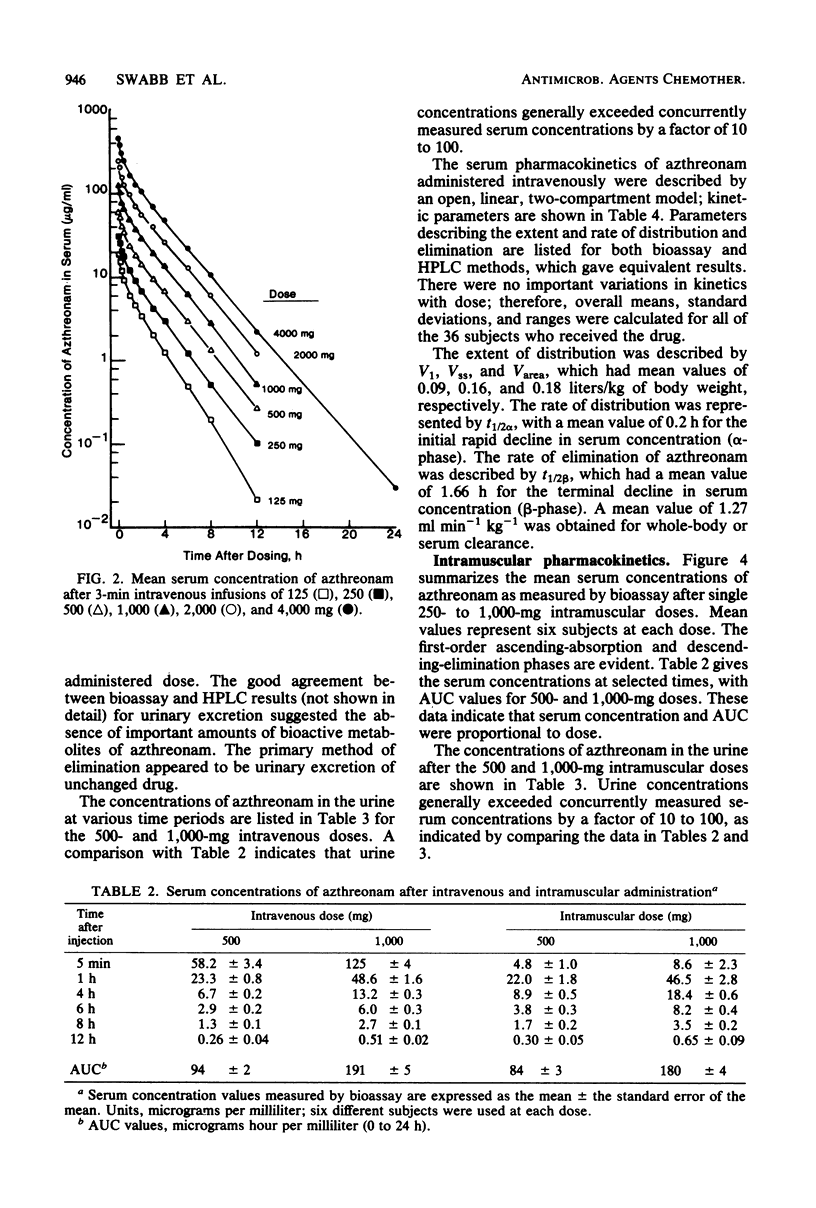
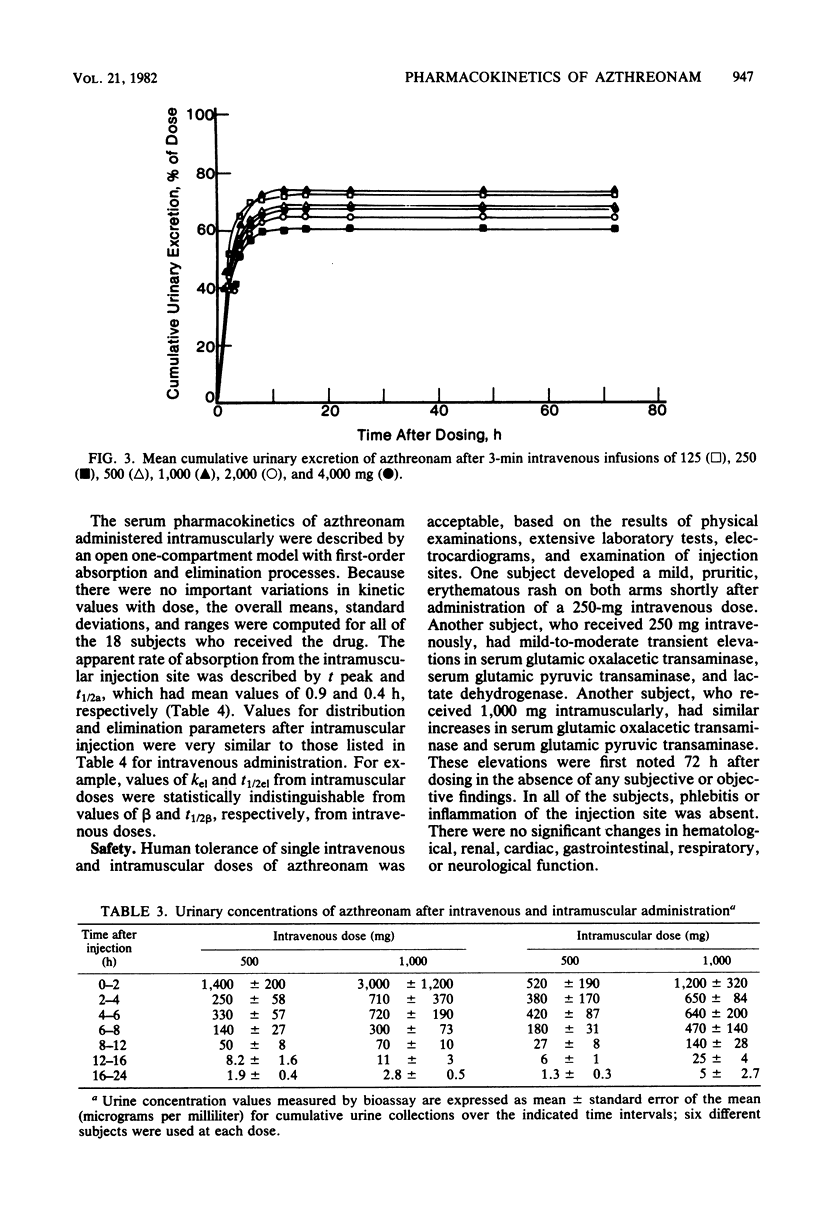
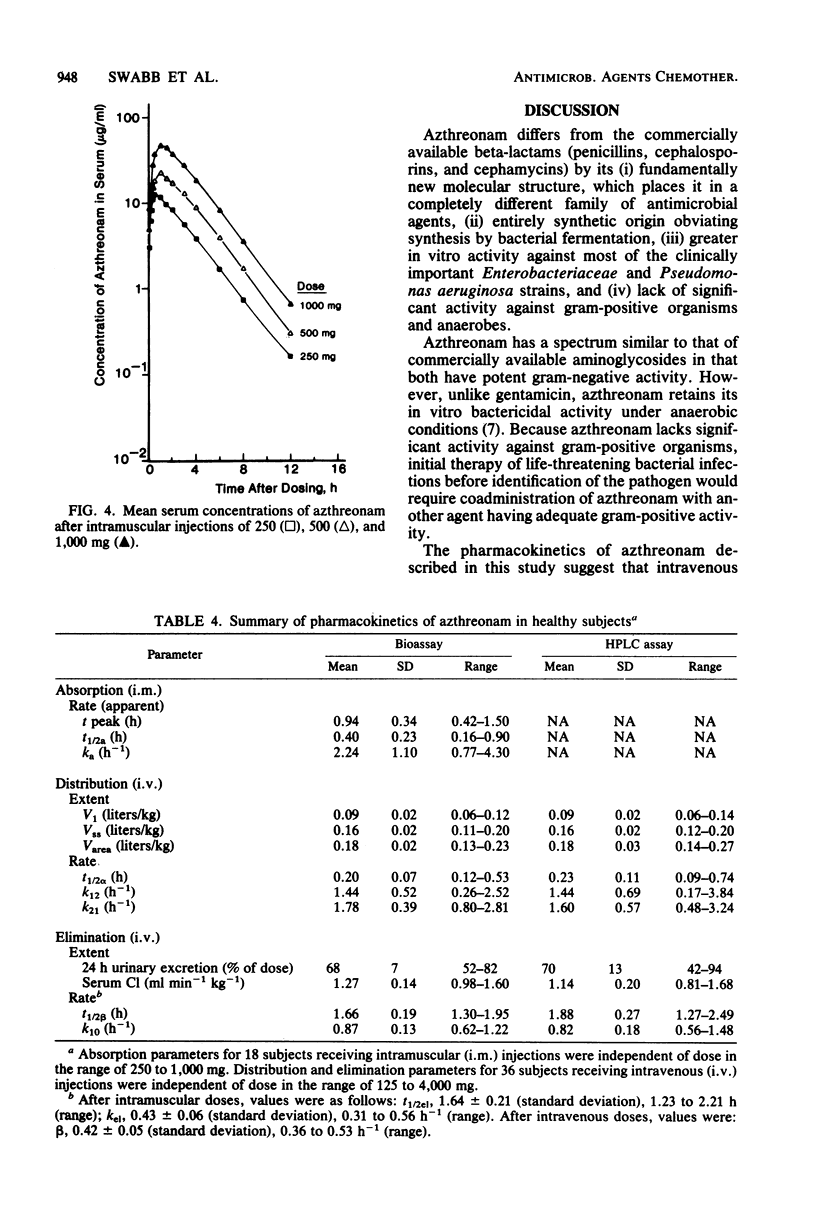
Abstract
Azthreonam (SQ 26,776) is a new, completely synthetic, monocyclic beta-lactam antimicrobial agent that is highly active in vitro against most gram-negative bacteria. The pharmacokinetics of single intravenous doses of 125 to 4,000 mg, studied in 36 healthy male subjects, were best described by an open, linear, two-compartment kinetic model. The mean peak serum levels at 5 min after completion of 3-min infusions of 500-, 1,000- and 2,000-mg doses were 58, 125, and 242 micrograms/ml, respectively. The mean terminal serum half-life for all doses was 1.66 h, and the apparent volume of distribution was 0.18 liter/kg. The mean serum clearance was 1.27 ml min-1 kg-1, and urinary excretion averaged 68% of the doses administered. The pharmacokinetics of single intramuscular doses of 250 to 1,000 mg, studied in 18 subjects, were best described by a linear, one-compartment model, with first-order absorption