Abstract
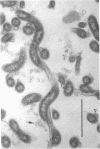
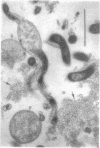
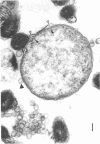
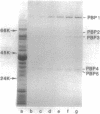
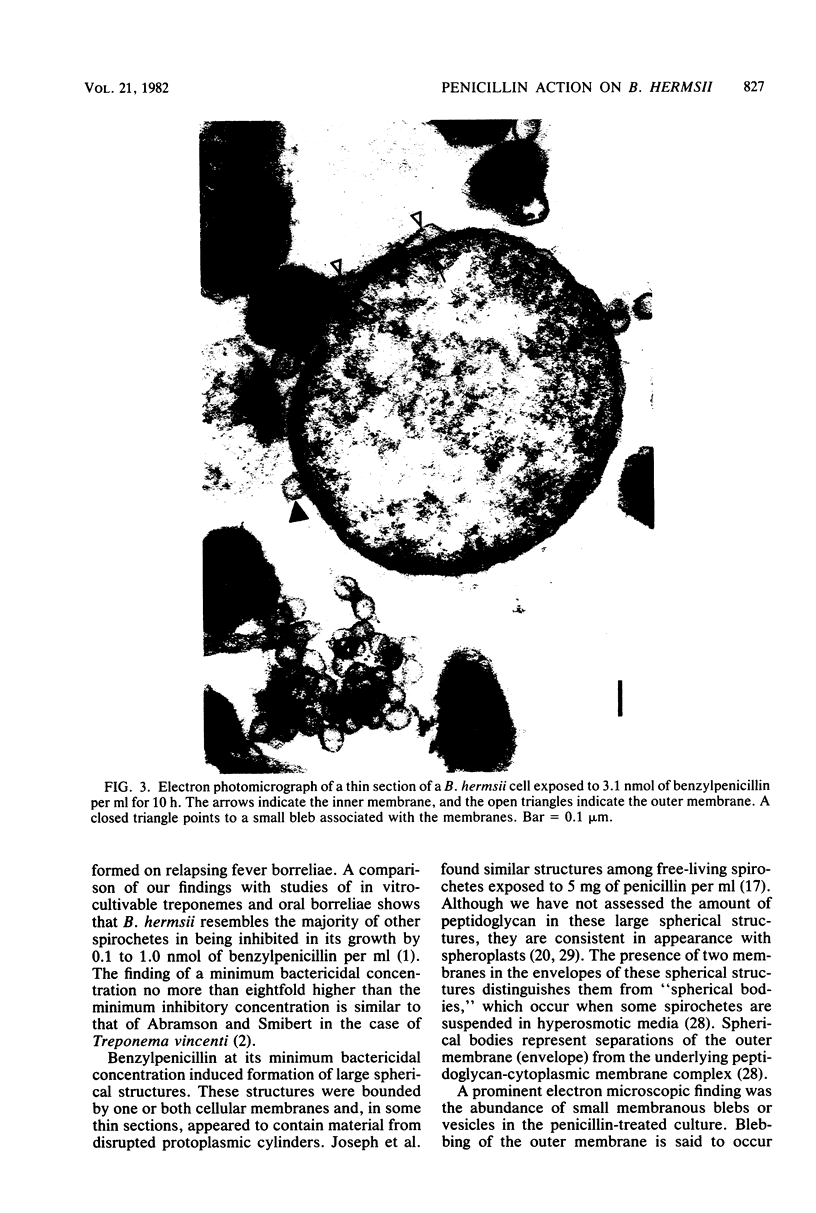
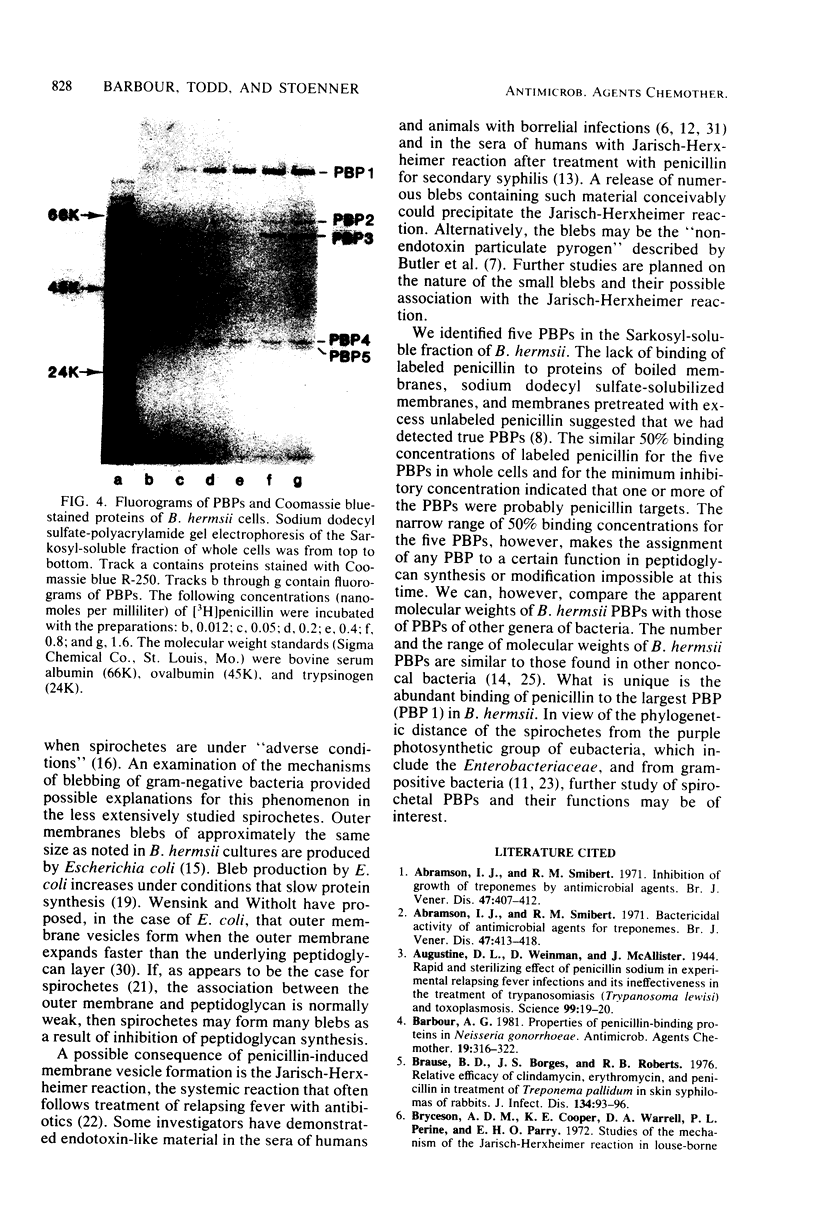
Borrelia hermsii, a spirochete and an etiological agent of relapsing fever, was cultivated in modified Kelly medium. Studies of the action of penicillin on B. hermsii strain HS1 revealed the following: (i) the in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration and minimum bactericidal concentration of benzylpenicillin for this strain were 0.4 and 3.1 nmol/ml (0.15 and 1.1 micrograms/ml), respectively; (ii) the primary morphological responses at the minimum bactericidal concentration of benzylpenicillin were the formation of spheroplast-like structures and an increased number of small, membranous blebs; (iii) radioactive benzylpenicillin bound to five penicillin-binding proteins in the whole cells of B. hermsii. The 50% binding concentrations of labeled penicillin for the five penicillin-binding proteins were within a factor of five of the minimum inhibitory concentration. More than one-half of the total bound labeled penicillin was associated with penicillin-binding protein 1, the penicillin-binding protein with the largest apparent molecular weight (90,000).
