Abstract
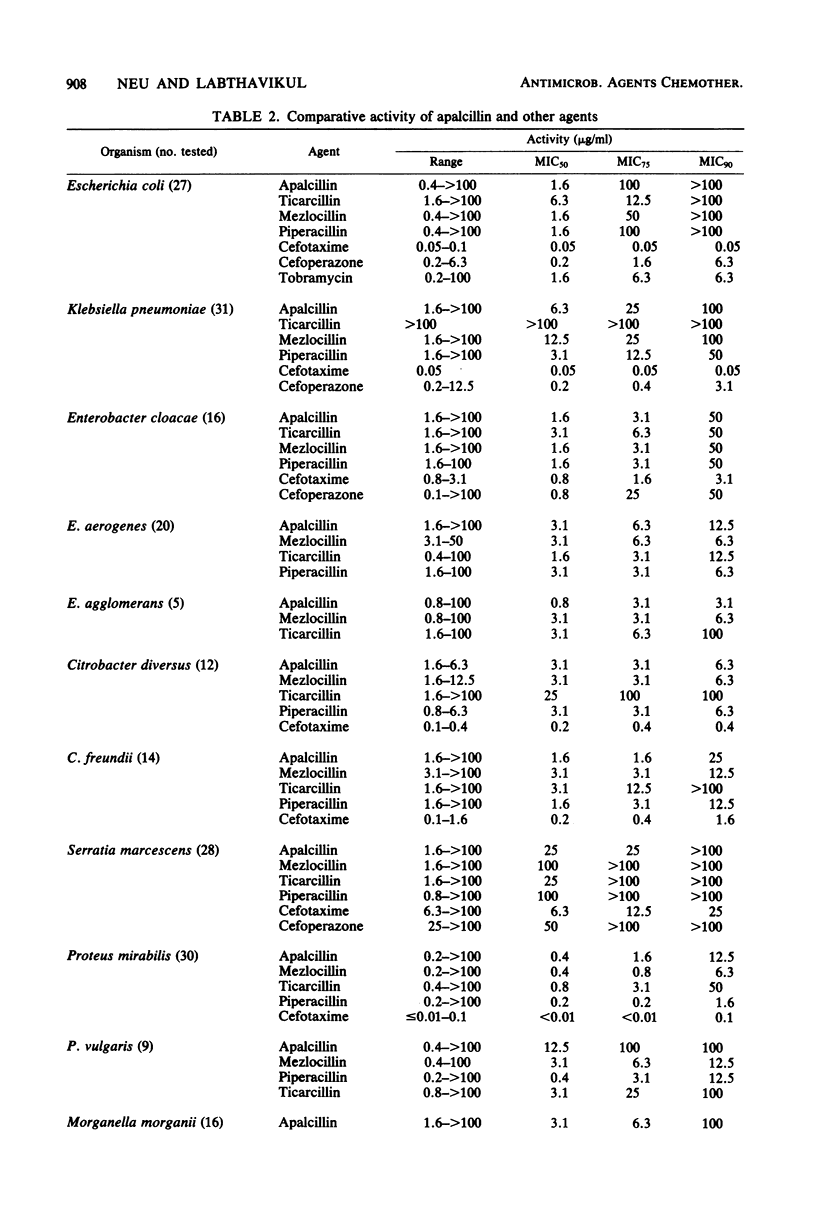
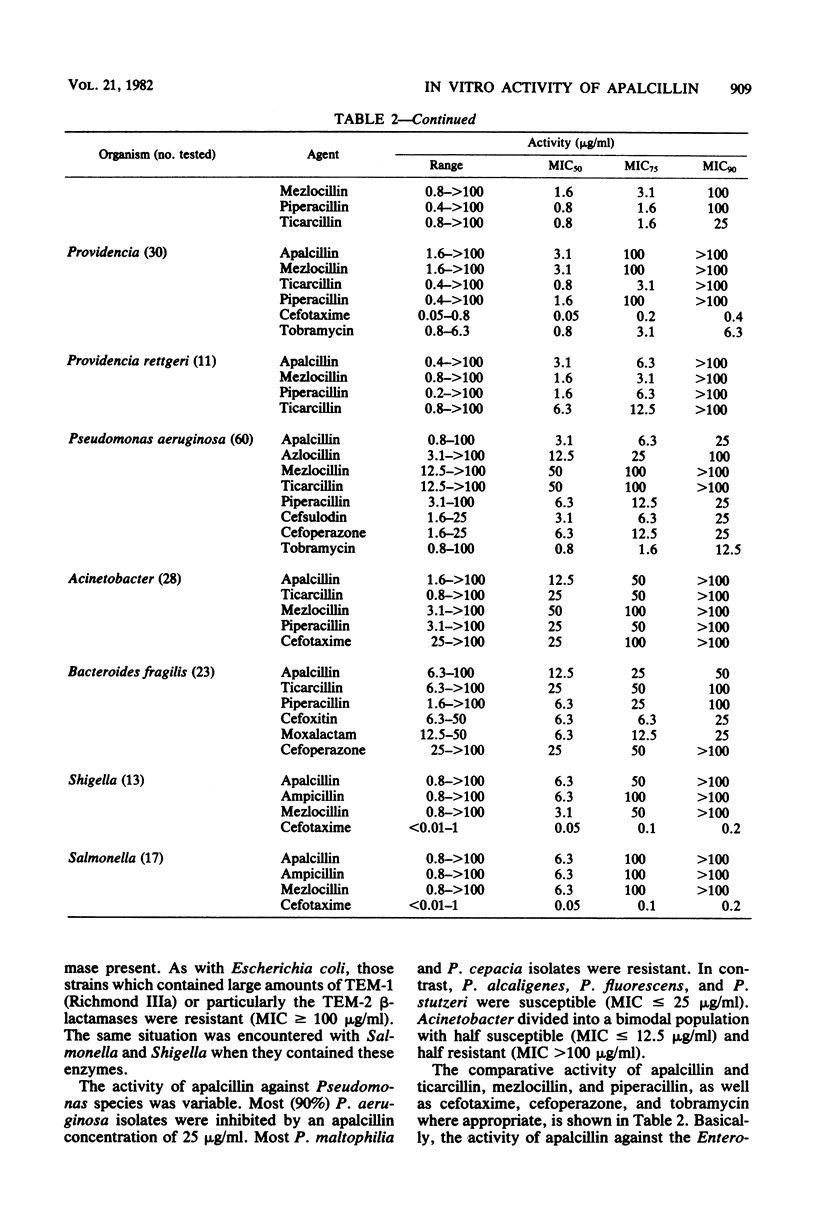
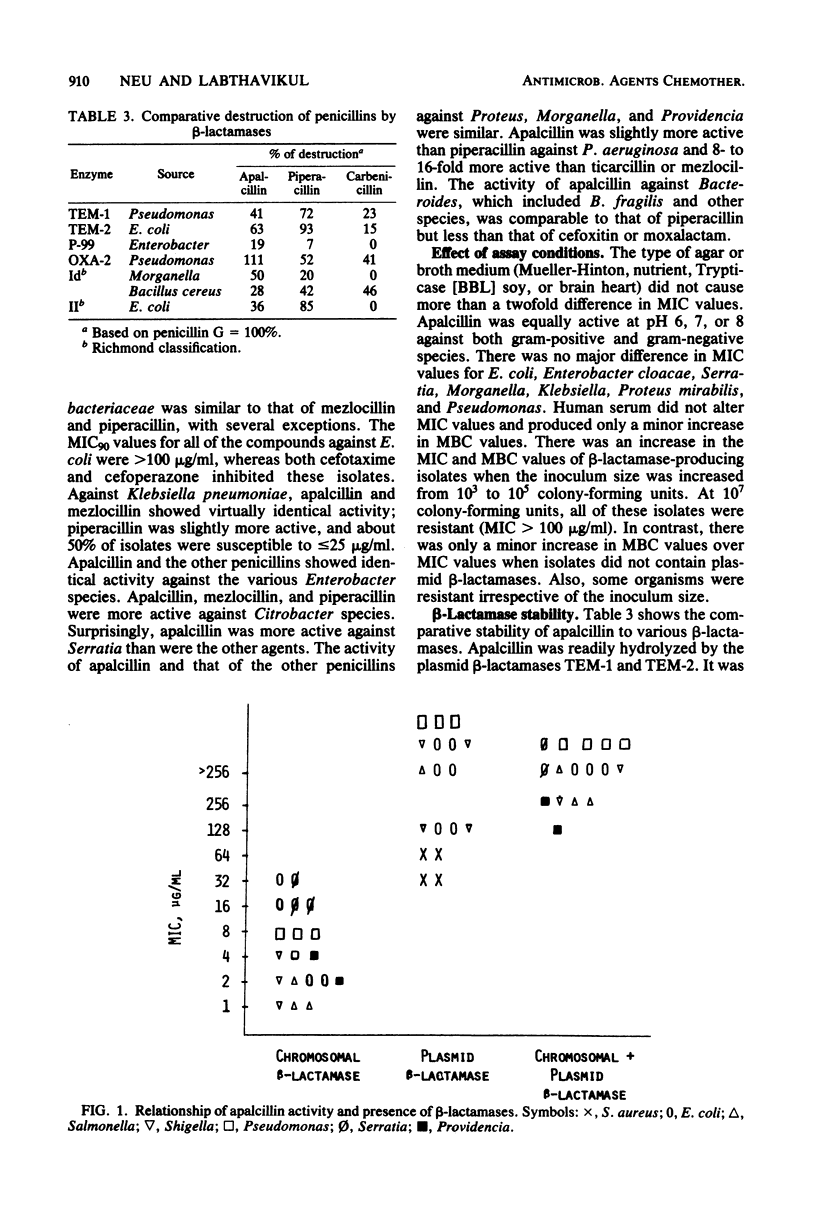
Apalcillin, a naphthydridine derivative of ampicillin, was compared with ticarcillin, azlocillin, mezlocillin, piperacillin, cefotaxime, and cefoperazone against gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial isolates and with cefsulodin and tobramycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The minimal concentrations of apalcillin at which 50 and 90% of hospital isolates of Escherichia coli were inhibited were similar to those of mezlocillin and piperacillin (1.6 and 100 micrograms/ml, respectively). Apalcillin had minimal inhibitory concentrations similar to those of piperacillin against Citrobacter freundii and Citrobacter diversus. Against Klebsiella, apalcillin inhibited 50% of organisms at a concentration of 6.3 micrograms/ml, similar to piperacillin. The activity of apalcillin against Enterobacter (E. aerogenes, E. cloacae, and E. agglomerans) was similar to that of mezlocillin and piperacillin and greater than that of ticarcillin. The activity of apalcillin against Proteus mirabilis was similar