Abstract
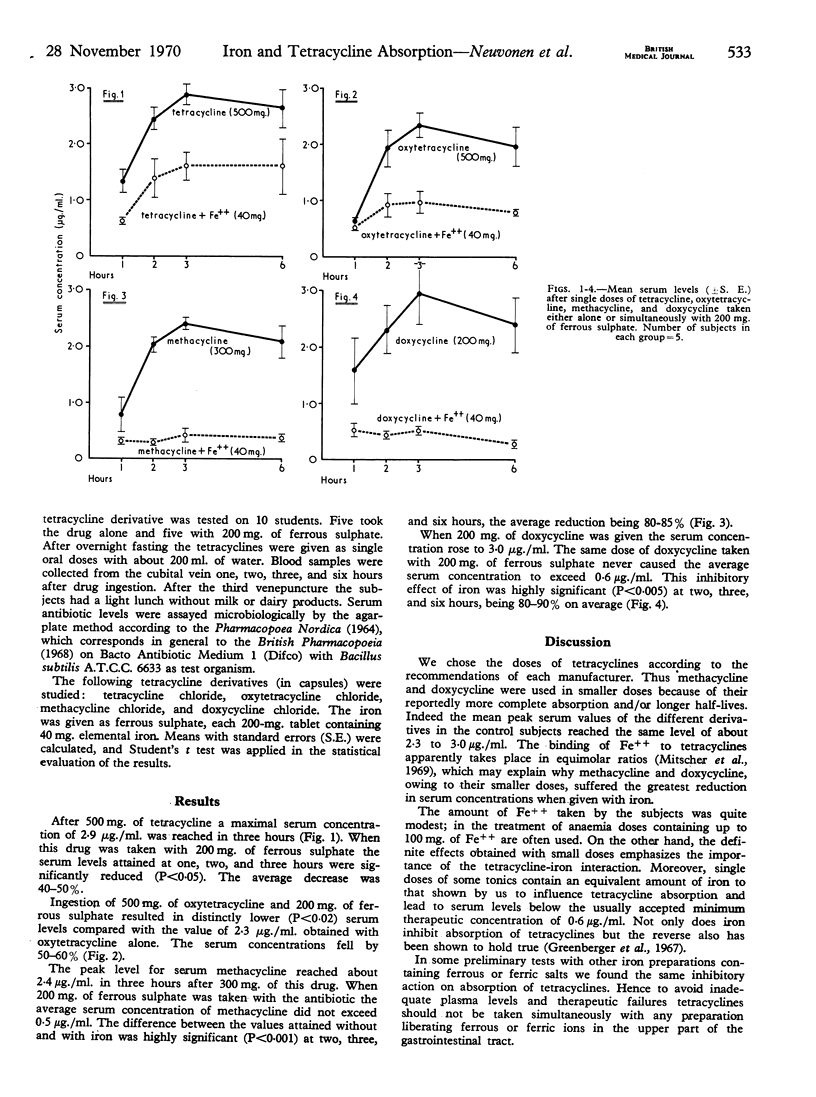
Ferrous sulphate administered together with tetracycline and three of its derivatives—oxytetracycline, methacycline, and doxycycline—was found seriously to impair the absorption of these antibiotics. Thus even small doses of iron taken simultaneously should be avoided during tetracycline treatment.
Full text
PDF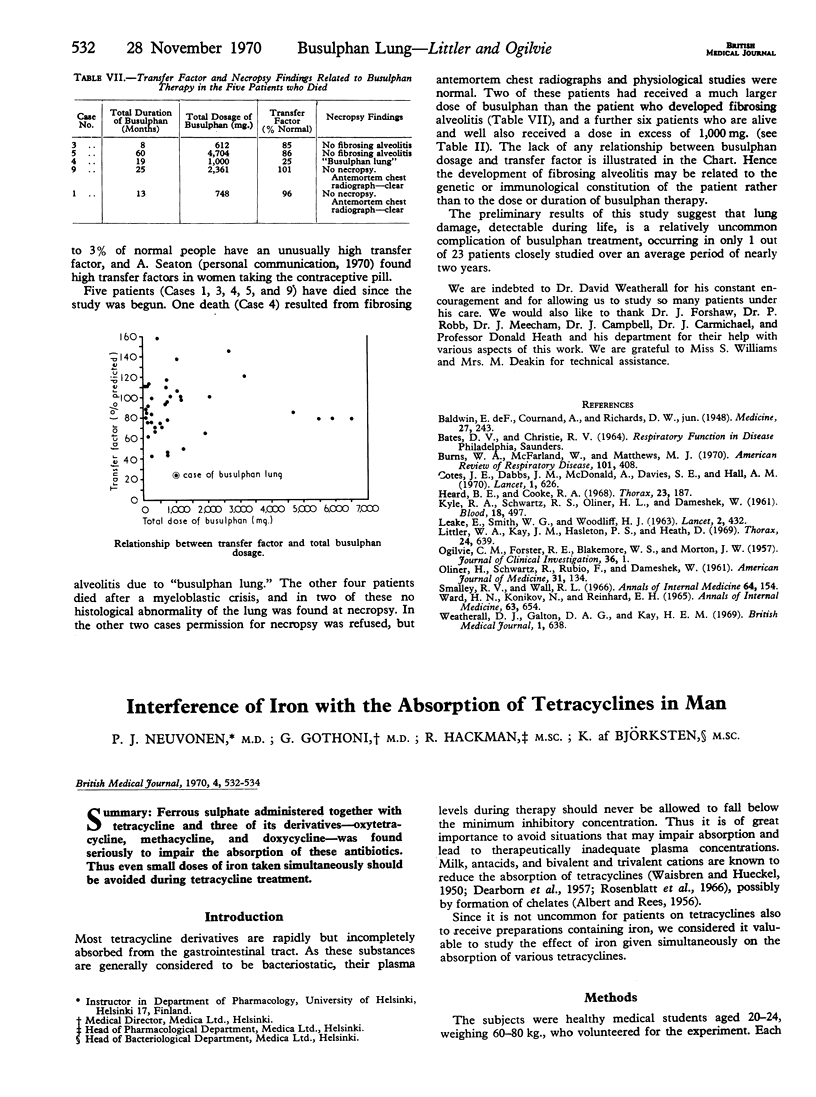

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT A., REES C. W. Avidity of the tetracyclines for the cations of metals. Nature. 1956 Mar 3;177(4505):433–434. doi: 10.1038/177433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEARBORN E. H., LITCHFIELD J. T., Jr, EISNER H. J., CORBETT J. J., DUNNETT C. W. The effects of various substances on the absorption of tetracycline in rats. Antibiotic Med Clin Ther (New York) 1957 Oct;4(10):627–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger N. J., Ruppert R. D., Cuppage F. E. Inhibition of intestinal iron transport induced by tetracycline. Gastroenterology. 1967 Oct;53(4):590–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. E., Barrett J. E., Brodie J. L., Kirby W. M. Comparison of in vitro activity and clinical pharmacology of doxycycline with other tetracyclines. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:134–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