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson I. J., Smibert R. M. Bactericidal activity of antimicrobial agents for treponemes. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Dec;47(6):413–418. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.6.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson I. J., Smibert R. M. Inhibition of growth of treponemes by antimicrobial agents. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Dec;47(6):407–412. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.6.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine D. L., Weinman D., McAllister J. RAPID AND STERILIZING EFFECT OF PENICILLIN SODIUM IN EXPERIMENTAL RELAPSING FEVER INFECTIONS AND ITS INEFFECTIVENESS IN THE TREATMENT OF TRYPANOSOMIASIS (TRYPANOSOMA LEWISI) AND TOXOPLASMOSIS. Science. 1944 Jan 7;99(2558):19–20. doi: 10.1126/science.99.2558.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Properties of penicillin-binding proteins in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):316–322. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brause B. D., Borges J. S., Roberts R. B. Relative efficacy of clindamycin, erythromycin, and penicillin in treatment of Treponema pallidum in skin syphilomas of rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):93–96. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryceson A. D., Cooper K. E., Warrell D. A., Perine P. L., Parry E. H. Studies of the mechanism of the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction in louse-borne relapsing fever: evidence for the presence of circulating Borrelia endotoxin. Clin Sci. 1972 Sep;43(3):343–354. doi: 10.1042/cs0430343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Hazen P., Wallace C. K., Awoke S., Habte-Michael A. Infection with Borrelia recurrentis: pathogenesis of fever and petechiae. J Infect Dis. 1979 Nov;140(5):665–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.5.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-susceptible and intrinsically resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):730–737. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway R. E., Levin J., Butler T., Naff G. B., Goldsmith G. H., Saito H., Awoke S., Wallace C. K. Activation of protein mediators of inflammation and evidence for endotoxemia in Borrelia recurrentis infection. Am J Med. 1977 Dec;63(6):933–938. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Elin R. J., Berry F. W., Jr, Frank M. M. Endotoxemia associated with the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jul 22;295(4):211–213. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197607222950409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Penicillin-binding proteins in bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):148–157. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., van der Laan J. W., de Leij L., Witholt B. Release of outer membrane fragments from normally growing Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;455(3):889–899. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C. The spirochetes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:89–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Holt S. C., Canale-Parola E. Peptidoglycan of free-living anaerobic spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):426–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.426-435.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. Cultivation of Borrelia hermsi. Science. 1971 Jul 30;173(3995):443–444. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3995.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Vesk M., Work E. Relation between excreted lipopolysaccharide complexes and surface structures of a lysine-limited culture of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1206–1217. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1206-1217.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. H. Bacterial protoplasts--a review. J Theor Biol. 1963 Jul;5(1):1–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(63)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morioka H., Ozasa H., Kishida T., Yokota Y., Suganuma A. The peptidoglycan layer of the Reiter treponeme as revealed by thin sectioning and freeze-etching techniques. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1979;28(3):189–192. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jmicro.a050175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUHARDT V. T. Treatment of relapsing fever with antibiotics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1952 Dec 30;55(6):1209–1221. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1952.tb22685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoenner H. G. Biology of Borrelia hermsii in Kelly medium. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):540–543. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.540-543.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. S., Burgdorfer W., Russell R., Francis B. J. Outbreak of tick-borne relapsing fever in Spokane County, Washington. JAMA. 1969 Nov 10;210(6):1045–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umemoto T., Namikawa I. Electron microscopy of the spherical body of oral spirochetes in vitro. Further studies. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(4):321–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink J., Witholt B. Outer-membrane vesicles released by normally growing Escherichia coli contain very little lipoprotein. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):331–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. J., Woodrow D. F. Terminal changes in mice experimentally infected with Borrelia duttoni. J Pathol. 1980 Feb;130(2):83–90. doi: 10.1002/path.1711300204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]