Abstract
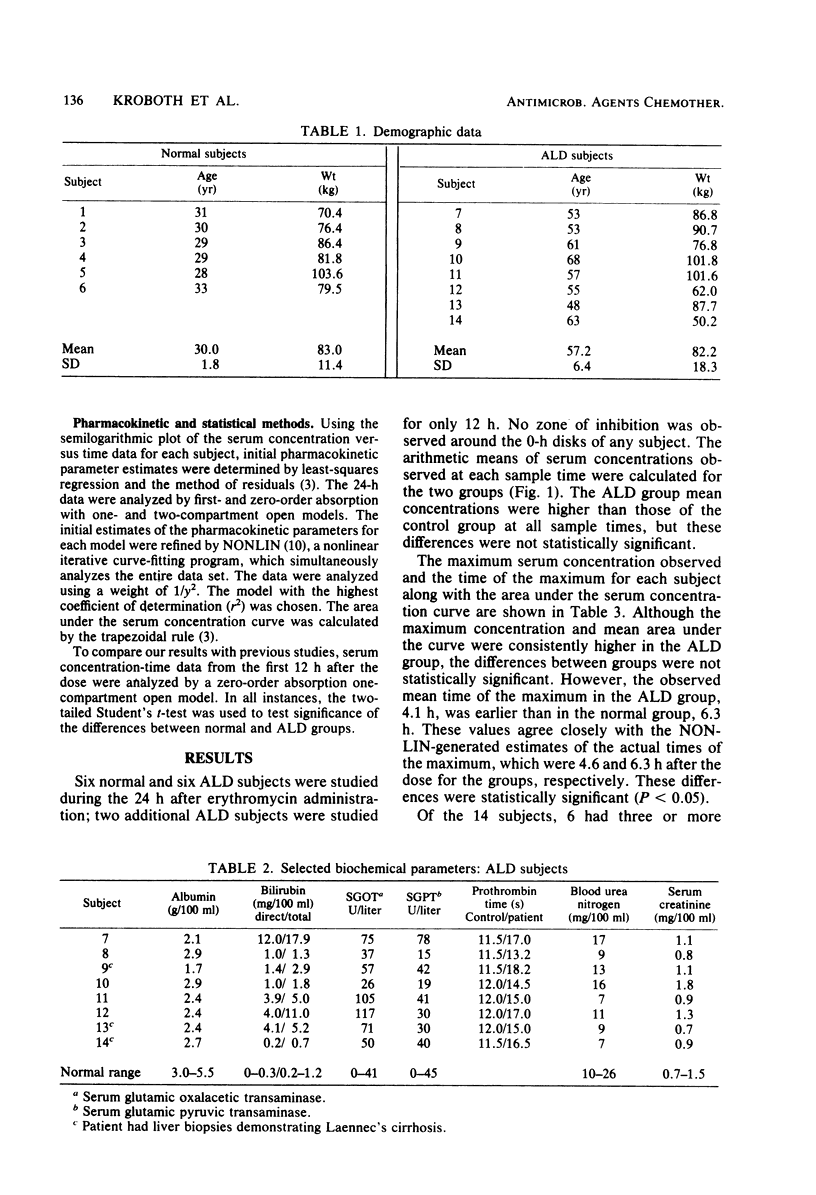
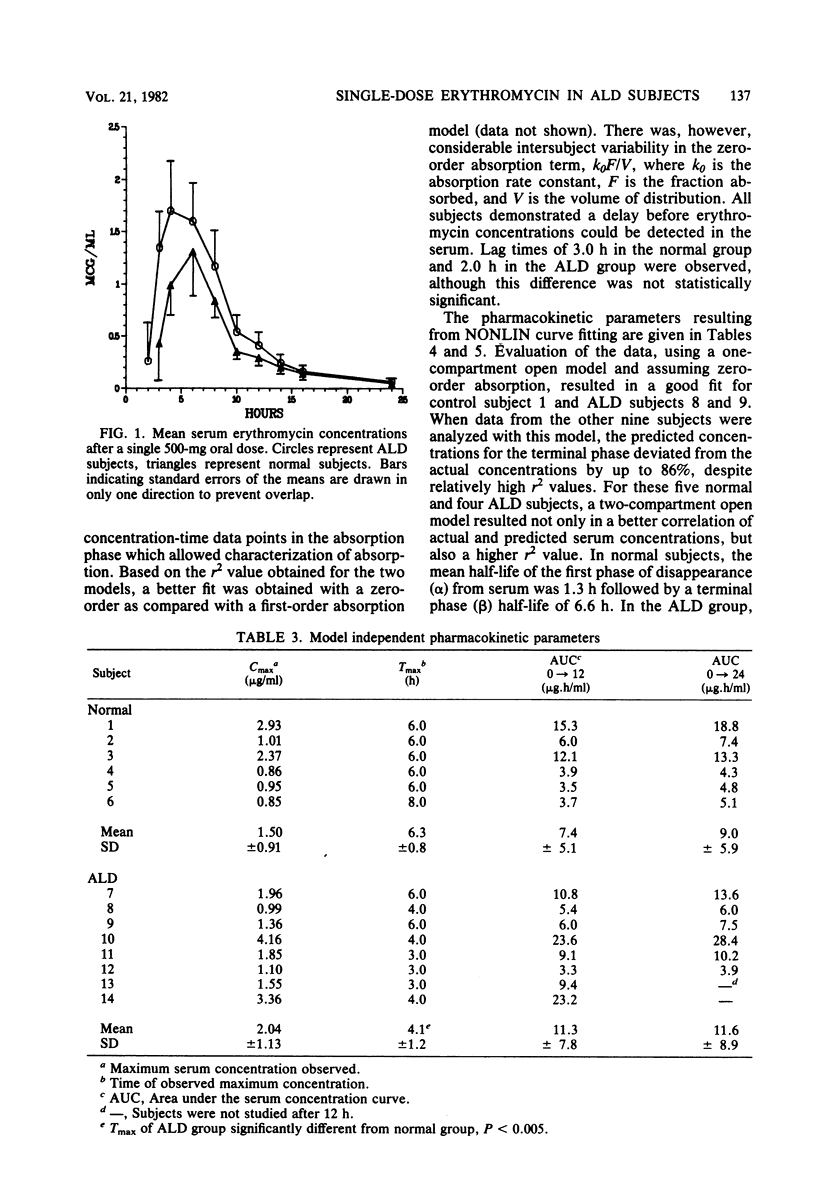
Six normal males and eight male subjects with alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and ascites were given a single 500-mg dose of erythromycin base. Twelve serum samples were collected at 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, and 24 h after dosing and assayed microbiologically for erythromycin concentration. Absorption was characterized by a zero-order model for both groups. ALD subjects demonstrated a shorter lag time (2.0 versus 3.0 h), an earlier peak (4.6 versus 6.3 h, P less than 0.05), and higher peak concentrations (2.04 versus 1.50 micrograms/ml) than normal subjects. Previously unreported biphasic elimination kinetics after oral dosing were observed in five and four ALD subjects. In the ALD group, the mean half lives for the first (alpha) and terminal (beta) phases were 1.6 and 4.5 h, respectively, and in normal subjects, were 1.3 and 6.6 h. The difference in alpha between groups was significant, P less than 0.05. The clinical significance of this finding for ALD patients receiving prolonged courses of erythromycin is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell S. C., Hamman J. W., Grundy W. E. Micromethod for assaying serum levels of erythromycin. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jan;17(1):88–92. doi: 10.1128/am.17.1.88-92.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colburn W. A., Di Santo A. R., Gibaldi M. Pharmacokinetics of erythromycin on repetitive dosing. J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;17(10 Pt 1):592–600. doi: 10.1177/009127007701701006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFITH R. S., BLACK H. R. Erythromycin. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1961 Nov;8:1115–1131. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)31198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAIGHT T. H., FINLAND M. The antibacterial action of erythromycin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Oct;81(1):175–183. doi: 10.3181/00379727-81-19815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMOND J. B., GRIFFITH R. S. Factors affecting the absorption and biliary excretion of erythromycin and two of its derivatives in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1961 May-Jun;2:308–312. doi: 10.1002/cpt196123308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavanagh F. Microbiological diffusion assay II: design and applications. J Pharm Sci. 1975 Jul;64(7):1224–1229. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600640723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G. P., Jusko W. J. Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin in cirrhosis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Oct;18(4):475–484. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975184475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald P. J., Mather L. E., Story M. J. Studies on absorption of a newly developed enteric-coated erythromycin base. J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;17(10 Pt 1):601–606. doi: 10.1177/009127007701701007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. L., Condon R. E., DiSanto A. R. Preoperative bowel preparation. Erythromycin base serum and fecal levels following oral administration. Arch Surg. 1977 Dec;112(12):1493–1496. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1977.01370120083010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale C. H., Dittert L. W., Tozer T. N. Erythromycin. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1976 Apr;16(4):203–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TWISS J. R., BERGER W. V., GILLETTE L., ARONSON A. R., SIEGEL L. The biliary excretion of erythromycin (ilotycin). Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1956 Mar;102(3):355–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling P. G., Elliott R. L., Pitterle M. E., Corrick-West H. P., Lyons L. L. Plasma levels following single and repeated doses of erythromycin estolate and erythromycin stearate. J Pharm Sci. 1979 Feb;68(2):150–155. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600680208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand R. G., Chun A. H. Serum protein binding of erythromycin and erythromycin 2'-propionate ester. J Pharm Sci. 1972 Mar;61(3):425–428. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600610322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