and elimination. The mean peak serum levels occurring at 1 h after doses of 250, 500, and 1,000 mg were 12, 22, and 46 micrograms/ml, respectively. Other kinetic parameters were similar to those for intravenous administration. Tolerance of azthreonam was good, with only a mild rash in one subject and with mild to moderate transient elevations in serum transaminases and lactate dehydrogenase in two subjects.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner D. P., Whitney R. R., Baughn C. O., Miller B. H., Olsen S. J., Sykes R. B. In-vivo properties of SQ 26,776. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):123–130. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim G. R., Sibley P. L., Hines F. A., Miller M. M., Peterson A. E., Yoon Y. H. Parenteral toxicological profile of the monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotic SQ 26,776 in mice, rats and dogs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):141–146. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Antibacterial activity of a monocyclic beta-lactam SQ 26,776. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):111–122. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Acred P., Harper P. B., Ryan D. M., Kirby S. M., Harding S. M. GR 20263, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin with anti-pseudomonal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):876–883. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swabb E. A., Leitz M. A., Pilkiewicz F. G., Sugerman A. A. Pharmacokinetics of the monobactam SQ 26,776 after single intravenous doses in healthy subjects. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):131–140. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Cimarusti C. M., Bonner D. P., Bush K., Floyd D. M., Georgopapadakou N. H., Koster W. M., Liu W. C., Parker W. L., Principe P. A. Monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotics produced by bacteria. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):489–491. doi: 10.1038/291489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



