Abstract
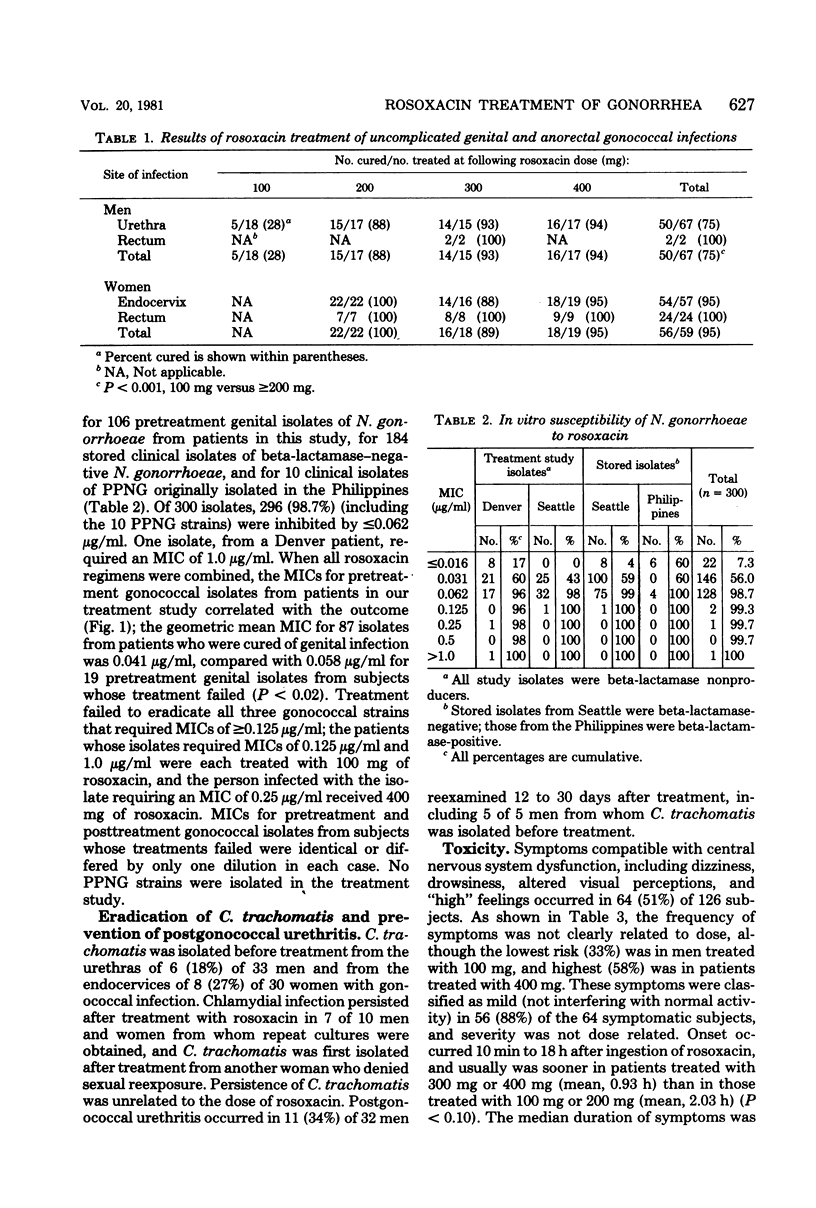
In a randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging study, single oral doses of rosoxacin were used to treat 126 patients with uncomplicated genital or anorectal gonorrhea. Neisseria gonorrhoeae was eradicated from 5 (28%) of 18 men treated with 100 mg, compared with 101 (94%) of 108 men and women treated with 200 mg, 300 mg, or 400 mg (P less than 0.001). Susceptibility to rosoxacin was determined for 6 pretreatment gonococcal isolates from these patients and for 194 stored clinical isolates; 296 (98.7%) of these 300 isolates, including 10 strains of penicillinase-producing N. gonorrhaeae, required a minimal inhibitory concentration of less than or equal to 0.062 microgram/ml. Urethral or cervical infection with Chlamydia trachomatis coexisted with gonococcal infection in 14 (22%) of 63 patients and persisted in 7 of 10 patients treated with rosoxacin. Postgonococcal urethritis developed in 11 (34%) of 32 men who were monitored for 12 to 30 days. Sixty-four subjects (51%) developed transient dizziness, drowsiness, altered visual perceptions, or other symptoms suggestive of central nervous system dysfunction after treatment with rosoxacin, but these symptoms were not clearly dose related. Rosoxacin in doses of greater than or equal to 200 mg appears to be effective for single-dose treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhea, but further studies of its possible central nervous system toxicity are indicated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowie W. R. Comparison of Gram stain and first-voided urine sediment in the diagnosis of urethritis. Sex Transm Dis. 1978 Apr-Jun;5(2):39–42. doi: 10.1097/00007435-197804000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Iodometric detection of Haemophilus influenzae beta-lactamase: rapid presumptive test for ampicillin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):265–270. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson R. A., O'Connor J. R., Poulin S. A., Kundsin R. B., Smith T. F., Came P. E. In vitro antimicrobial activity of rosoxacin against Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, and Ureaplasma urealyticum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):738–740. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. K., Handsfield H. H., Wang S. P., Wentworth B. B., Turck M., Anderson J. B., Alexander E. R. Etiology of nongonococcal urethritis. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jun 5;292(23):1199–1205. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197506052922301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriel J. D., Powis P. A., Reeve P., Miller A., Nicol C. S. Chlamydial infections of the cervix. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Feb;50(1):11–16. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perine P. L., Morton R. S., Piot P., Siegel M. S., Antal G. M. Epidemiology and treatment of penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Sex Transm Dis. 1979 Apr-Jun;6(2 Suppl):152–158. doi: 10.1097/00007435-197904000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesner P. J., Holmes K. K., Sparling P. F., Maness M. J., Bear D. M., Gutman L. T., Karney W. W. Single doses of methacycline and doxycycline for gonorrhea: a cooperative study of the frequency and cause of treatment failure. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):461–466. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder B. L., Stamm W. E., Koester C. M., Alexander E. R. Microtest procedure for isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1036-1039.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



