Abstract
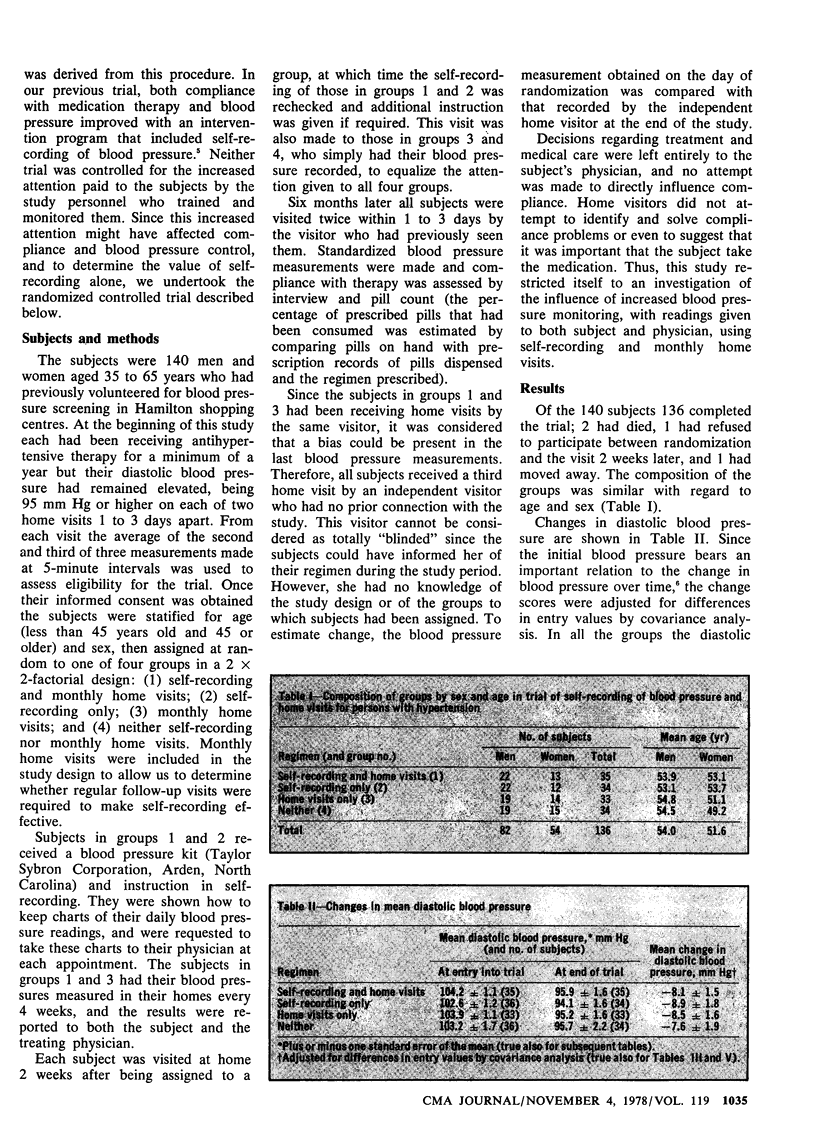
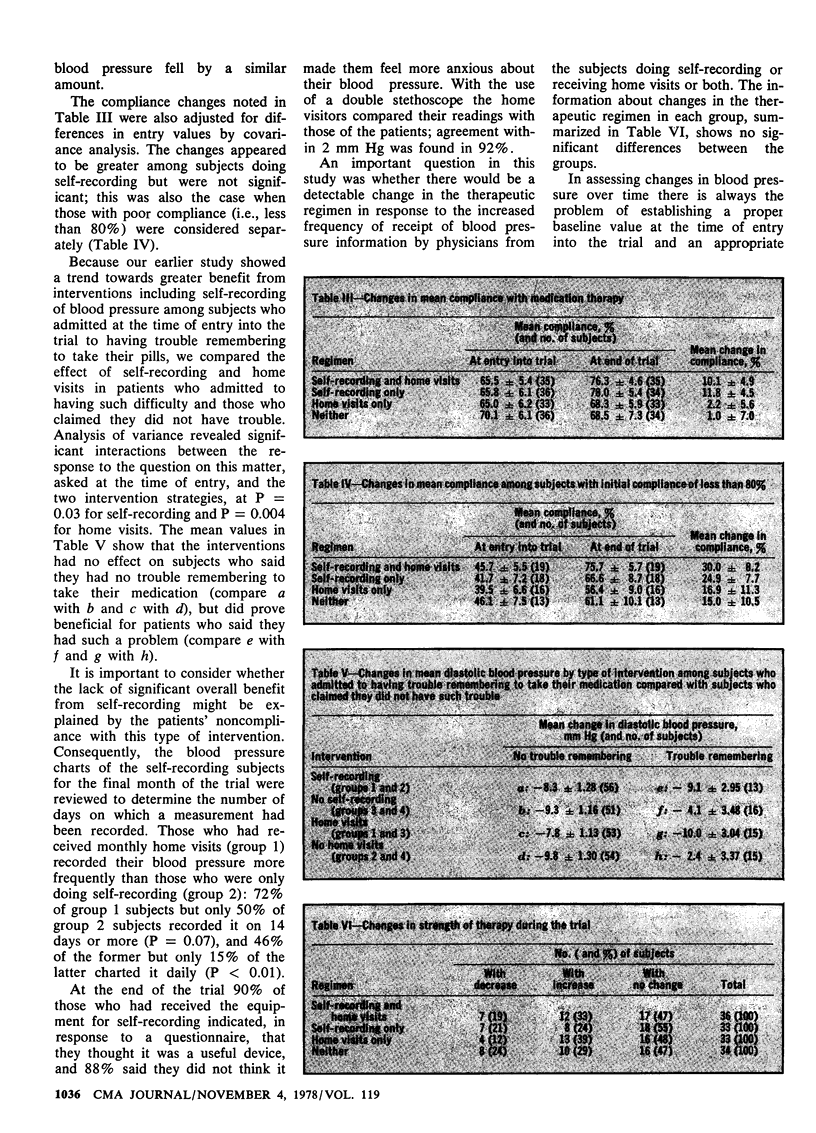
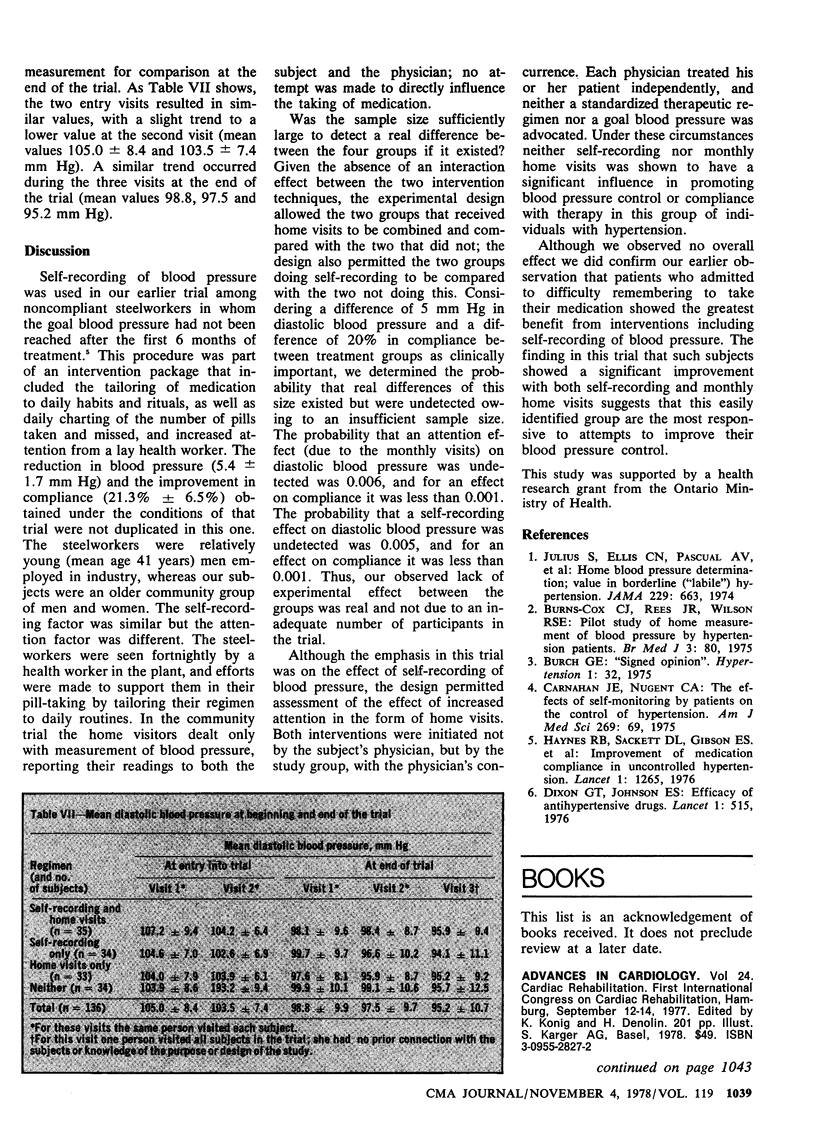
The efficacy of self-recording of blood pressure in the management of hypertension was assessed in a randomized clinical trial involving 140 persons who had been receiving antihypertensive therapy for a year or more, but whose diastolic blood pressure had remained at 95 mm Hg or higher. To control for the increased attention implicit in self-recording, which might affect blood pressure, the patients were assigned at random to one of the four groups: self-recording and monthly home visits, self-recording only, monthly home visits only, and neither self-recording nor monthly home visits. This design also permitted assessment of the effect of home visits. During the 6-month experiment no significant differences were apparent between the groups in either compliance or diastolic blood pressure. However, both self-recording and monthly home visits produced a reduction in blood pressure among patients who admitted to difficulty remembering to take their pills; a reduction was not seen among patients who said they had no such difficulty. This confirmed an earlier observation suggesting that this easily identified group of patients may be the most responsive to intervention programs.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carnahan J. E., Nugent C. A. The effects of self-monitoring by patients on the control of hypertension. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Jan-Feb;269(1):69–73. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197501000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon G. T., Johnson E. S. Efficacy of antihypertensive drugs. Lancet. 1976 Mar 6;1(7958):515–518. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes R. B., Sackett D. L., Gibson E. S., Taylor D. W., Hackett B. C., Roberts R. S., Johnson A. L. Improvement of medication compliance in uncontrolled hypertension. Lancet. 1976 Jun 12;1(7972):1265–1268. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91737-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius S., Ellis C. N., Pascual A. V., Matice M., Hansson L., Hunyor S. N., Sandler L. N. Home blood pressure determination. Value in borderline ("labile") hypertension. JAMA. 1974 Aug 5;229(6):663–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


