Abstract
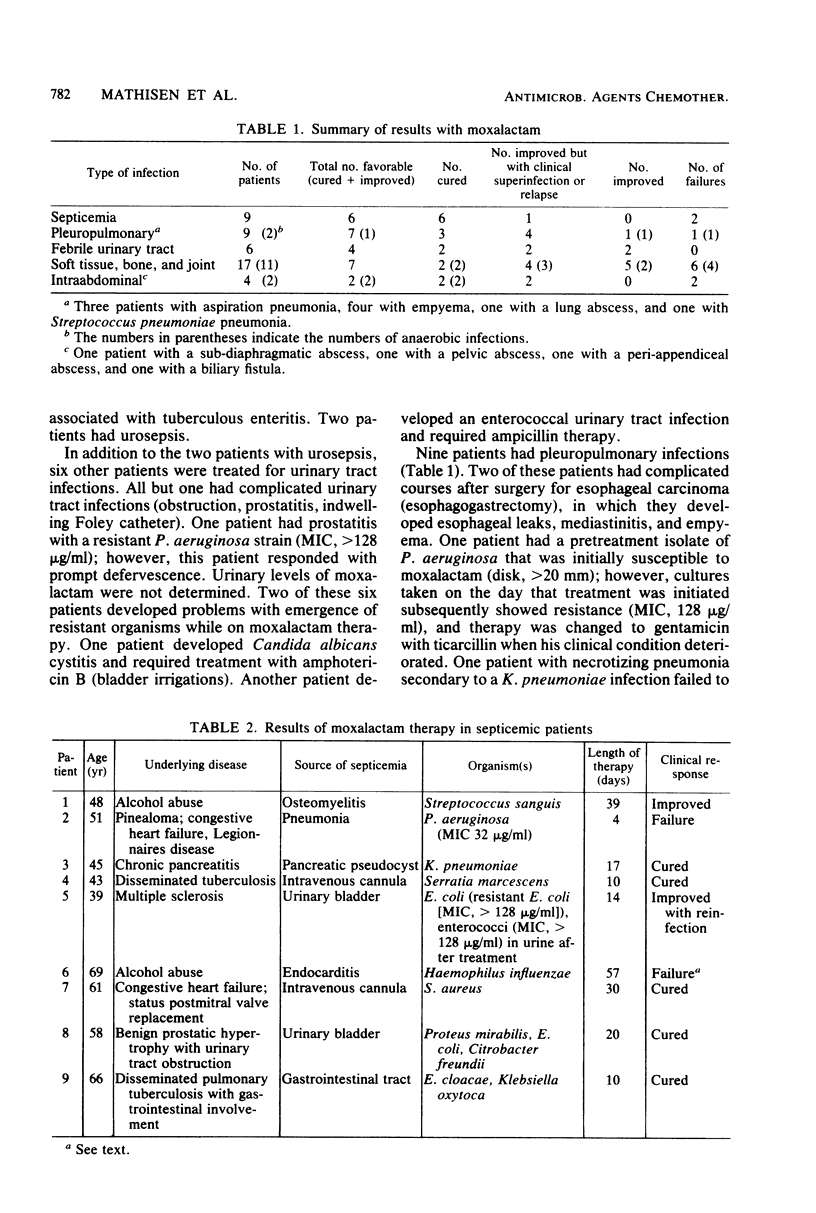
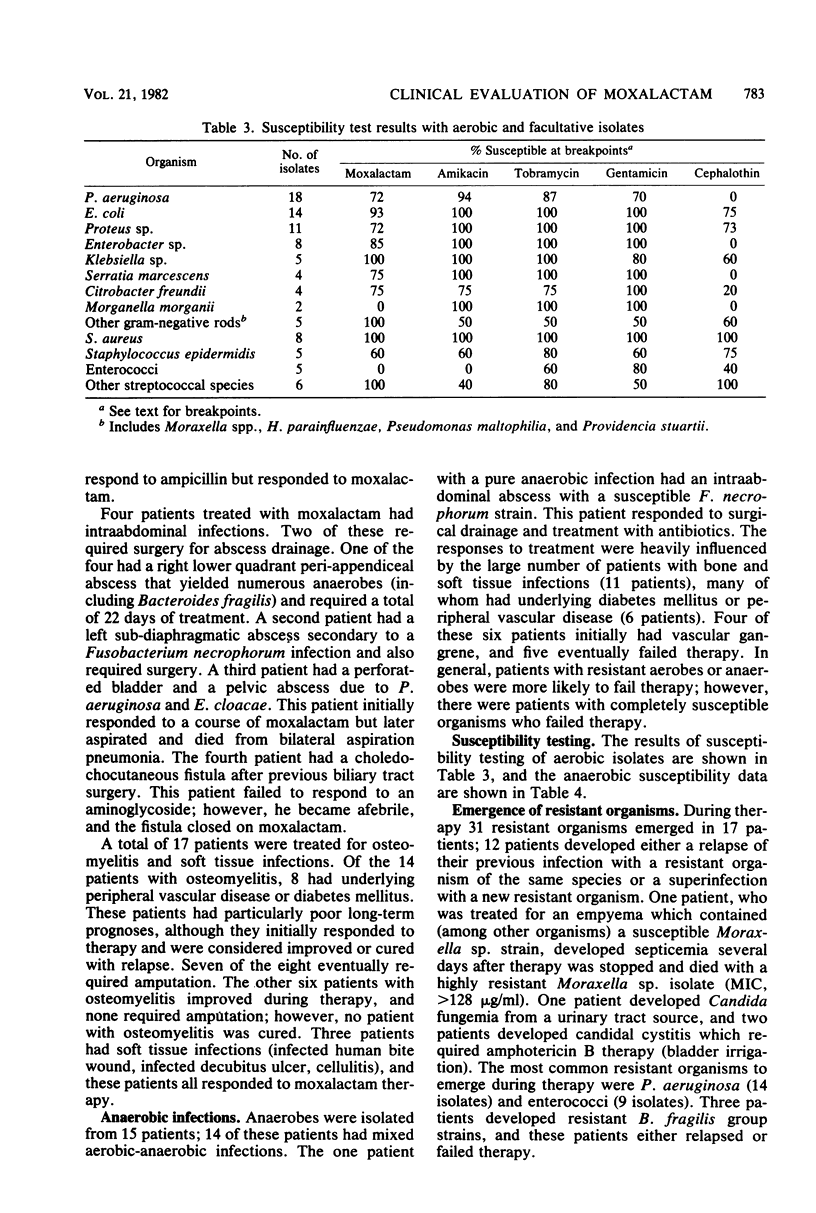
Moxalactam was administered intravenously or intramuscularly or both in doses of 1 to 12 g/day to 45 patients with clinically significant infections (17 soft tissue or bone, 9 pleuropulmonary, 9 septicemic, 6 urinary tract, and 4 intraabdominal infections). Mean 0.5-h postinfusion levels were 105 micrograms/ml for a 4.0-g dose, 44.7 micrograms/ml for a 2.0-g dose, and 18 micrograms/ml for a 1.0-g dose. We identified 28 isolates of Enterobacteriaceae, 10 Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates, 9 Staphylococcus aureus isolates, and 15 anaerobic bacterial isolates. A total of 15 patients were clinically cured, 8 patients improved, 13 patients improved initially but suffered subsequent relapses or superinfections, and 10 patients failed therapy. Toxicity was generally minimal (reversible eosinophilia, and mild liver function abnormalities, and elevated prothrombin time). The selection or emergence of resistant organisms in 17 patients during treatment (particularly Pseudomonas, enterococci, and Candida) was a disturbing feature of therapy. Our results were generally favorable, considering the complicated underlying medical problems of this group of patients.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barza M., Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. In vitro activity of LY127935. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):287–292. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton W. K., Scheld W. M., Spyker D. A., Overby T. L., Sande M. A. Pharmacokinetics of moxalactam in subjects with various degrees of renal dysfunction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):933–938. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. F., Carter M. J., Parsons J., Rissing J. P. Moxalactam (LY127935) in treatment of meningitis due to gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):218–221. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs R. S., Blanco J. D., Castaneda Y. S., St Clair P. J. Therapy of obstetrical infections with moxalactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):1004–1007. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby B. D., Snyder K. M., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Legionnaires' disease: clinical features of 24 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Sep;89(3):297–309. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landesman S. H., Corrado M. L., Cherubin C. C., Gombert M., Cleri D. Diffusion of a new beta-lactam (LY 127935) into cerebrospinal fluid. Implications for therapy of gram-negative bacillary meningitis. Am J Med. 1980 Jul;69(1):92–98. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90505-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentino J. R., Rytel M. W., Moore E. Therapy of lower respiratory tract infections with moxalactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):801–806. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston W. K., Elliott A. M., Dismukes W. E., Avent C. K., Cobbs C. G. Clinical evaluation of moxalactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):88–97. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson D. A., Hoeprich P. D., Nolan S. M., Goldstein E. Successful treatment of gram-negative bacillary meningitis with moxalactam. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Sep;95(3):302–305. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-3-302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt R., Ehrlich S. L., Afarian J., O'Brien T. F., Pennington J. E., Kass E. H. Moxalactam therapy of infections caused by cephalothin-resistant bacteria: influence of serum inhibitory activity on clinical response and acquisition of antibiotic resistance during therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Sep;20(3):351–355. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe R. D., Finegold S. M. Comparative in vitro activity of new beta-lactam antibiotics against anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):600–609. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan S., Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Pharmacokinetics of moxalactam and cefazolin compared in normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):302–305. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofte R. W., Rotschafer J., Solliday J., Crossley K. B. Moxalactam therapy for a wide spectrum of bacterial infections in adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):740–744. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldvogel F. A., Medoff G., Swartz M. N. Osteomyelitis: a review of clinical features, therapeutic considerations and unusual aspects. 3. Osteomyelitis associated with vascular insufficiency. N Engl J Med. 1970 Feb 5;282(6):316–322. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197002052820606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Busuttil R. W., Kurtz T. O., Young L. S. Moxalactam therapy for bacterial infections. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Nov;141(12):1607–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. L. Enterococcal superinfection and colonization after therapy with moxalactam, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jun;94(6):784–785. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-6-784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



