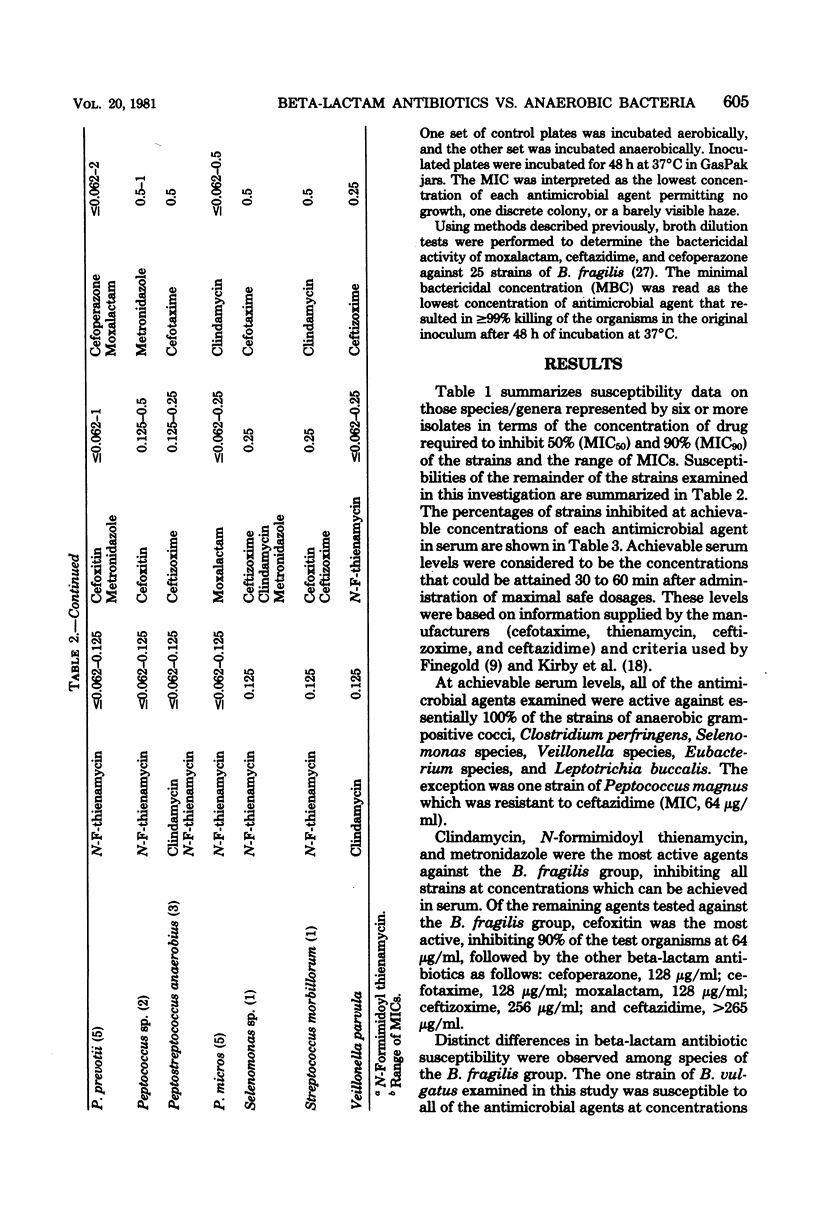
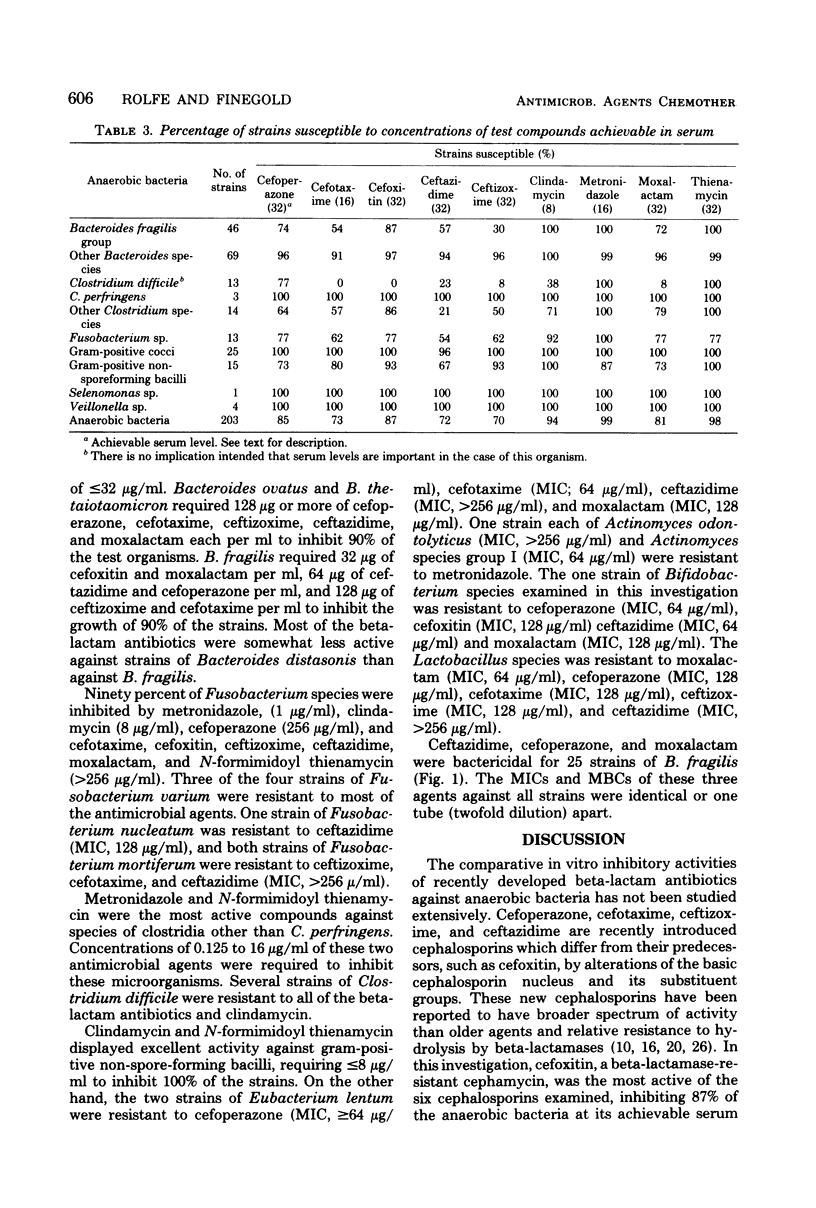
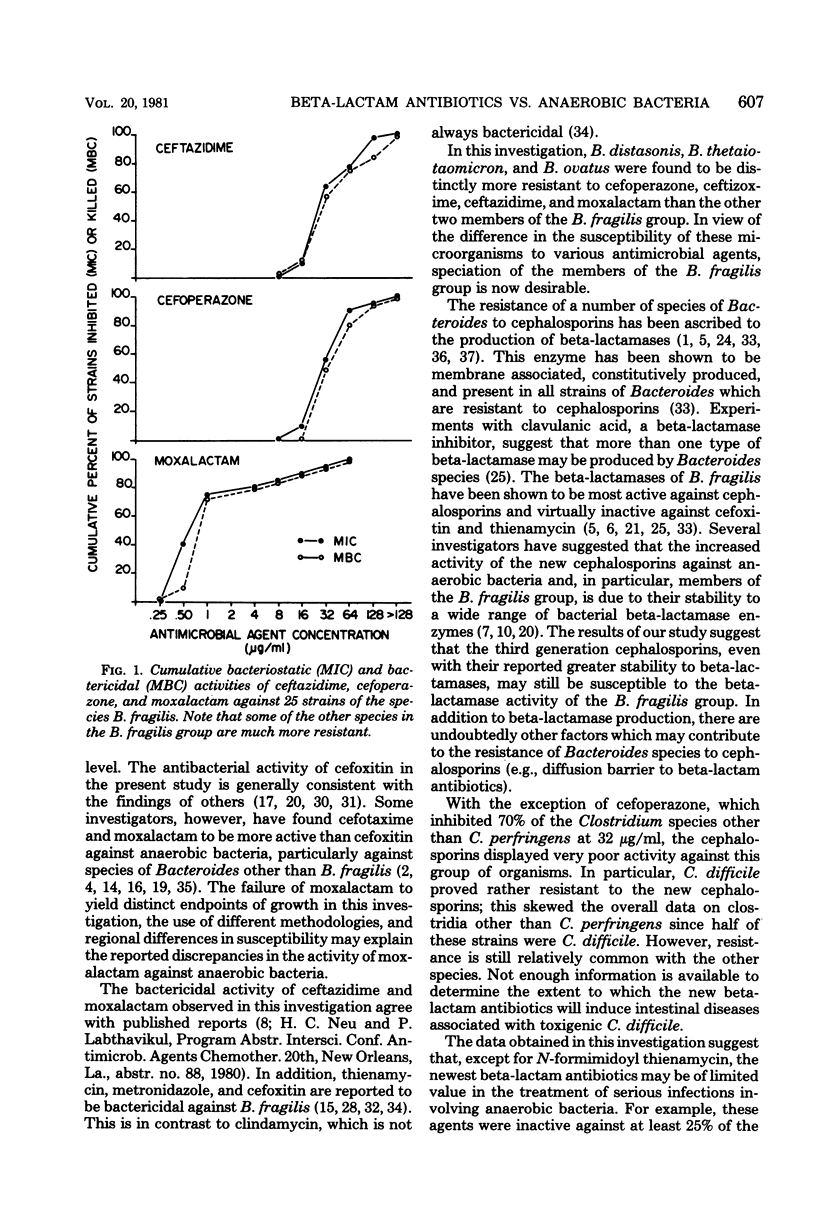
Abstract
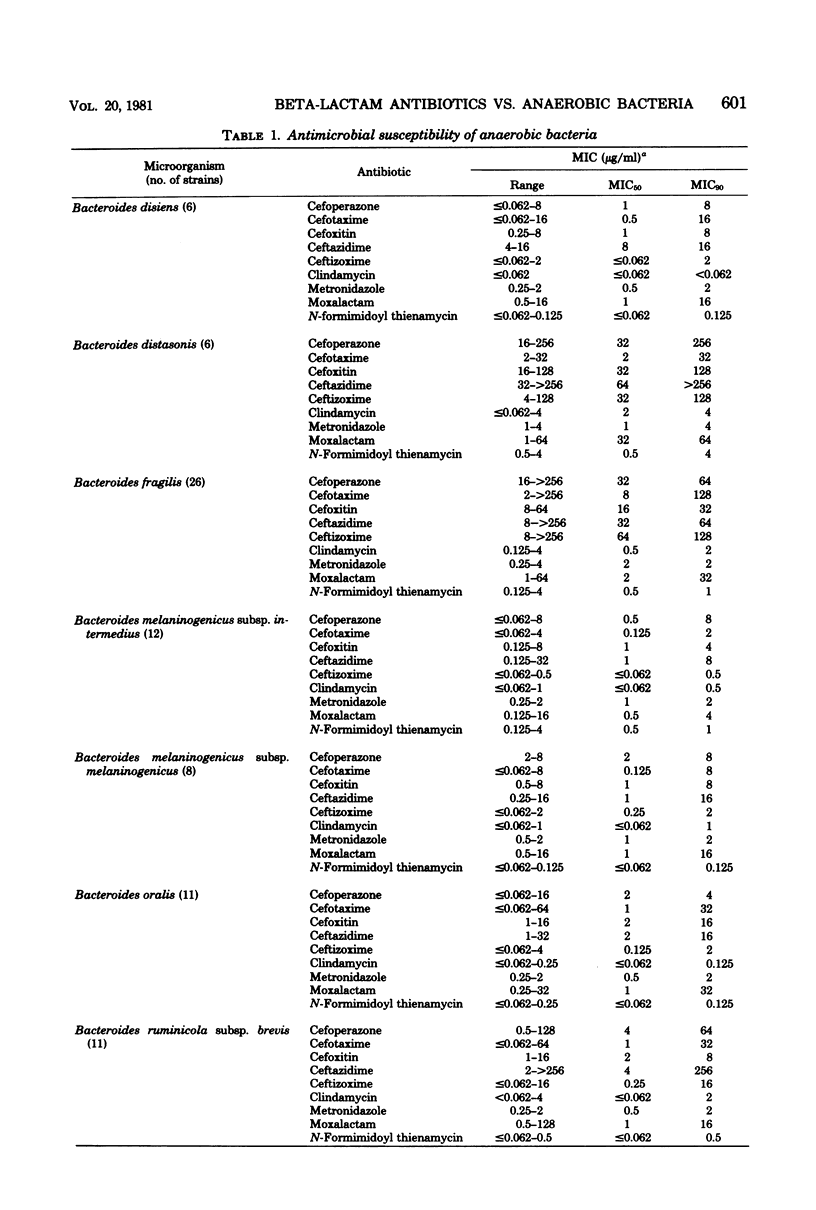
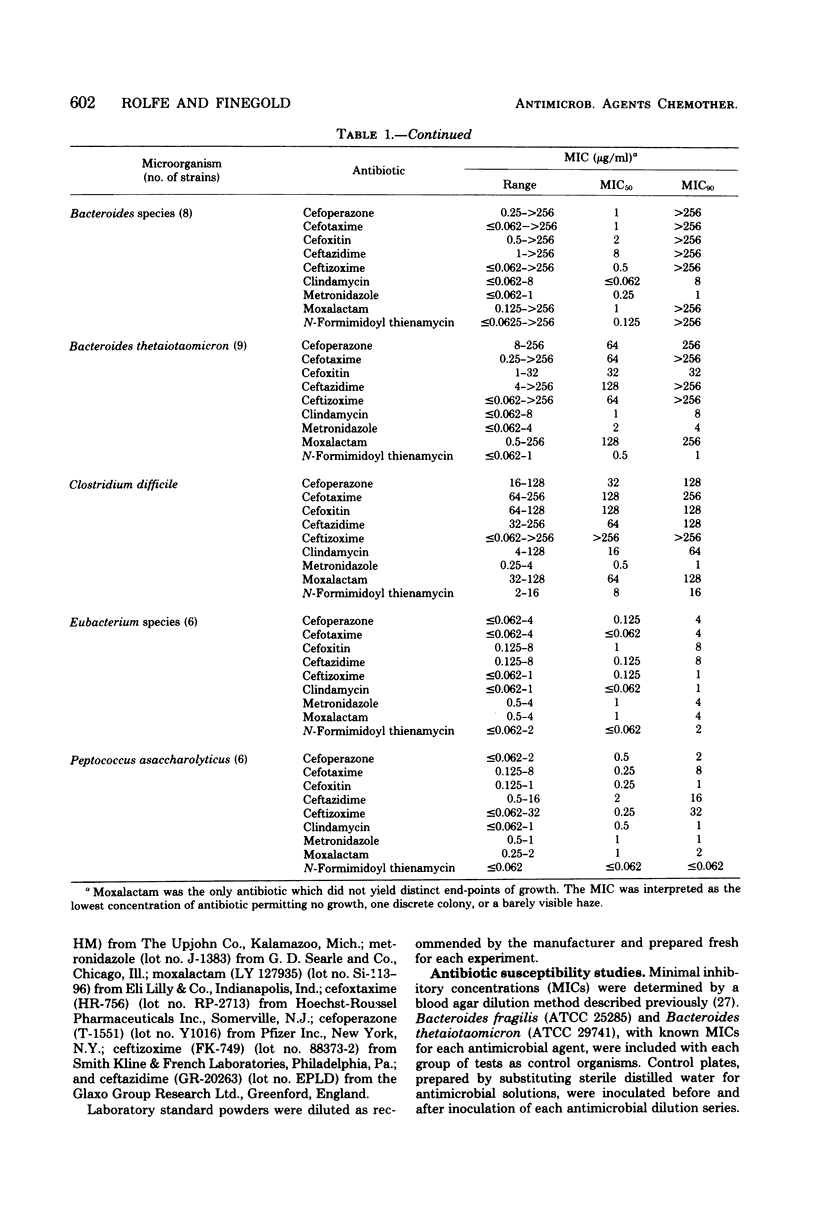
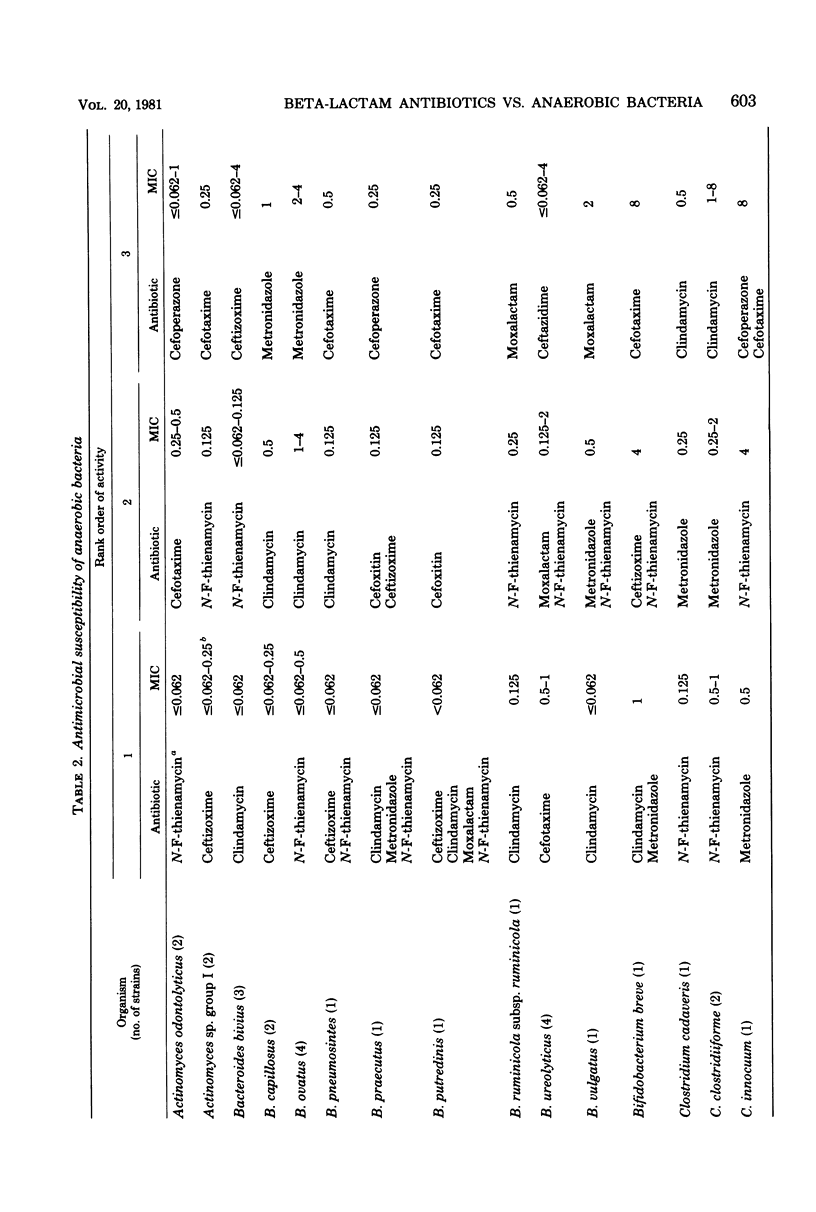
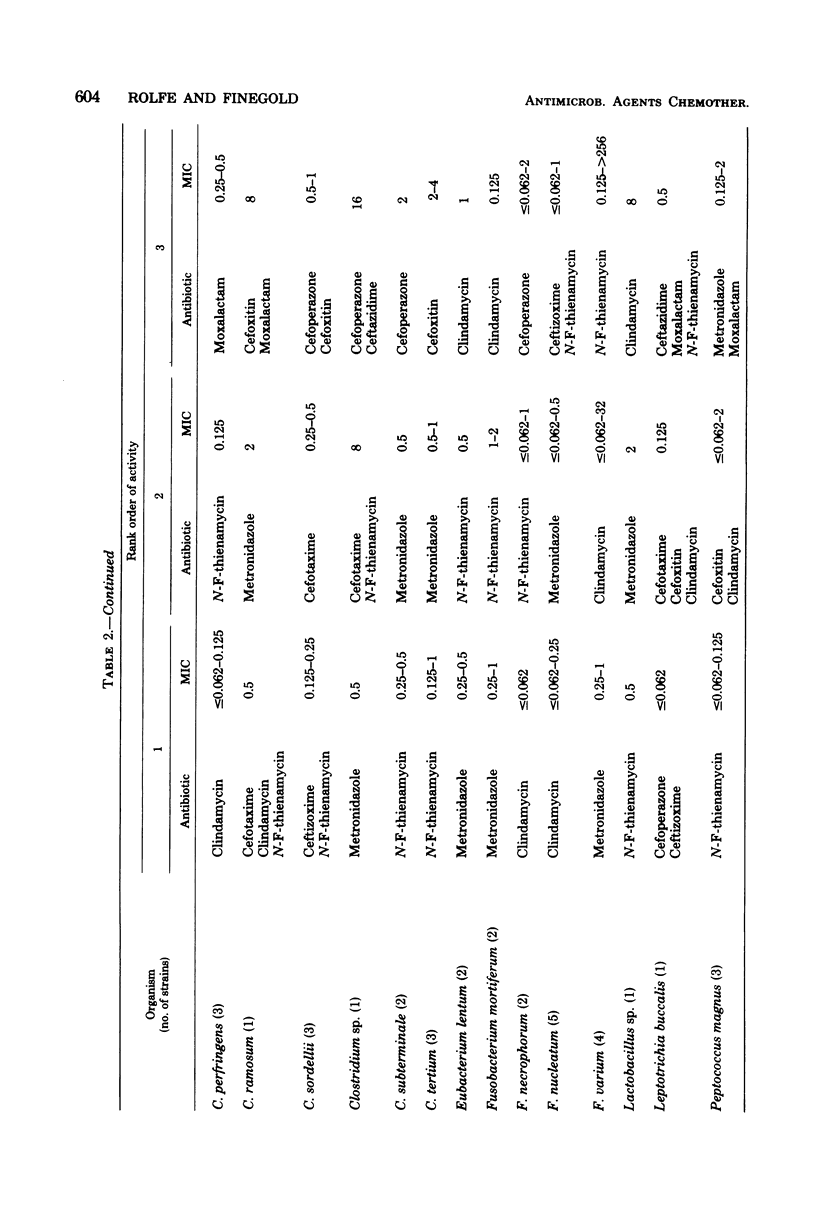
Several new beta-lactam antimicrobial agents have been introduced in the last few years. In this investigation, the in vitro activities of several recently introduced cephalosporins (cefoperazone, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, and ceftizoxime), moxalactam, and N-formimidoyl thienamycin were compared with those of cefoxitin, clindamycin, and metronidazole against 203 strains of anaerobic bacteria. At achievable serum levels, all of the antimicrobial agents were active against essentially 100% of the strains of anaerobic gram-positive cocci, Clostridium perfringens, Leptotrichia buccalis, and species of Selenomonas, Veillonella, and Eubacterium. Clindamycin, metronidazole, and N-formimidoyl thienamycin were the most active agents against the Bacteroides fragilis group, inhibiting all strains at concentrations which can be achieved in serum. Of the remaining agents tested against the B. fragilis group, cefoxitin (which required 64 μg/ml to inhibit 90% of the strains) was the most active, followed by cefoperazone (128 μg/ml), cefotaxime (128 μg/ml), moxalactam (128 μg/ml), ceftizoxime (256 μg/ml), and ceftazidime (>256 