Abstract
From a group of industrial workers who had a noise-induced hearing loss of at least 30 dB at 4000 Hz 62 were randomly selected after stratification. Controls matched for age and duration of employment were also selected. Resting blood pressures were measured and audiometry was repeated. The findings are presented by age group and for the two groups as a whole. No relation between systolic or diastolic blood pressure and hearing loss was found, and equal proportions of each group had blood pressures exceeding 140/90 mm Hg. Persons with greater hearing loss (more than 60 dB at 4000 Hz) did not have significantly higher blood pressures than their matched controls.
Full text
PDF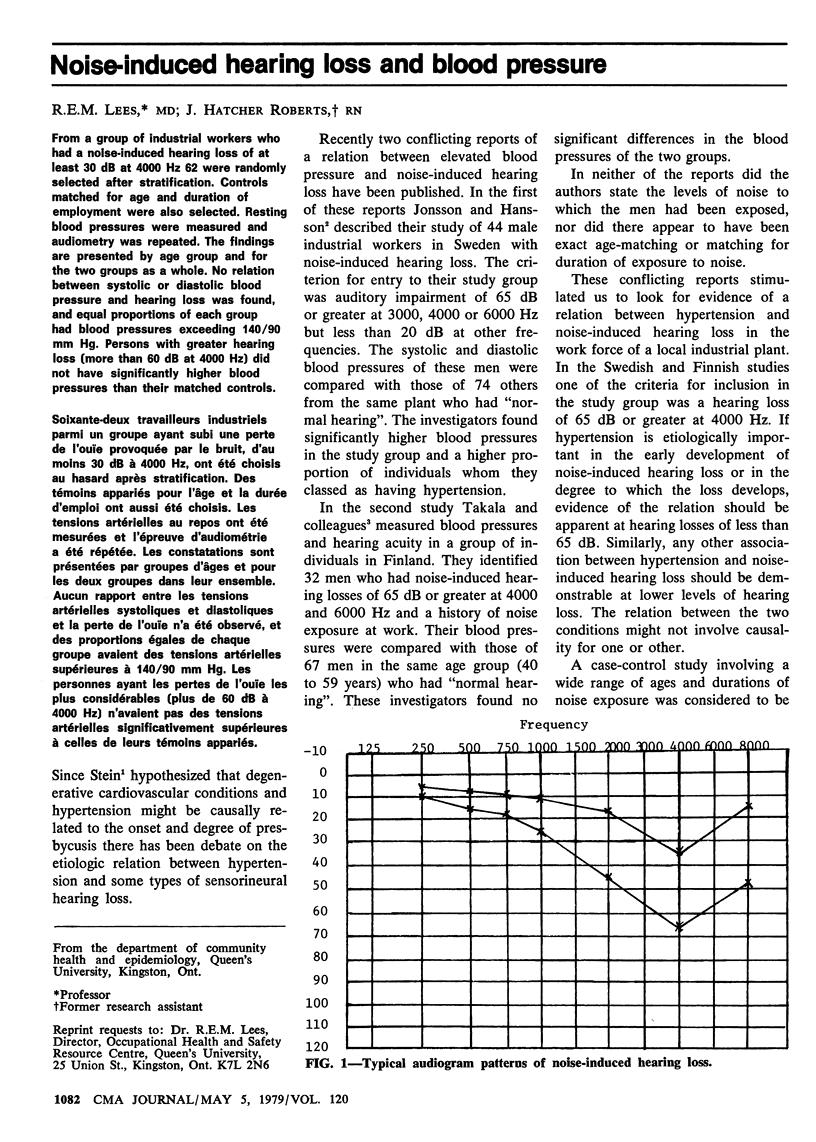


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CATLIN F. I. NOISE AND EMOTIONAL STRESS. J Chronic Dis. 1965 Jun;18:509–518. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(65)90073-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski R. R., Miller M. H. Audiometric configurations of drop forge hammermen and helpers. J Occup Med. 1977 May;19(5):333–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takala J., Varke S., Vaheri E., Sievers K. Noise and blood-pressure. Lancet. 1977 Nov 5;2(8045):974–975. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90908-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


