Abstract
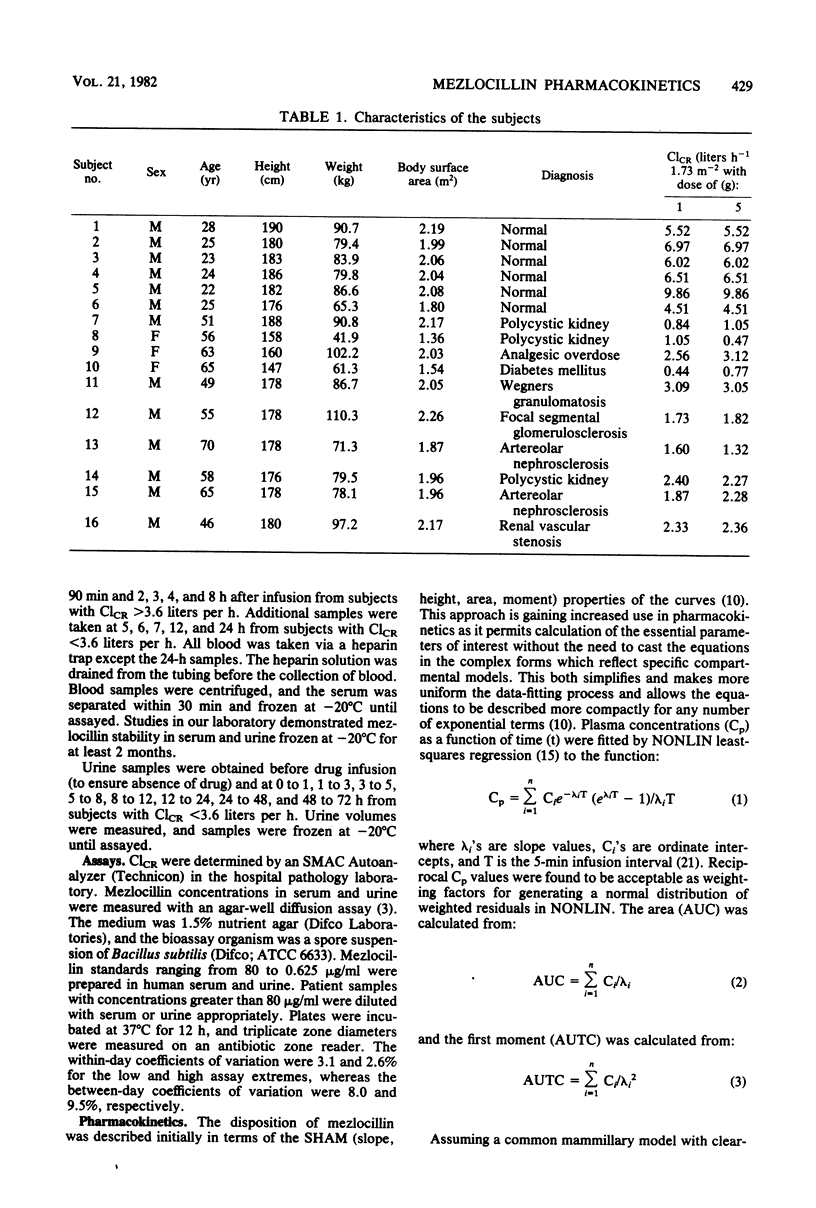
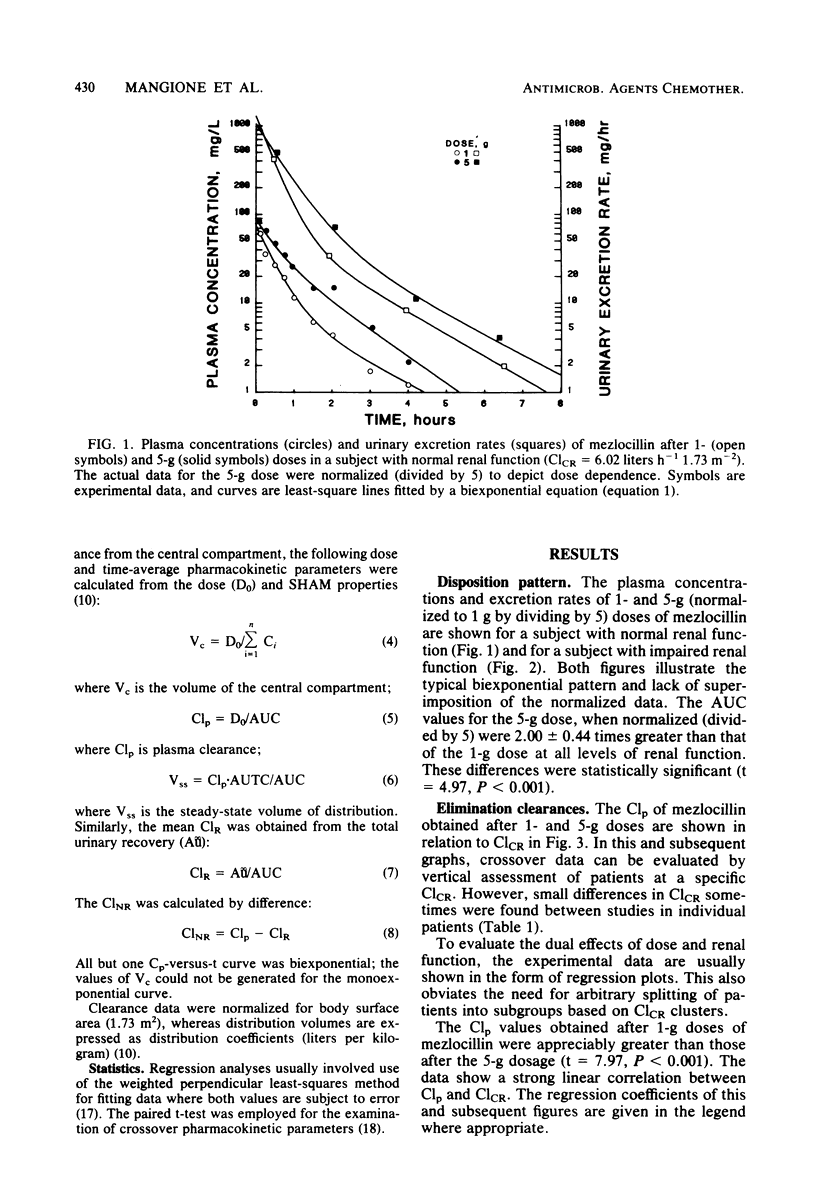
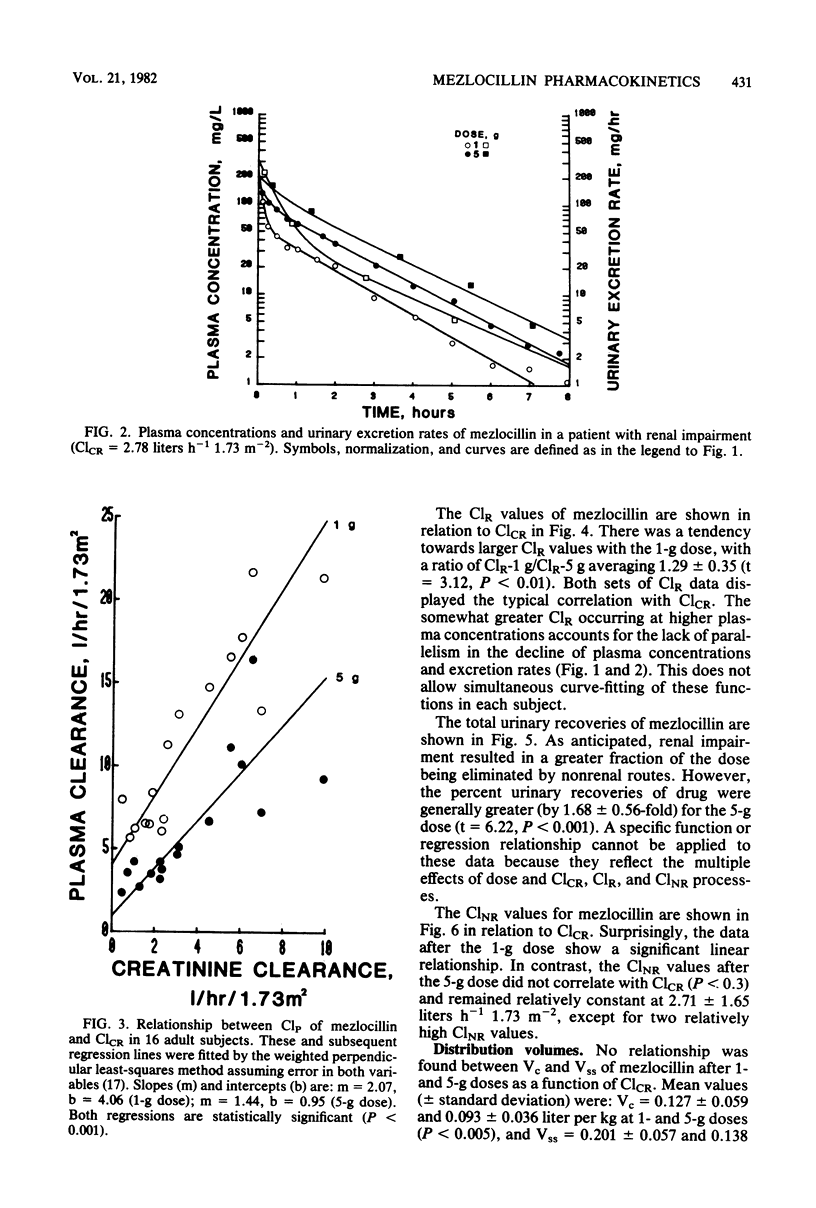
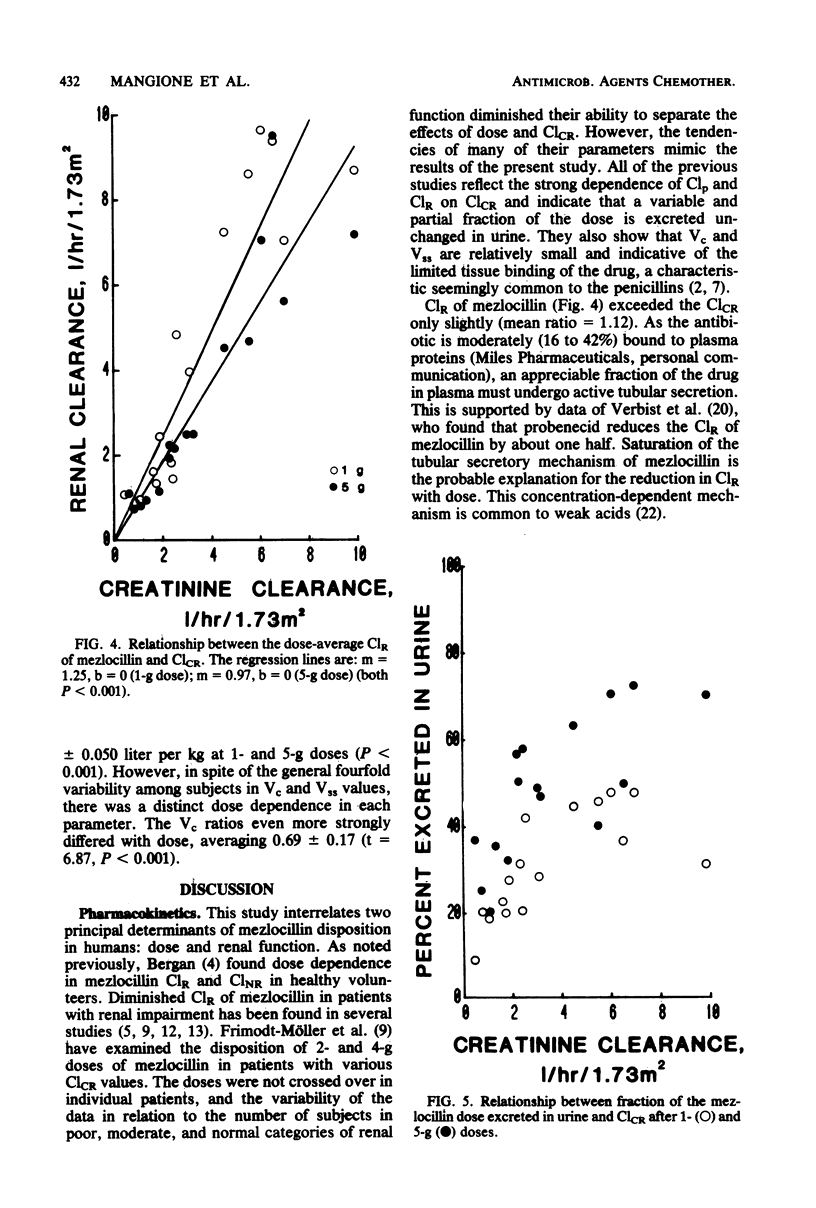
The dose dependence of mezlocillin pharmacokinetics was examined in relation to renal function after intravenous doses of 1 and 5 g in 16 subjects with various degrees of renal impairment. Dose and time-average model-independent physiological parameters were calculated from plasma concentration and urinary excretion data. Lack of superimposition of plasma concentration profiles occurred between dosage levels with a twofold exaggeration of areas under the curve produced between doses of 1 and 5 g. Decreased plasma clearances at the higher dose were caused partly by nonlinear renal clearance, but more markedly by dose dependence in nonrenal clearances. At each dosage level, these parameters were examined in relation to creatinine clearances. Plasma and renal clearances exhibited