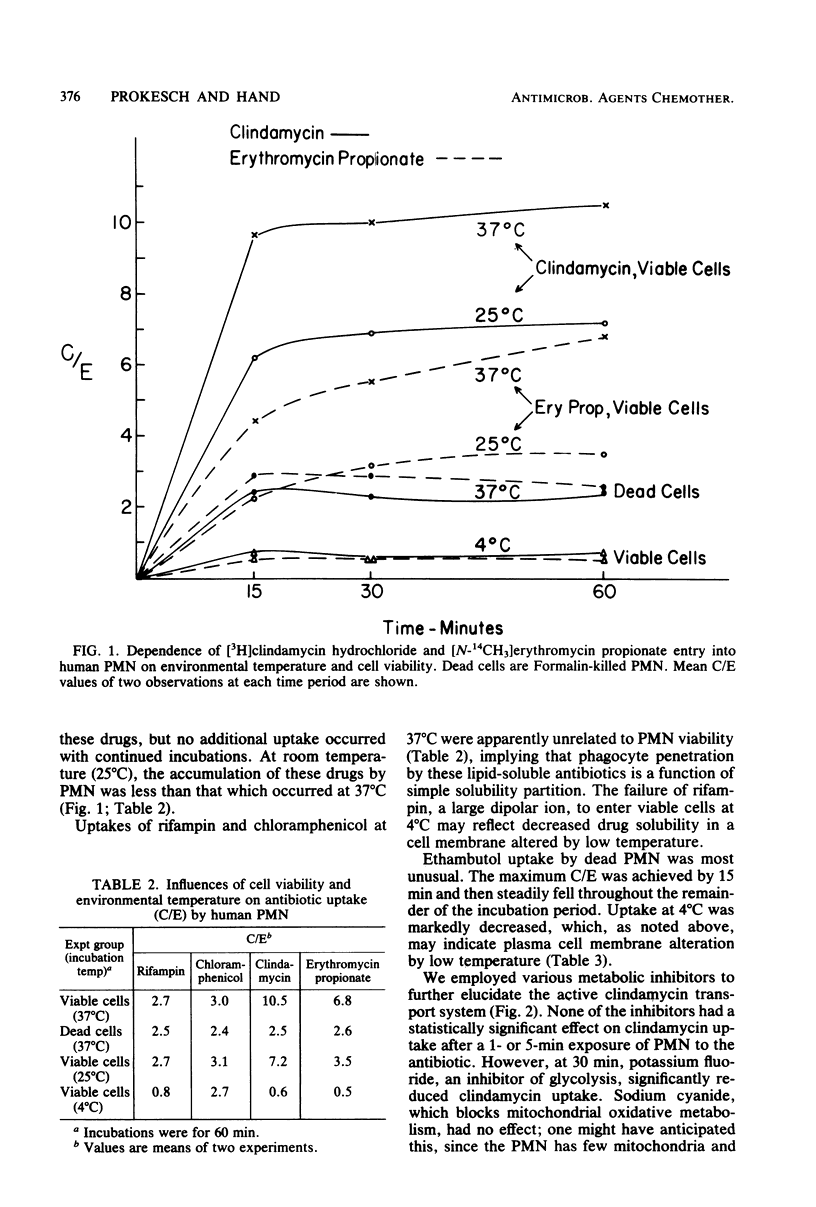
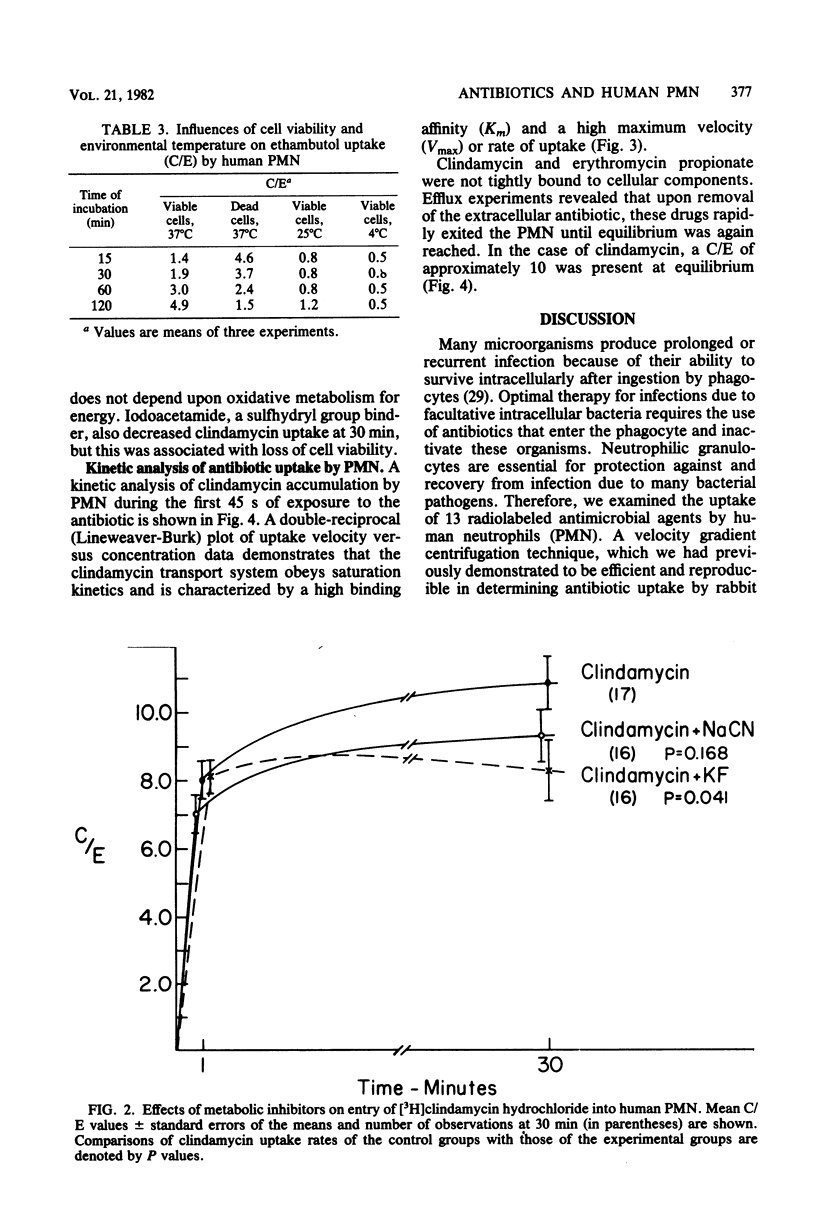
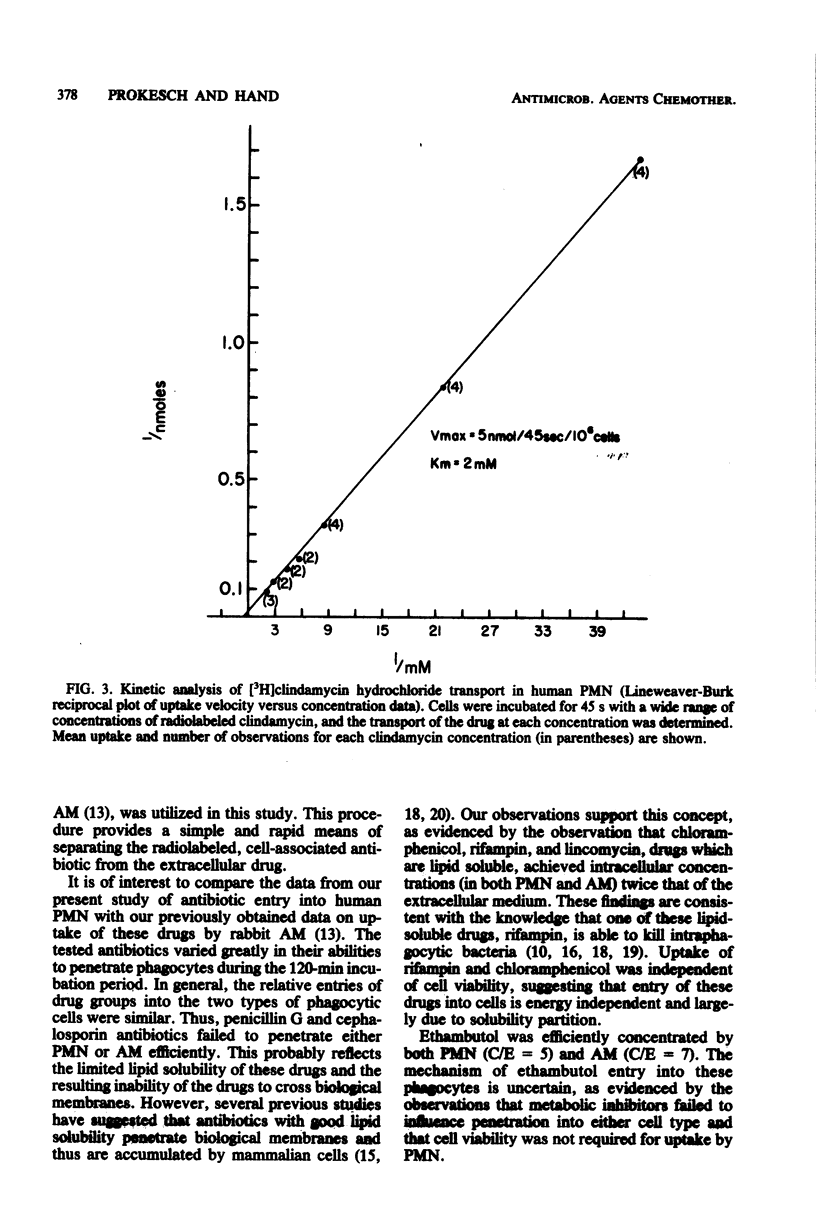
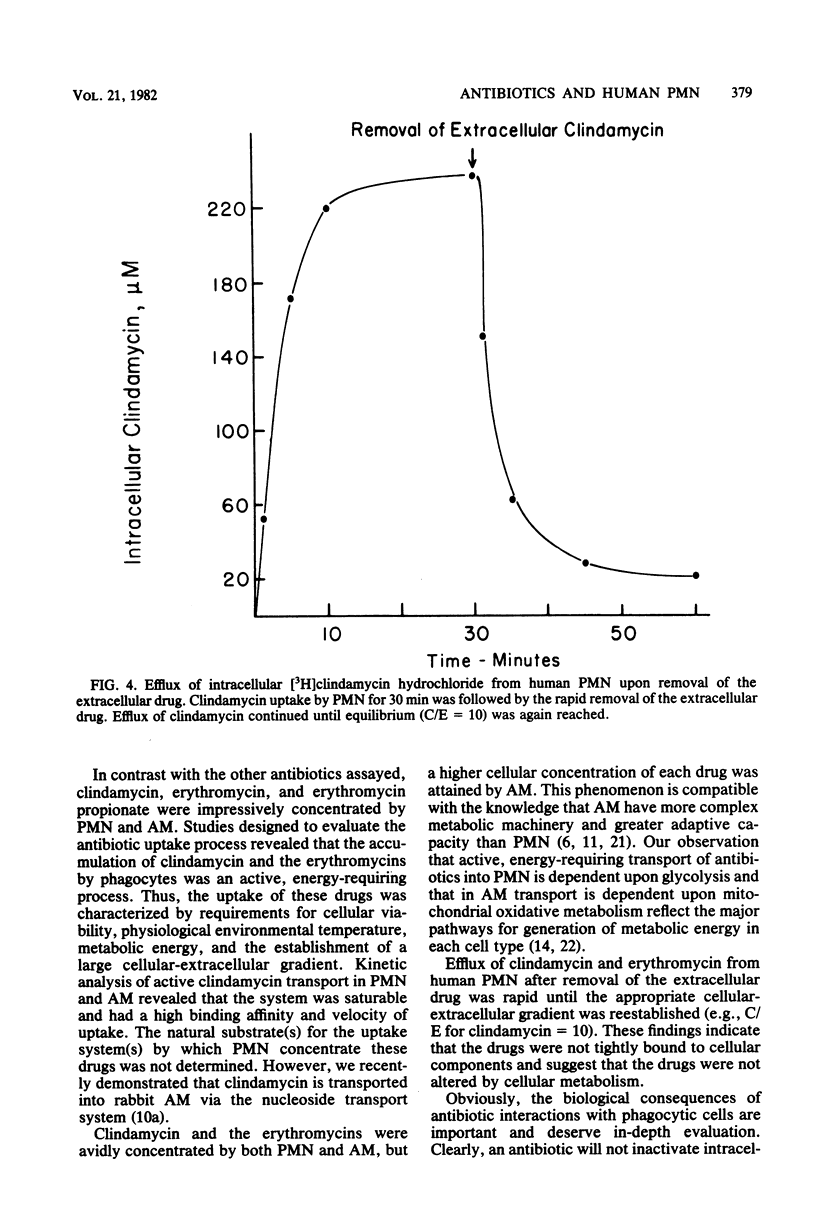
Abstract
Since bacteria which survive within phagocytes may produce serious infection, antibiotics which inactivate these intracellular organisms are needed. To establish those factors which mediate entry of antimicrobial agents into human phagocytes, we studied the uptake of 13 radiolabeled antibiotics by peripheral blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN). At intervals during a 2-h incubation period, antibiotic uptake by PMN was determined by means of velocity gradient centrifugation, which separates the cell-associated antibiotic from the extracellular antibiotic. Penicillin G and three cephalosporin antibiotics penetrated PMN poorly. The ratio of cellular concentration to extracellular concentration (C/E) of