Abstract
Eleven patients infected with ampicillin-resistant organisms were treated with a combination of CP-45,899, a β-lactamase inhibitor, and ampicillin. All infections were controlled within 7 days without any signs of toxicity.
Full text
PDF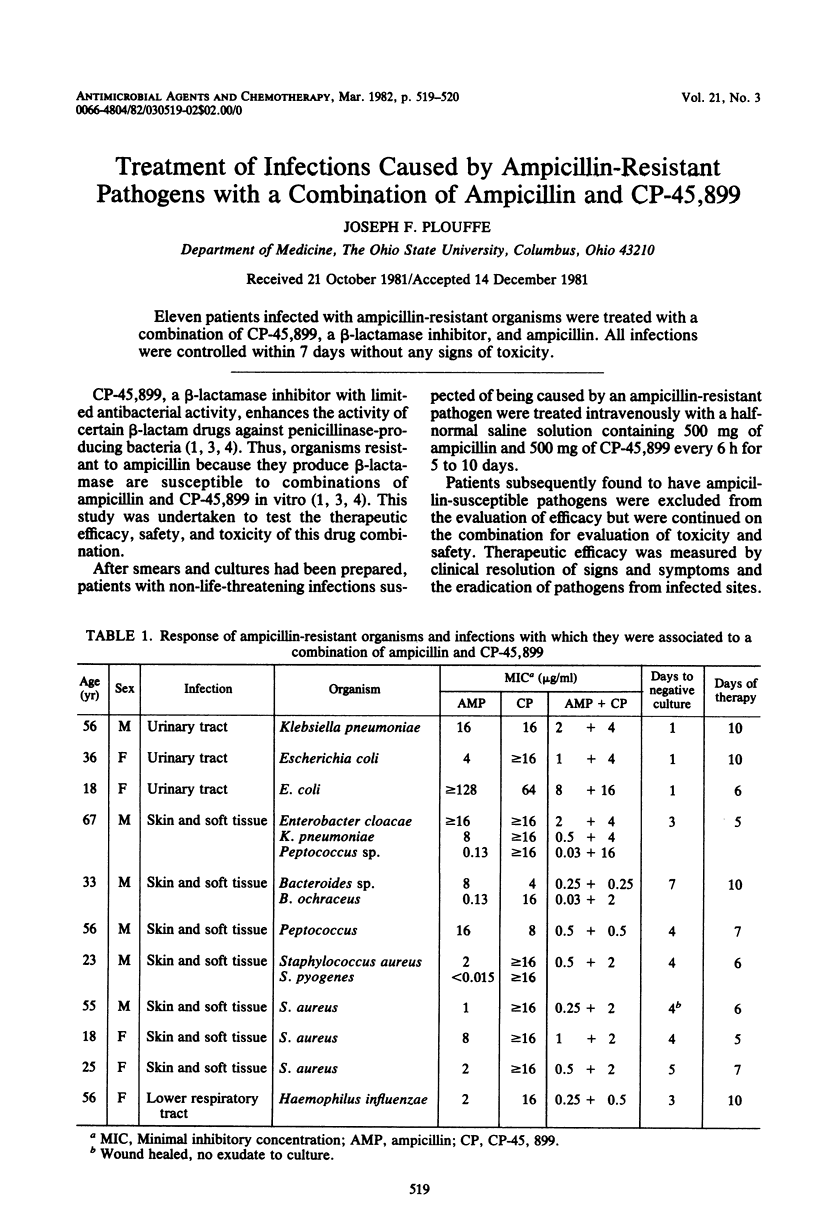

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fass R. J., Rotilie C. A., Prior R. B. Interaction of clindamycin and gentamicin in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):582–587. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Comparative inhibition beta-lactamases by novel beta-lactam compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):171–176. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retsema J. A., English A. R., Girard A. E. CP-45,899 in combination with penicillin or ampicillin against penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, and Bacteroides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):615–622. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


