Abstract
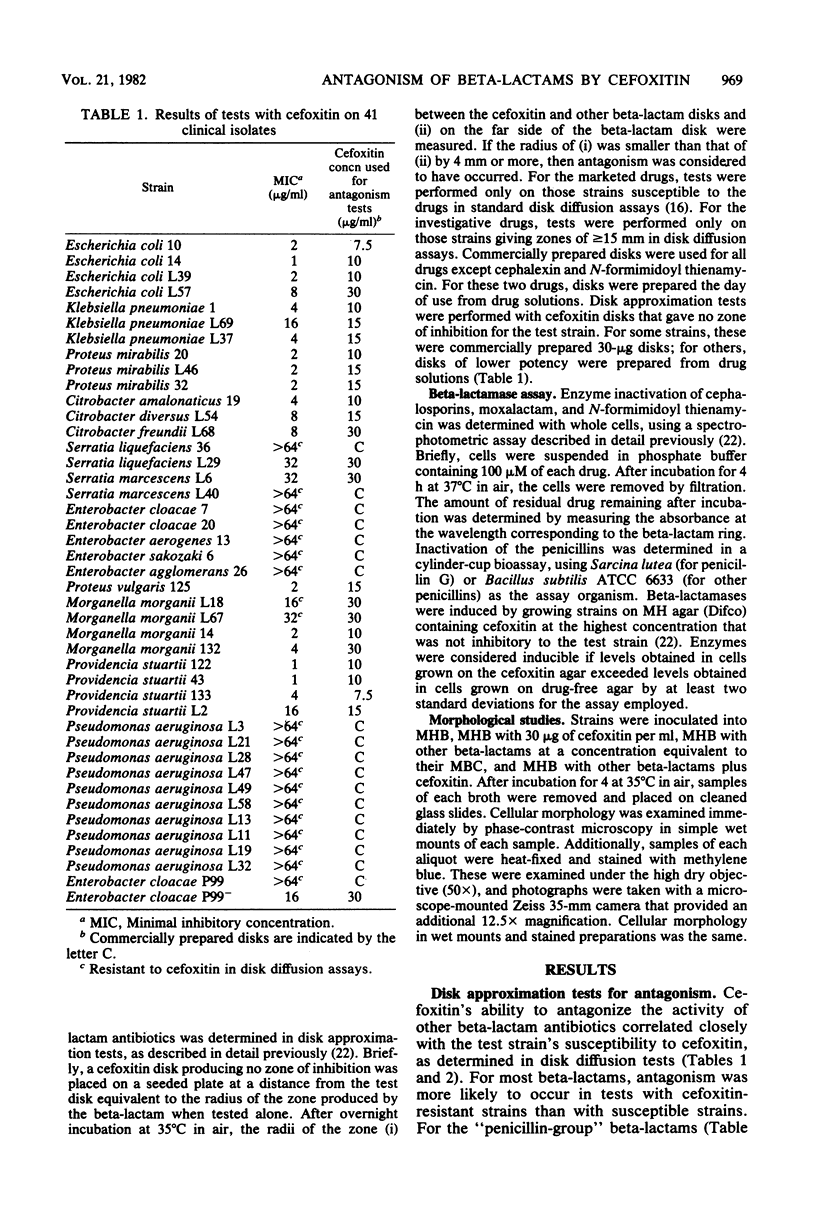
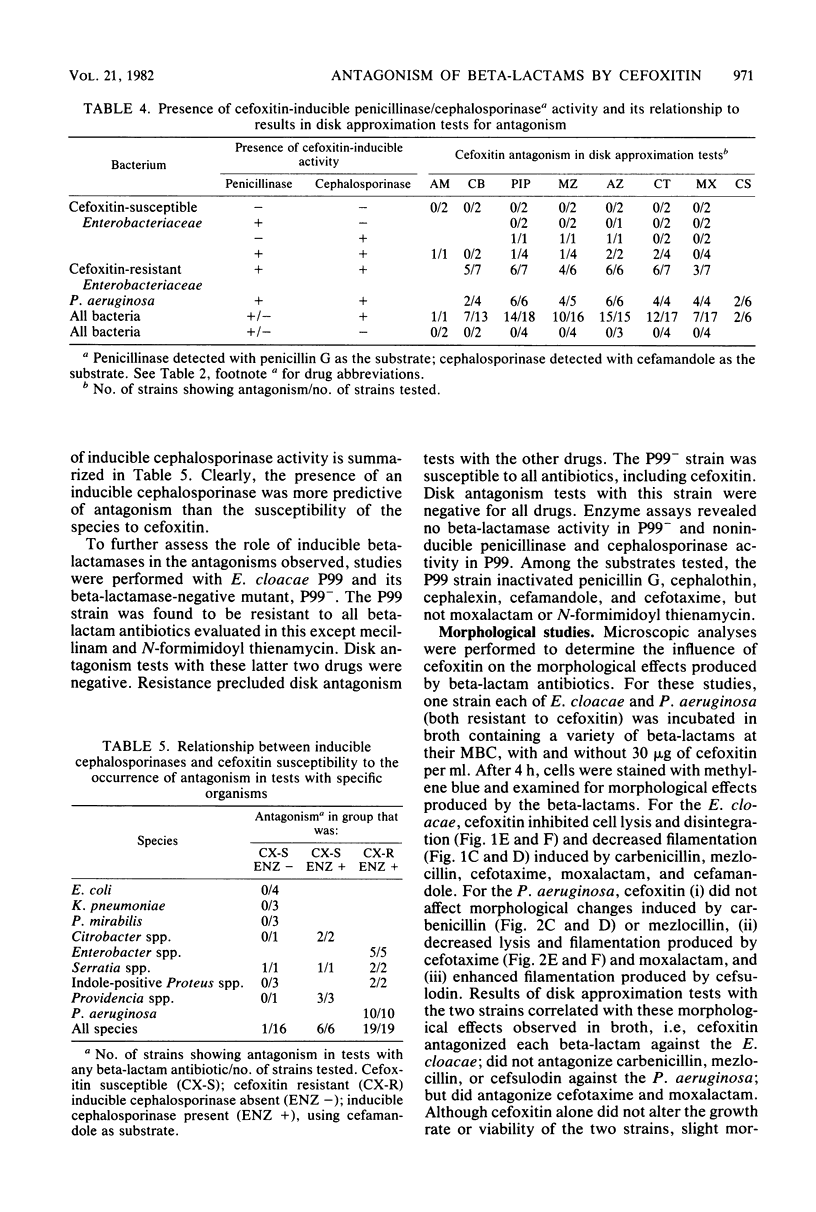
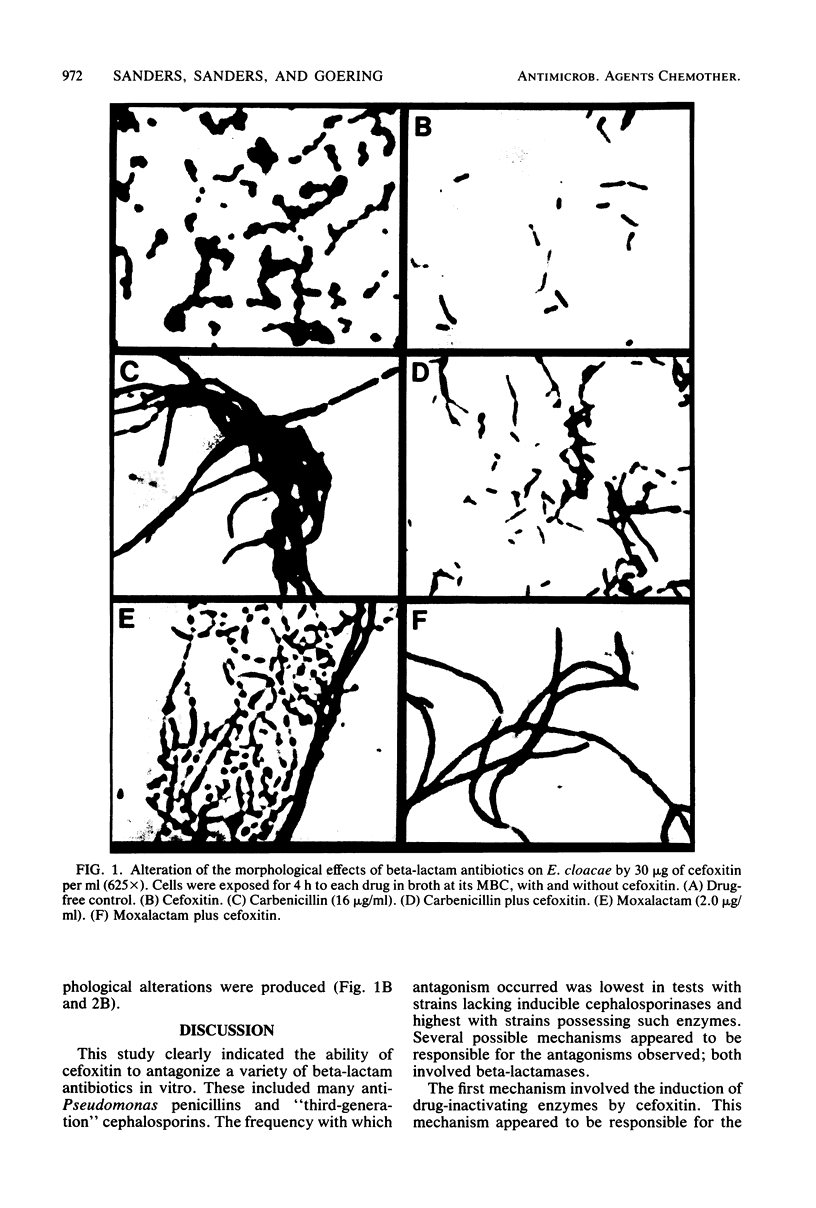
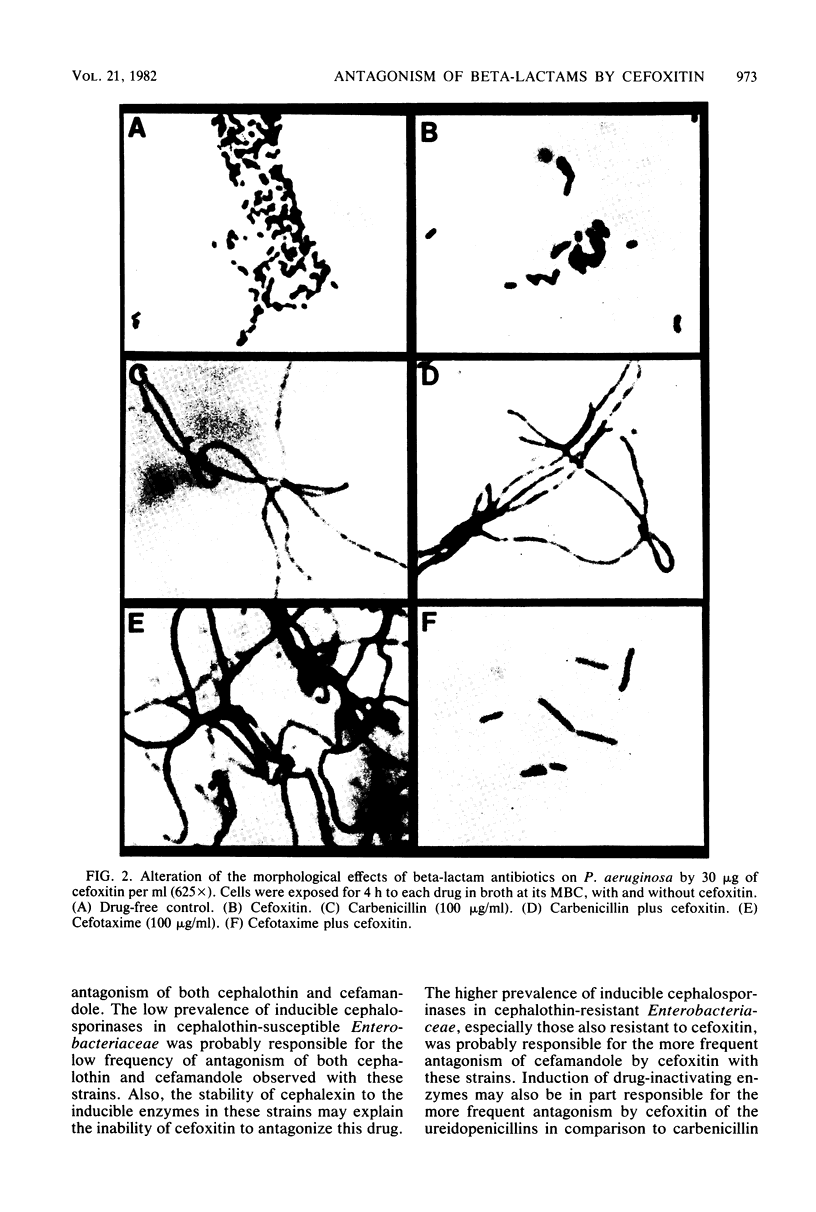
We assessed the extent and mechanisms of antagonism of beta-lactam antibiotics by cefoxitin. In tests with 41 gram-negative isolates, cefoxitin antagonized cephalothin, cefamandole, cefsulodin, cefotaxime, moxalactam, ampicillin, carbenicillin, piperacillin, mezlocillin, and azlocillin, but not cephalexin, mecillinam, or N-formimidoyl thienamycin. The extent of antagonism varied with the beta-lactam and genus studied. However, antagonism occurred most often with strains possessing inducible cephalosporinases. Antagonism of cephalothin and cefamandole correlated closely with the induction of beta-lactamases capable of inactivating these drugs. Although antagonism of the remaining drugs occurred more often with strains possessing inducible beta-lactamases, these enzymes did not inactivate the drugs. Morphological studies revealed that cefoxitin inhibited filamentation and lysis produced by various beta-lactam drugs. Results of this investigation suggest that cefoxitin antagonizes beta-lactams via (i) induction of drug-inactivating beta-lactamases, and (ii) the induction of beta-lactamases that cannot inactivate the drug but serve as barriers against access to target proteins. This barrier appears most efficient for drugs that bind to penicillin-binding proteins 1 and 3.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaum J., Stapley E. O., Miller A. K., Wallick H., Hendlin D., Woodruff H. B. Cefoxitin, a semi-synthetic cephamycin: a microbiological overview. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Jul;4(B):15–32. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.suppl_b.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay B., Hall I. Antagonism between cefoxitin and cefuroxime. