Abstract
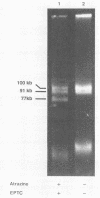
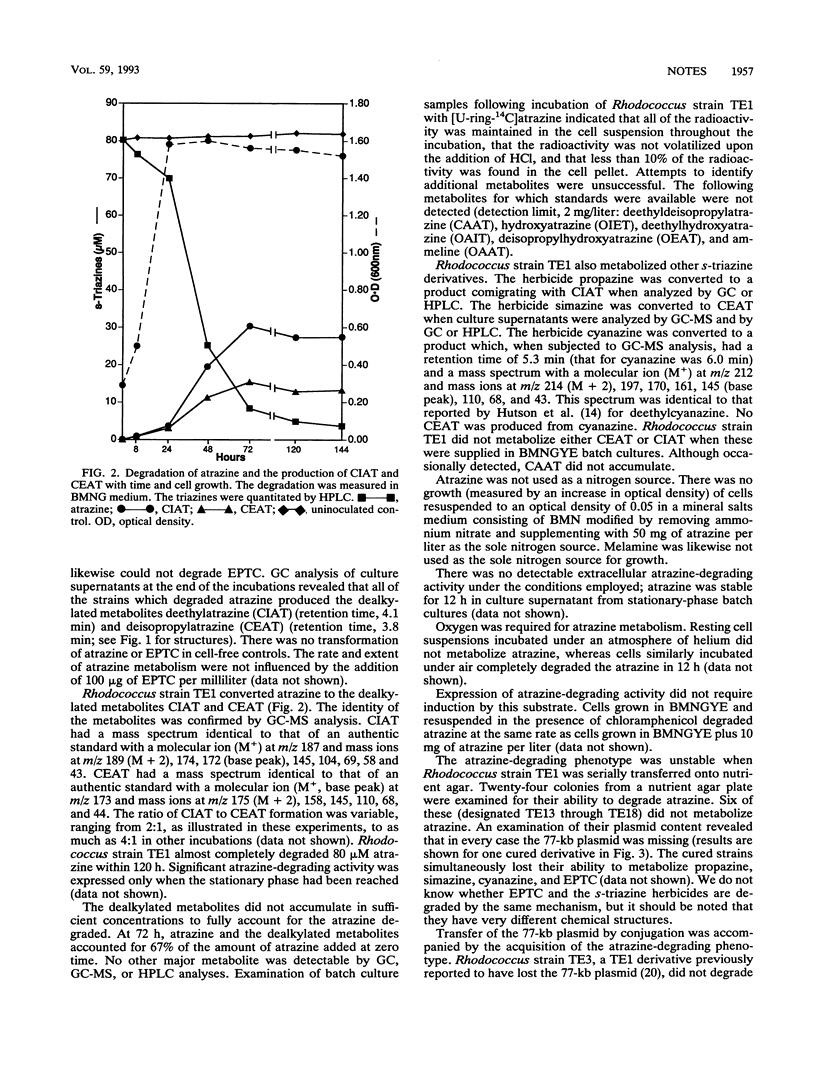
Rhodococcus strains were screened for their ability to degrade the herbicide atrazine. Only rhodococci that degrade the herbicide EPTC (s-ethyl-dipropylthiocarbamate) metabolized atrazine. Rhodococcus strain TE1 metabolized atrazine under aerobic conditions to produce deethyl- and deisopropylatrazine, which were not degraded further and which accumulated in the incubation medium. The bacterium also metabolized the other s-triazine herbicides propazine, simazine, and cyanazine. The N dealkylation of triazine herbicides by Rhodococcus strain TE1 was associated with a 77-kb plasmid previously shown to be required for EPTC degradation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Frear D. S. Microsomal N-demethylation, by a cotton leaf oxidase system, of 3-(4'-chloropENYL)-1, 1-dimethylurea (monuron). Science. 1968 Nov 8;162(3854):674–675. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3854.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow M., Williams S. T. Ecology of actinomycetes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:189–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. Enzymatic oxidation of xenobiotic chemicals. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(2):97–153. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson D. H., Hoadley E. C., Griffiths M. H., Donninger C. Mercapturic acid formation in the metabolism of 2-chloro-4-ethylamino-6-(1-methyl-1-cyanoethylamino)-s-triazine in the rat. J Agric Food Chem. 1970 May-Jun;18(3):507–512. doi: 10.1021/jf60169a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam A. C., Behki R. M., Khan S. U. Isolation and characterization of an s-ethyl-N,N-dipropylthiocarbamate-degrading Arthrobacter strain and evidence for plasmid-associated s-ethyl-N,N-dipropylthiocarbamate degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1088–1093. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1088-1093.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp E., Akhtar M. H. Identification and characterization of a pseudomonas strain capable of metabolizing phenoxybenzoates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1294–1300. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1294-1300.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihama M., Higashiro K., Rao E. A., Akedo M., Shanabruch W. G., Follettie M. T., Walker G. C., Sinskey A. J. Cloning vector system for Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):591–597. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.591-597.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]