a typical linear correlation with creatinine clearance for each dose level. However, nonrenal clearances demonstrated a linear relationship with creatinine clearance at the 1-g dose, but apparent saturation of this pathway produced lower and relatively constant nonrenal clearance values at the 5-g dose. Mezlocillin pharmacokinetics are thus influenced by both dose and renal function over the dosage range of 1 to 5 g. Saturation in renal clearance and probably in biliary clearance explains the unusual disposition characteristics of mezlocillin observed in this and previously reported studies.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergan T., Brodwall E. K., Wiik-Larsen E. Mezlocillin pharmacokinetics in patients with normal and impaired renal functions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):651–654. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergan T. Pharmacokinetics of mezlocillin in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):801–806. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. L., Owens E. S., Rall D. P. Evidence of active transport of benzyl-14C-penicillin from cerebrospinal fluid to blood. J Pharm Sci. 1969 Sep;58(9):1106–1109. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600580914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosmidis J., Doundoulaki P., Stathakis C., Zerefos N., Bounia A., Daikos G. K. Elimination kinetics of mezlocillin in normal and impaired renal function including the effects of dialysis. Arzneimittelforschung. 1979;29(12A):1960–1962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer H. J., Bäcker A., Krück F. Inhibition of intestinal (Na+--K+)-ATPase in experimental uremia. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Jan 19;50(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancoast S. J., Jahre J. A., Neu H. C. Mezlocillin in the therapy of serious infections. Am J Med. 1979 Nov;67(5):747–752. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90729-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Nakashima E., Kagami I., Asano T., Nakashima R., Yamana T. Kinetics of Michaelis-Menten absorption of amino-penicillins in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 Aug;30(8):508–509. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G. Linear pharmacokinetic equations allowing direct calculation of many needed pharmacokinetic parameters from the coefficients and exponents of polyexponential equations which have been fitted to the data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1976 Oct;4(5):443–467. doi: 10.1007/BF01062831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. Azlocillin and mezlocillin, two new alpha-amino-substituted penicillins. A comparison of the in vitro activity with other penicillins. Arzneimittelforschung. 1979;29(12A):1929–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