to that of the other agents, as was its activity against indole-positive Proteus and Providencia. Only 40% of Serratia were inhibited at an apalcillin concentration of 25 micrograms/ml. Apalcillin was as active as piperacillin but twofold less active than cefoxitin or moxalactam against Bacteroides fragilis. It was as active as piperacillin, cefoperazone, and cefsulodin against P. aeruginosa (apalcillin inhibited 90% of organisms at a concentration of 25 mg/ml). There was an inoculum effect and a difference in the minimal inhibitory concentration and minimal bactericidal concentration with beta-lactamase strains. Apalcillin was hydrolyzed by plasmid beta-lactamase but not as well by cephalosporinases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P., Weaver S., Pan T. PC-904, a new semisynthetic penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):14–18. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Piperacillin, a new penicillin active against many bacteria resistant to other penicillins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):358–367. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P. Synergy of azlocillin and mezlocillin combined with aminoglycoside antibiotics and cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):813–819. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Eda Y., Tobiki H., Nakagome T., Komatsu T. PC-904, a novel broad-spectrum semisynthetic penicillin with marked antipseudomonal activity: microbiological evaluation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Feb;9(2):262–273. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Kubo M., Kurashige S., Mitsuhashi S. Antibacterial activity of apalcillin (PC-904) against gram-negative bacilli, especially ampicillin-, carbenicillin-, and gentamicin-resistant clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):745–752. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Matsuhashi M., Mitsuhashi S. Comparative studies of penicillin-binding proteins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Matsuhashi M., Takaoka M., Mitsuhashi S. New antipseudomonal penicillin, PC-904: affinity to penicillin-binding proteins and inhibition of the enzyme cross-linking peptidoglycan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):617–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


