Abstract
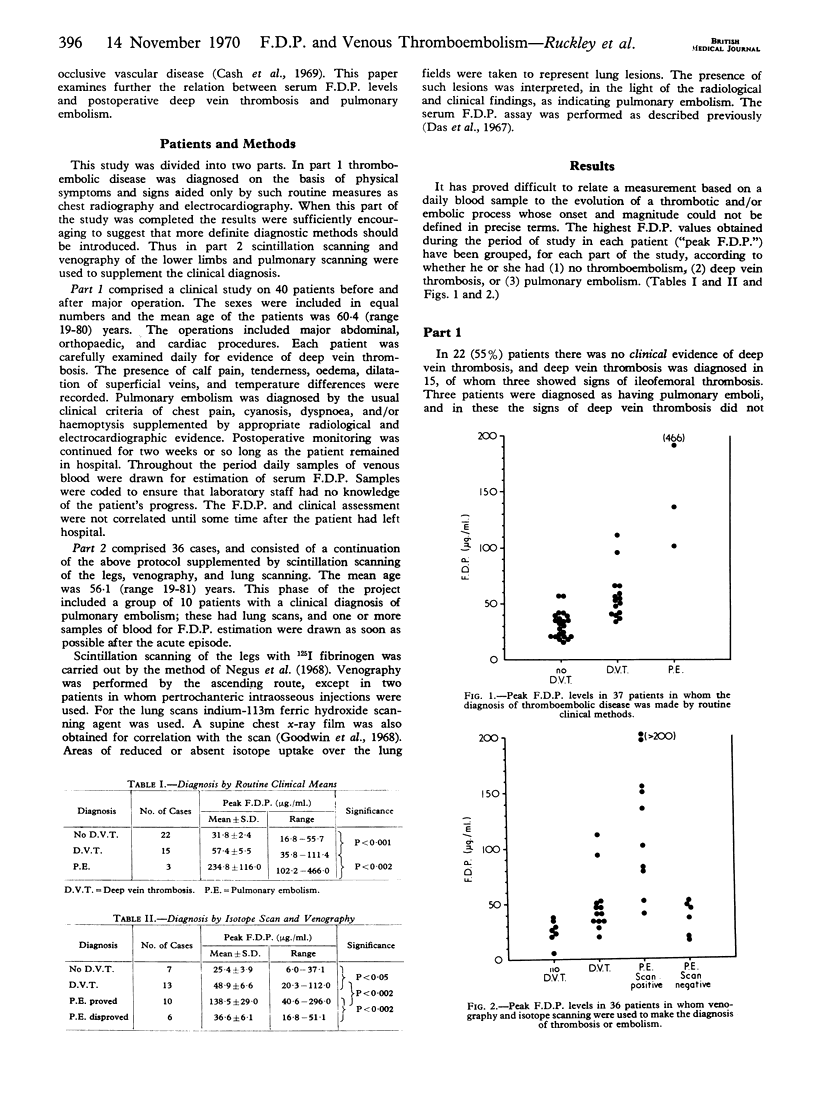
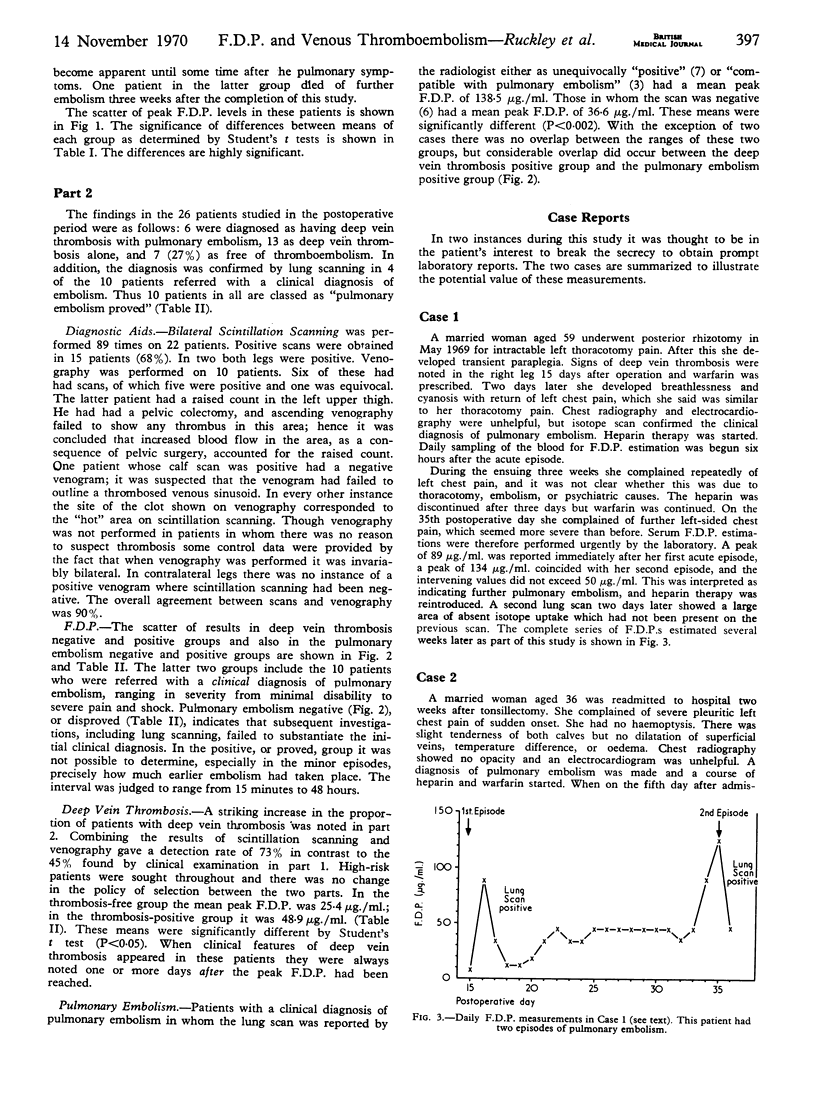
A total of 76 “high-risk” surgical patients were studied for evidence of venous thromboembolic disease. Episodes of deep vein thrombosis and of pulmonary embolism were related to changes in blood levels of fibrin degradation products (F.D.P.). When diagnosed either by ordinary clinical means or by venography and isotope scanning significantly raised F.D.P. levels were found in all cases. Serum F.D.P. estimations are unlikely to help in detecting deep vein thrombosis, but may prove valuable in diagnosing pulmonary embolism.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. Pathogenesis of the coagulation defect developing during pathological plasma proteolytic ("fibrinolytic") states. II. The significance, mechanism and consequences of defective fibrin polymerization. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:917–934. doi: 10.1172/JCI104547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins P., Hawkins L. A. The diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis in the leg using 125-I-Fibrinogen. Br J Surg. 1968 Nov;55(11):825–830. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800551106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. V. The adsorption of proteins on erythrocytes treated with tannic acid and subsequent hemagglutination by antiprotein sera. J Exp Med. 1951 Feb;93(2):107–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOLEY R. N. PULMONARY THROMBOEMBOLISM--THE CASE FOR THE PULMONARY ANGIOGRAM. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1964 Sep;92:693–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash J. D., Woodfield D. G., Das P. C., Allan A. G. Diagnosis of suspected or occult pulmonary embolus. Br Med J. 1969 May 31;2(5656):576–576. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5656.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das P. C., Allan A. G., Woodfield D. G., Cash J. D. Fibrin degradation products in sera of normal subjects. Br Med J. 1967 Dec 23;4(5581):718–720. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5581.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREIMAN D. G., SUYEMOTO J., WESSLER S. FREQUENCY OF PULMONARY THROMBOEMBOLISM IN MAN. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jun 17;272:1278–1280. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196506172722406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBS N. M. Venous thrombosis of the lower limbs with particular reference to bed-rest. Br J Surg. 1957 Nov;45(191):209–236. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004519102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin D. A., Stern H. S., Wagner H. N., Jr Ferric hydroxide particles labeled with indium in 113m for lung scanning. JAMA. 1968 Oct 7;206(2):339–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner C. R., Jr, Miller L. D., Dudrick S. J., Eskin D. J., Bloom P. Reflected ultrasound in the study of diseases of the chest. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1967;78:28–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRELL M. T., TRUELOVE S. C., BARR A. PULMONARY EMBOLISM. Br Med J. 1963 Oct 5;2(5361):830–835. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5361.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Kleiner G. J., Johnson A. J. Quantitative estimation of split products of fibrinogen in human serum, relation to diagnosis and treatment. Blood. 