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Jul;5(4):490–491. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.4.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis N. A., Orr D., Ross G. W., Boulton M. G. Competition of beta-lactam antibiotics for the penicillin-binding proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter cloacae, Klebsiella aerogenes, Proteus rettgeri, and Escherichia coli: comparison with antibacterial activity and effects upon bacterial morphology. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):325–328. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. The role of inducible beta-lactamases in the antagonism seen with certain cephalosporin combinations. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jan;7(1):104–107. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. beta-lactamase stability of HR 756, a novel cephalosporin, compared to that of cefuroxime and cefoxitin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):322–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldner M., Glass D. G., Fleming P. C. Characteristics of Aerobacter beta-lactamase. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Feb;14(2):139–145. doi: 10.1139/m68-023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldner M., Glass D. G., Fleming P. C. Spontaneous mutant with loss of beta-lactamase in Aerobacter cloacae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):961–961. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.961-.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm H. Bakteriologische Untersuchungen zum Antagonismus zwischen Acylureidopenicillinen und Cephalosporinen. Arzneimittelforschung. 1980;30(6):999–1000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessey T. D. Inducible beta-lactamase in Enterobacter. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Nov;49(2):277–285. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer W., Neuhaus B. In-vitro-Antagonismus von Cefoxitin und Azlozillin im Agar-Diffusionstest. Offentl Gesundheitswes. 1978 Sep;40(9):621–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Shannon K., Phillips I. In vitro antibacterial activity and susceptibility of cefsulodin, an antipseudomonal cephalosporin, to beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):165–169. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu Y., Nishikawa T. Moxalactam (6059-S), a new 1-oxa-beta-lactam: binding affinity for penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):316–321. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuck N. A., Testa R. T., Forbes M. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial effects of combinations of beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):634–638. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H. R., Daoust D. R., Zimmerman S. B., Hendlin D., Stapley E. O. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: resistance to beta-lactamase inactivation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):38–48. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIchmond M. H. The semi-synthetic thienamycin derivative MK0787 and its properties with respect to a range of beta-lactamases from clinically relevant bacterial species. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Mar;7(3):279–285. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.3.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H. In vitro studies with mecillinam on Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Jul;3 (Suppl B):29–39. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.suppl_b.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H. The beta-lactamase stability of a novel beta-lactam antibiotic containing a 7 alpha-methoxyoxacephem nucleus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Jul;6(4):445–453. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.4.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Jago M., Abraham E. P. Cephalosporinase and penicillinase activities of a beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas pyocyanea. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):739–752. doi: 10.1042/bj0960739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Emergence of resistance to cefamandole: possible role of cefoxitin-inducible beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):792–797. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi I., Sawai T., Ando T., Yamagishi S. Cefoxitin resistance by a chromosomal cephalosporinase in Escherichia coli. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1980 Sep;33(9):1037–1042. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.33.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. From penicillin-binding proteins to the lysis and death of bacteria: a 1979 view. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):434–467. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterworth P. M., Emmerson A. M. Dissociated resistance among cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):497–503. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Beta-lactamase-directed barrier for penicillins of Escherichia coli carrying R plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):936–940. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W. Penetration of beta-lactam antibiotics into their target enzymes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of a highly sensitive mutant with its parent strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




