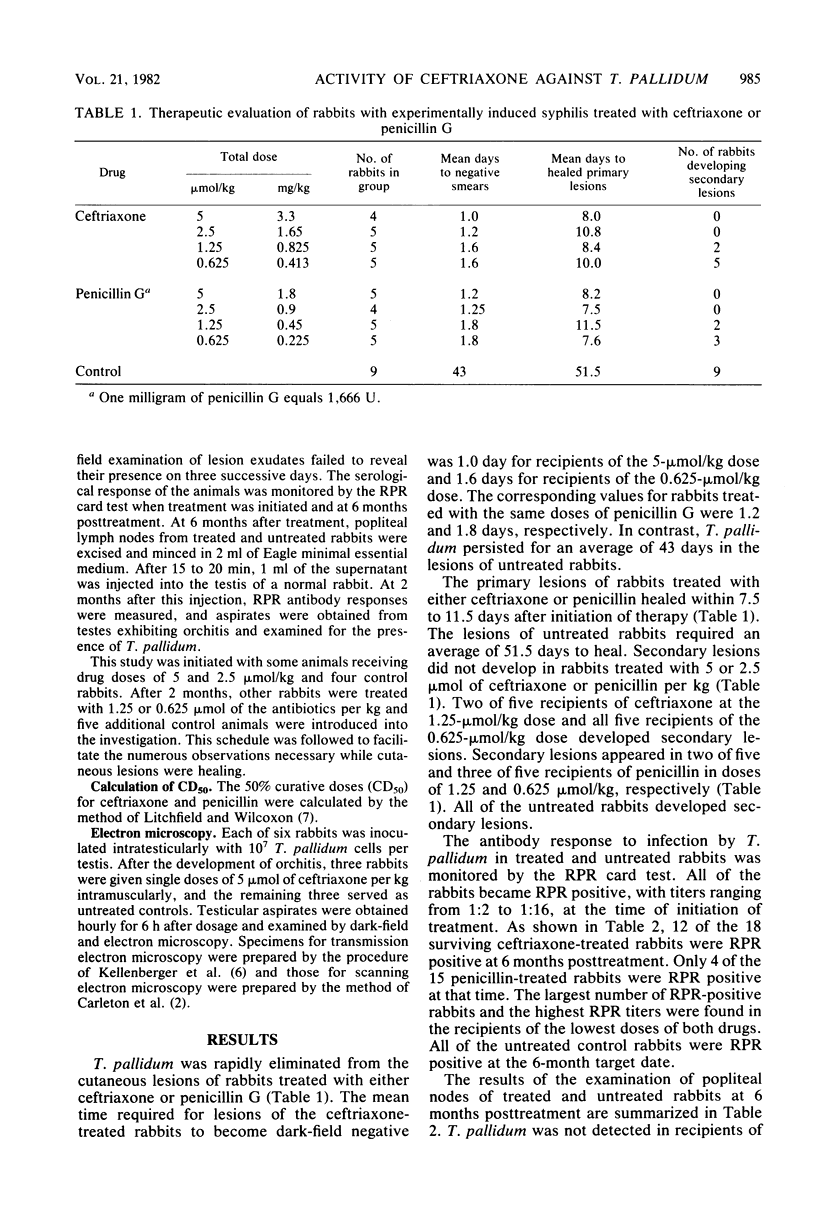
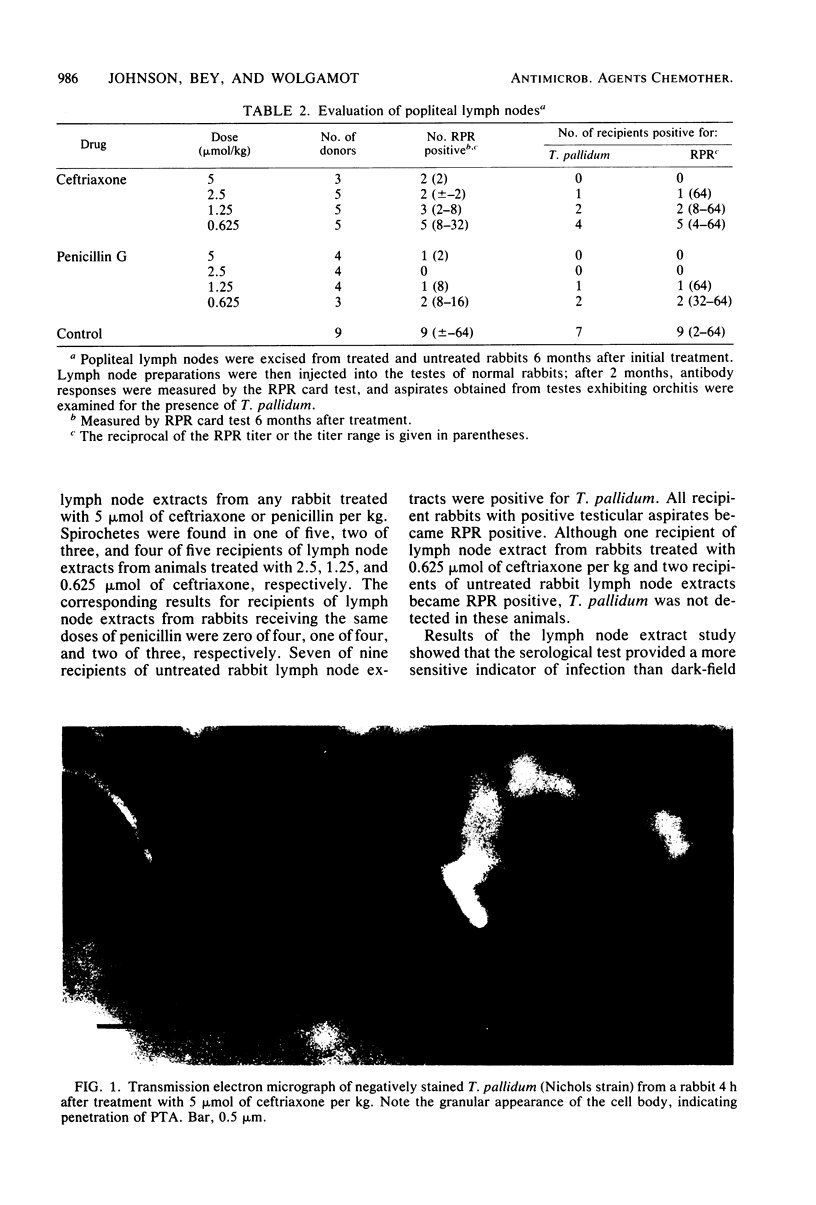
Abstract
The activity of ceftriaxone, a newly developed cephalosporin, against early cutaneous infections with Treponema pallidum in rabbits was compared with that of equimolar doses of penicillin G. Activity was related to the time required for cutaneous lesions to become dark-field negative, serological response, and the disappearance of T. pallidum from the popliteal lymph nodes. Both antibiotics were very effective in the treatment of syphilis in this animal model. The 50% curative dose for penicillin G was 0.8 mumol/kg (0.29 mg or 480 U/kg) and for ceftriaxone, it was 1.45 mumol/kg (0.96 mg/kg). Overall, ceftriaxone was slightly less effective than penicillin G was. Transmission and scanning electron microscopy studies of testicular aspirates obtained from rabbits treated with ceftriaxone revealed alterations in the treponeme surface which apparently resulted in changes in cell permeability and morphology.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARK J. W., Jr, YOBS A. R. EFFECT OF ACTINOSPECTACIN IN EXPERIMENTAL SYPHILIS IN THE RABBIT. I. EARLY LESION SYPHILIS. Br J Vener Dis. 1963 Sep;39:184–189. doi: 10.1136/sti.39.3.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carleton O., Charon N. W., Allender P., O'Brien S. Helix handedness of Leptospira interrogans as determined by scanning electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1413–1416. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1413-1416.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann A., Weidmann G., Havas L. One-dose treatment of acute uncomplicated gonorrhoea of male patients with ceftriaxone Ro 13-9904, a new parenteral cephalosporin. A dose-range finding pilot study using doses of 500, 250, 125 and 50 mg respectively, in descending order. Chemotherapy. 1981;27 (Suppl 1):62–69. doi: 10.1159/000238031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C. The spirochetes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:89–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchou B., Tran Van Tho, Armengaud M. Diffusion of ceftriaxone (Ro 13-9004/001) in the cerebrospinal fluid. Comparison with other beta-lactam antibiotics in dogs with healthy meninges and in dogs with experimental meningitis. Chemotherapy. 1981;27 (Suppl 1):37–41. doi: 10.1159/000238027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckel K. Pharmacokinetics of Rocephin, a highly active new cephalosporin with an exceptionally long biological half-life. Chemotherapy. 1981;27 (Suppl 1):42–46. doi: 10.1159/000238028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thabaut A., Durosoir J. L., Saliou P. Comparative in vitro activity of 8 cephalosporins on 109 strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and 60 strains of Neisseria meningitidis. Chemotherapy. 1981;27 (Suppl 1):19–24. doi: 10.1159/000238024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