1966 Jul;28(1):1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrell M. T., Dunnill M. S. The post-mortem incdence of pulmonary embolism in a hospital population. Br J Surg. 1968 May;55(5):347–352. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800550506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Sekimoto H., Yasuda Y., Masuda S., Motoda T. [A new method for the determination of fibrinolytic activity by means of immunoassay of breakdown products of fibrin and fibrinogen]. Rinsho Byori. 1965 Oct;13(10):542–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUSSENZWEIG V., SELIGMANN M. [Analysis, by immuno-chemical methods, of the degradation by plasmin of human fibrinogen and fibrin, at different stages]. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1960 Nov-Dec;15:451–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negus D., Pinto D. J., Le Quesne L. P., Brown N., Chapman M. 125-I-labelled fibrinogen in the diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis and its correlation with phlebography. Br J Surg. 1968 Nov;55(11):835–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVITT S., GALLAGHER N. Venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. A clinico-pathological study in injured and burned patients. Br J Surg. 1961 Mar;48:475–489. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004821103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabiston D. C., Jr, Wolfe W. G. Pulmonary embolism. Annu Rev Med. 1967;18:443–458. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.18.020167.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel B., Popky G. L., Wagner D. K., Boland J. P., Mapp E. M., Feigl P. Comparison of clinical and Doppler ultrasound evaluation of confirmed lower extremity venous disease. Surgery. 1968 Jul;64(1):332–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. D., O'Connor J. F., Dalen J. E., Pur-Shahriari A. A., Hoppin F. G., Jr, Hammond D. T., Haynes F. W., Fleischner F. G., Dexter L. The angiographic diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism: evaluation of criteria. Am Heart J. 1967 Jun;73(6):730–741. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(67)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandness D. E., Jr, Schultz R. D., Sumner D. S., Rushmer R. F. Ultrasonic flow detection. A useful technic in the evaluation of peripheral vascular disease. Am J Surg. 1967 Mar;113(3):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(67)90272-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. P. Treatment of pulmonary embolic disease. A critical review of some aspects of current therapy. N Engl J Med. 1965 Oct 21;273(17):885–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196510212731701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttley W. S., Allan A. G., Cash J. D. Fibrin-fibrinogen degradation products in sera of normal infants and children. Arch Dis Child. 1969 Dec;44(238):761–764. doi: 10.1136/adc.44.238.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER H. N., Jr, SABISTON D. C., Jr, MCAFEE J. G., TOW D., STERN H. S. DIAGNOSIS OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN MAN BY RADIOISOTOPE SCANNING. N Engl J Med. 1964 Aug 20;271:377–384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196408202710801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



