Abstract
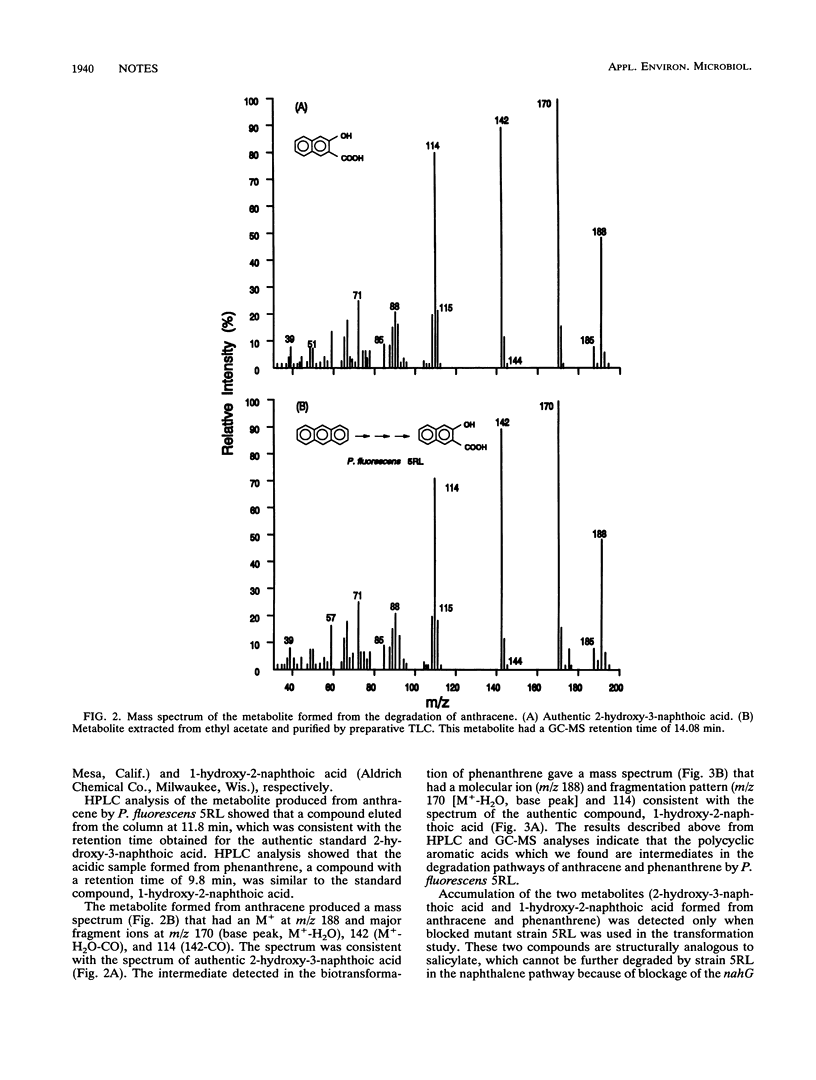
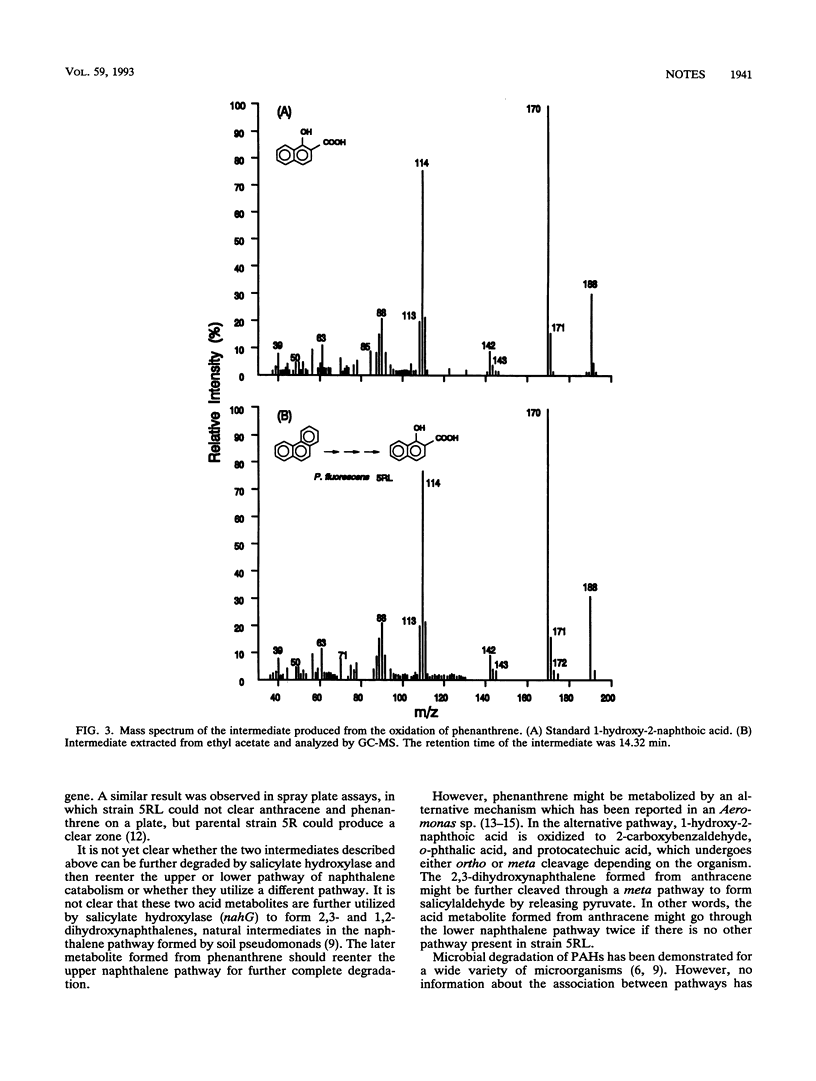
Pseudomonas fluorescens 5R contains an NAH7-like plasmid (pKA1), and P. fluorescens 5R mutant 5RL contains a bioluminescent reporter plasmid (pUTK21) which was constructed by transposon mutagenesis. Polymerase chain reaction mapping confirmed the localization of lux transposon Tn4431 300 bp downstream from the start of the nahG gene. Two degradation products, 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid and 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, were recovered and identified from P. fluorescens 5RL as biochemical metabolites from the biotransformation of anthracene and phenanthrene, respectively. This is the first report which provides direct biochemical evidence that the naphthalene plasmid degradative enzyme system is involved in the degradation of higher-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons other than naphthalene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar M. N., Boyd D. R., Thompson N. J., Koreeda M., Gibson D. T., Mahadevan V., Jerina D. M. Absolute sterochemistry of the dihydroanthracene-cis- and -trans-1,2-diols produced from anthracene by mammals and bacteria. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1975;(23):2506–2511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J. E., Capone D. G. Degradation and mineralization of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons anthracene and naphthalene in intertidal marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):81–90. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.81-90.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J. E., Capone D. G. Effects of co-occurring aromatic hydrocarbons on degradation of individual polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine sediment slurries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1649–1655. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1649-1655.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS W. C., FERNLEY H. N., GRIFFITHS E. OXIDATIVE METABOLISM OF PHENANTHRENE AND ANTHRACENE BY SOIL PSEUDOMONADS. THE RING-FISSION MECHANISM. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:819–831. doi: 10.1042/bj0950819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., You I. S., Gunsalus I. C. Nucleotide sequence and expression of gene nahH of plasmid NAH7 and homology with gene xylE of TOL pWWO. Gene. 1987;55(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M., Selander H., Yagi H., Wells M. C., Davey J. F., Mahadevan V., Gibson D. T. Dihydrodiols from anthracene and phenanthrene. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Sep 15;98(19):5988–5996. doi: 10.1021/ja00435a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. M., Digrazia P. M., Applegate B., Burlage R., Sanseverino J., Dunbar P., Larimer F., Sayler G. S. Rapid, sensitive bioluminescent reporter technology for naphthalene exposure and biodegradation. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):778–781. doi: 10.1126/science.249.4970.