin), 3-deazaguanine, 3-deazauridine, and 9-(S)-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)adenine. Ribavirin-2',3',5'-triacetate (ribavirin triacetate) was evaluated in vivo against CTFV. Inhibition of cytopathic effect and plaque reduction were used to evaluate antiviral activity. In cytopathic effect inhibition studies, bluetongue virus was markedly inhibited by 3-deazaguanine and 3-deazauridine in Vero cells with moderate inhibition by the other agents. Ribavirin and 3-deazaguanine markedly inhibited CTFV in MA-104 cells, 3-deazauridine was slightly less active, and 9-(S)-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)adenine was negative. Ribavirin was less effective in Vero cells against CTFV. When mice were inoculated intracerebrally with CTFV and treated by a single intracerebral injection with drug, ribavirin triacetate increased the number of survivors, 3-deazaguanine increased mean survival time, and ribavirin was negative. Intraperitoneal treatment of infected mice with ribavirin triacetate for 1 week significantly increased the number of survivors and mean survival time, providing strong evidence that the agent is active across the blood-brain barrier.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borden E. C., Shope R. E., Murphy F. A. Physicochemical and morphological relationships of some arthropod-borne viruses to bluetongue virus--a new taxonomic group. Physiocochemical and serological studies. J Gen Virol. 1971 Nov;13(2):261–271. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman B. M. Variation in orbiviruses. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jul;44(1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. E., Morahan P., Coleman P. Teratogenic effects of Colorado tick fever virus in mice. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):397–402. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffman J. H., Sidwell R. W., Khare G. P., Witkowski J. T., Allen L. B., Robins R. K. In vitro effect of 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (virazole, ICN 1229) on deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid viruses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):235–241. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huismans H. Protein synthesis in bluetongue virus-infected cells. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khare G. P., Sidwell R. W., Huffman J. H., Tolman R. L., Robins R. K. Inhibition of RNA virus replication in vitro by 3-deazacytidine and 3-deazauridine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jul;140(3):880–884. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luedke A. J., Jochim M. M., Jones R. H. Bluetongue in cattle: effects of Culicoides variipennis-transmitted bluetongue virus on pregnant heifers and their calves. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Nov;38(11):1687–1695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. P., Kigwana L. J., Streeter D. G., Robins R. K., Simon L. N., Roboz J. The relationship between the metabolism of ribavirin and its proposed mechanism of action. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:211–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb21953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon W. M., Arnett G., Schabel F. M., Jr 3-Deazauridine: inhibition of ribonucleic acid virus-induced cytopathogenic effects in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):159–163. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon W. M. Selective inhibition of RNA tumor virus replication in vitro and evaluation of candidate antiviral agents in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:472–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb21983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Huffman J. H. Use of disposable micro tissue culture plates for antiviral and interferon induction studies. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):797–801. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.797-801.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Robins R. K., Hillyard I. W. Ribavirin: an antiviral agent. Pharmacol Ther. 1979;6(1):123–146. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(79)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwoerd D. W. Purification and characterization of bluetongue virus. Virology. 1969 Jun;38(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90361-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]