these drugs was less than 0.01 to 0.5. For gentamicin and isoniazid, the C/E values were approximately 0.8 to 1.0. Chloramphenicol, rifampin, and lincomycin, antibiotics with good lipid solubility, were concentrated twofold (C/E = 2) in PMN. Ethambutol (C/E = 5), clindamycin (C/E = 11), and two erythromycin preparations (C/E = 10 to 13) were markedly concentrated within PMN. Clindamycin uptake was rapid: greater than 70% of the total drug entry occurred within the first minute. Accumulation of clindamycin and erythromycin was an active, energy-requiring process, dependent at least in part upon glycolysis. Clindamycin entered PMN by means of an active membrane transport system which was saturable and had a high binding affinity (Km = 2 mM) and maximum velocity of uptake (Vmax = 5 nmol/45 s per 10(6) cells). These observations, together with studies of the biological consequences of intracellular antibiotics, should lead to more effective therapy for infection due to intracellular pathogens..
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W., Good R. A. Effect of antibiotics on the bactericidal activity of human leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jun;71(6):971–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyum A. Separation of blood leucocytes, granulocytes and lymphocytes. Tissue Antigens. 1974;4(4):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking W. G., Golde D. W. The pulmonary-alveolar macrophage (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 Sep 13;301(11):580–587. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197909133011104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Quie P. G., Windhorst D. B., Pollara B., Good R. A. Protection of phagocytized bacteria from the killing action of antibiotics. Nature. 1966 Jun 11;210(5041):1131–1132. doi: 10.1038/2101131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Hand W. L., Francis J. B., King-Thompson N., Corwin R. W. Antibiotic uptake by alveolar macrophages. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Mar;95(3):429–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo M. C., Mandell G. L. The effect of antibiotics on Escherichia coli ingested by macrophages. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Mar;142(3):1048–1050. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Interaction of intraleukocytic bacteria and antibiotics. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1673–1679. doi: 10.1172/JCI107348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. The macrophage as an effector cell. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 11;303(11):622–626. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