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaffey W. R., Gibson D. T., Cerniglia C. E. Bacterial oxidation of chemical carcinogens: formation of polycyclic aromatic acids from benz[a]anthracene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2415–2423. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2415-2423.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGOFF M. H., WENDER I. 3-Hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid as an intermediate in bacterial dissimilation of anthracene. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jul;74(1):108–109. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.1.108-109.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGOFF M. H., WENDER I. The microbiology of coal. I. Bacterial oxidation of phenanthrene. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):264–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.264-268.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanseverino J., Applegate B. M., King J. M., Sayler G. S. Plasmid-mediated mineralization of naphthalene, phenanthrene, and anthracene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jun;59(6):1931–1937. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.6.1931-1937.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A. Homology between nucleotide sequences of promoter regions of nah and sal operons of NAH7 plasmid of Pseudomonas putida. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):369–373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt R., Altenbuchner J., Wiebauer K., Arnold W., Pühler A., Schöffl F. Basis of transposition and gene amplification by Tn1721 and related tetracycline-resistance transposons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):59–65. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrill T. W., Sayler G. S. Phenanthrene biodegradation in freshwater environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):172–178. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.172-178.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiaris M. P. Seasonal Biotransformation of Naphthalene, Phenanthrene, and Benzo[a]pyrene in Surficial Estuarine Sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1391–1399. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1391-1399.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisler F. D., Zobell C. E. Microbial Utilization of Carcinogenic Hydrocarbons. Science. 1947 Nov 28;106(2761):521–522. doi: 10.1126/science.106.2761.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Gunsalus I. C. Plasmid gene organization: naphthalene/salicylate oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):874–878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Gunsalus I. C. Regulation of naphthalene catabolic genes of plasmid NAH7. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1008–1013. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1008-1013.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Serdar C. M. Genetics of naphthalene catabolism in pseudomonads. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1988;15(3):247–268. doi: 10.3109/10408418809104459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]