μg/ml). Important differences in cephalosporin susceptibility among species of the B. fragilis group were observed. Metronidazole and N-formimidoyl thienamycin were the most active drugs against species of clostridia other than C. perfringens; the other antibiotics displayed poor activity, although this is partly due to inclusion of a relatively large number of strains of Clostridium difficile which were very resistant to several of the cephalosporins. Only metronidazole was active against all species of Fusobacterium. Clindamycin and N-formimidoyl thienamycin displayed excellent activity against gram-positive, non-spore-forming bacilli, requiring ≤8 μg/ml to inhibit 100% of the strains. Ceftazidime, cefoperazone, and moxalactam were bactericidal for 25 strains of B. fragilis at concentrations equal or close to those required for inhibition. On the basis of its activity in vitro, N-formimidoyl thienamycin appears to be the most promising of the new beta-lactam antibiotics for the treatment of infections involving anaerobic bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. D., Sykes R. B. Characterisation of a -lactamase obtained from a strain of Bacteroides fragilis resistant to -lactam antibiotics. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):201–206. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. In vitro activity of LY127935. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):287–292. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bawdon R. E., Rozmiej E., Palchaudhuri S., Krakowiak J. Variability in the susceptibility pattern of Bacteroides fragilis in four Detroit area hospitals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):664–666. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borobio M. V., Aznar J., Jimenez R., Garcia F., Perea E. J. Comparative in vitro activity of 1-oxa-beta-lactam (LY127935) and cefoperazone with other beta-lactam antibiotics against anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):129–131. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darland G., Birnbaum J. Cefoxitin resistance to beta-lactamase: a major factor for susceptibility of bacteroides fragilis to the antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):725–734. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K., Olsson-Lijequist B., Nord C. E. Antibacterial activity of new beta-lactam antibiotics on cefoxitin-resistant strains of Bacteroides fragilis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Mar;6(2):207–216. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar F. A., Farrell W., Howard A. J., Hince C., Leung T., Williams J. D. Activity of HR 756 against Haemophilus influenzae, Bacteroides fragilis and Gram-negative rods. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Sep;4(5):445–450. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.5.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. In vitro activity of LY127935. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):503–509. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. beta-lactamase stability of HR 756, a novel cephalosporin, compared to that of cefuroxime and cefoxitin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):322–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E. J., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Comparative susceptibilities of anaerobic bacteria to metronidazole, ornidazole, and SC-28538. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):609–613. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Fuchs P. C., Sommers H. M., Gavan T. L., Barry A. L., Gerlach E. H. Moxalactam (LY127935), a new semisynthetic 1-oxa-beta-lactam antibiotic with remarkable antimicrobial activity: in vitro comparison with cefamandole and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):750–756. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Barry A. L., Fuchs P. C., Gavin T. L., Gerlach E. H. BL-S786, a new parenteral cephalosporin. II. In vitro antimicrobial activity comparison with six related cephalosporins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Jul;30(7):583–592. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Crawford S. A., Alexander G. A. Comparison of moxalactam (LY127935) and cefotaxime against anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):901–904. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D., Kobasa W., Kaye K. Susceptibilities of anaerobic bacteria to cefoperazone and other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):957–960. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby B. D., George W. L., Sutter V. L., Citron D. M., Finegold S. M. Gram-negative anaerobic bacilli: their role in infection and patterns of susceptibility to antimicrobial agents. I. Little-known Bacteroides species. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Nov-Dec;2(6):914–951. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.6.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz T. O., Winston D. J., Hindler J. A., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L., Martin W. J. Comparative in vitro activity of moxalactam, cefotaxime, cefoperazone, piperacillin, and aminoglycosides against gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):645–648. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Aswapokee N., Aswapokee P., Fu K. P. HR 756, a new cephalosporin active against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):273–281. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Kirby W. M. Unique bactericidal action of metronidazole against Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium perfringens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Oct;8(4):409–414. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaki J. S., Black R., Tally F. P., Kislak J. W. Bacteroides fragilis resistant to the administration of clindamycin. Am J Med. 1976 Mar;60(3):426–428. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90759-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Wong J., Wilkins T. D. Beta-Lactamase activity in strains of Bacteroides melaninogenicus and Bacteroides oralis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):142–146. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Activity of beta-lactamase produced by Bacteroides fragilis against newly introduced cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):736–737. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrinner E., Limbert M., Penasse L., Lutz A. Antibacterial activity of cefotaxime and other newer cephalosporins (in vitro and in vivo). J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Sep;6 (Suppl A):25–30. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.suppl_a.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of Anaerobic bacteria to carbenicillin, cefoxitin, and related drugs. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):417–422. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to 23 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):736–752. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Kirby B., Finegold S. M. In vitro activity of cefoxitin and parenterally administered cephalosporins against anaerobic bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Jan-Feb;1(1):218–223. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.1.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Susceptibility of anaerobes to cefoxitin and other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):128–132. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. In vitro activity of thienamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):436–438. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., O'Keefe J. P., Sullivan N. M., Gorbach S. L. Inactivation of cephalosporins by Bacteroides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):565–571. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Metronidazole versus anaerobes. In vitro data and initial clinical observations. Calif Med. 1972 Dec;117(6):22–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager G. M., White G. W., Zimelis V. M., Bryk D. A., Panwalker A. P. In vitro comparison of three new cephalosporins: LY-127935, cefotaxime and cefoperazone. Chemotherapy. 1981;27(1):34–38. doi: 10.1159/000237952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrich A. E., Del bene V. E. Beta-lactamase activity in anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):106–111. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüst J., Wilkins T. D. Effect of clavulanic Acid on anaerobic bacteria resistant to Beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):130–133. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


