Abstract
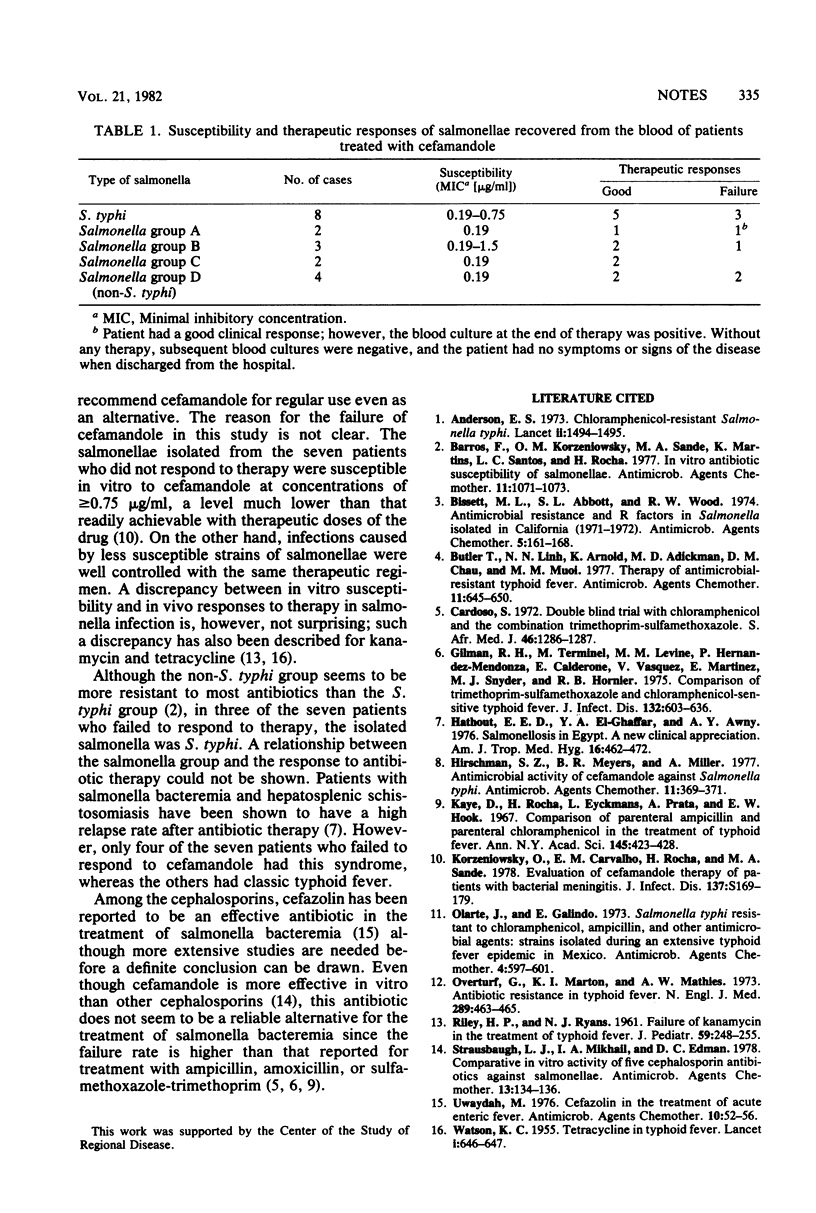
The efficacy of cefamandole in the treatment of 19 patients with salmonella bacteremia was evaluated. Although all of the salmonella strains isolated were highly susceptible to cefamandole in vitro, a therapeutic failure was observed in 7 (36.8%) of the 19 patients.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barros F., Korzeniowski O. M., Sande M. A., Martins K., Santos L. C., Rocha H. In vitro antibiotic susceptibility of salmonellae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):1071–1073. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett M. L., Abbott S. L., Wood R. M. Antimicrobial resistance and R factors in Salmonella isolated in California (1971-1972). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):161–168. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Linh N. N., Arnold K., Adickman M. D., Chau D. M., Muoi M. M. Therapy of antimicrobial-resistant typhoid fever. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):645–650. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso N. Double-blind trial with chloramphenicol and the combination trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in typhoid. S Afr Med J. 1972 Sep 9;46(36):1286–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman R. H., Terminel M., Levine M. M., Hernandez-Mendosa P., Calderone E., Vasquez V., Martinez E., Snyder M. J., Hornick R. B. Comparison of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and amoxicillin in therapy of chloramphenicol-resistant and chloramphenicol-sensitive typhoid fever. J Infect Dis. 1975 Dec;132(6):630–636. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.6.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathout S el-D, Abd el-Ghaffar Y., Awny A. Y. Salmonellosis complicating schistosomiasis in Egypt. A new clinical appreciation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 Jul;16(4):462–472. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1967.16.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman S. Z., Meyers B. R., Miller A. Antimicrobial activity of cefamandole against Salmonella typhi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):369–371. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D., Eyckmans L., Rocha H., Prata A., Hook E. W. Comparison of parenteral ampicillin and parenteral chloramphenicol in the treatment of typhoid fever. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Sep 27;145(2):423–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korzeniowski O. M., Carvalho E. M., Jr, Rocha H., Sande M. A. Evaluation of cefamandole therapy of patients with bacterial meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137 (Suppl):S169–S179. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.supplement.s169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olarte J., Galindo E. Salmonella typhi resistant to chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and other antimicrobial agents: strains isolated during an extensive typhoid fever epidemic in Mexico. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):597–601. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overturf G., Marton K. I., Mathies A. W., Jr Antibiotic resistance in typhoid fever. Chloramphenicol resistance among clinical isolates of Salmonella typhosa in Los Angeles, 1972--epidemiologic and bacteriologic characteristics. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 30;289(9):463–465. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308302890906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RILEY H. D., Jr, RYAN N. J. Failure of kanamycin in the treatment of typhoid fever. J Pediatr. 1961 Aug;59:248–255. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(61)80088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausbaugh L. J., Mikhail I. A., Edman D. C. Comparative in vitro activity of five cephalosporin antibiotics against salmonellae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):134–136. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uwaydah M. Cefazolin in the treatment of acute enteric fever. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):52–56. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON K. C. Tetracycline in typhoid fever. Lancet. 1955 Mar 26;268(6865):646–647. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


