Abstract
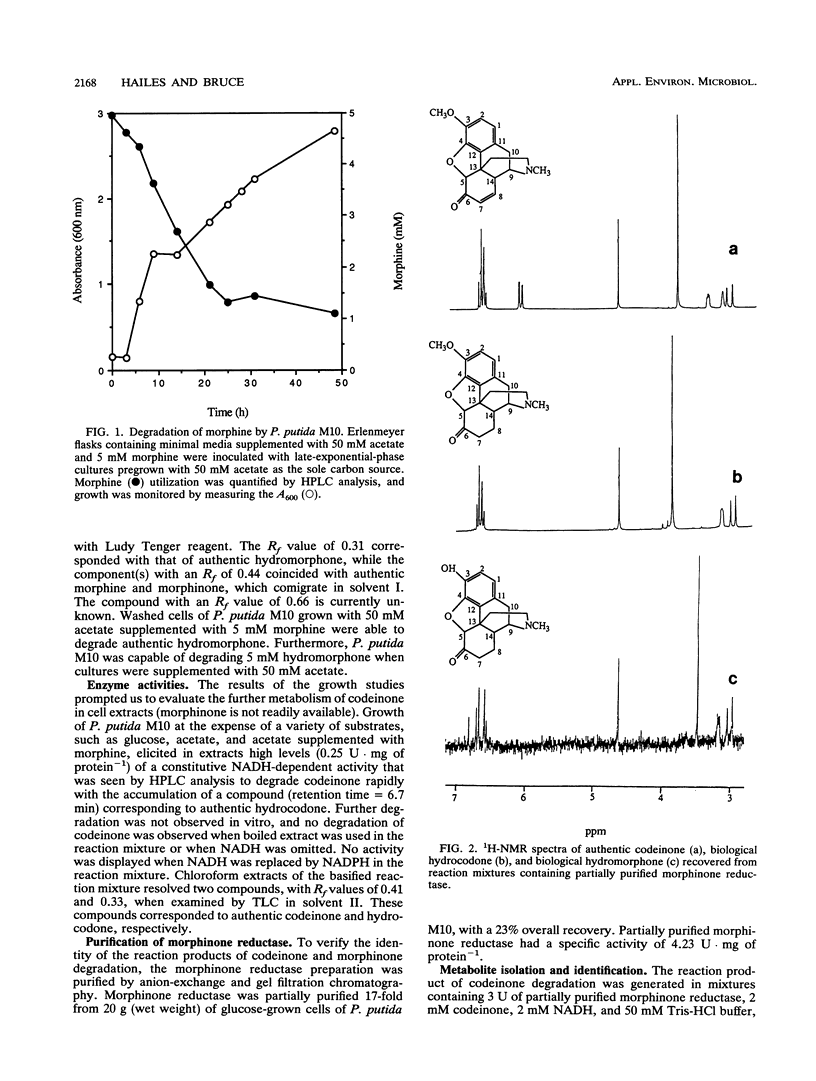
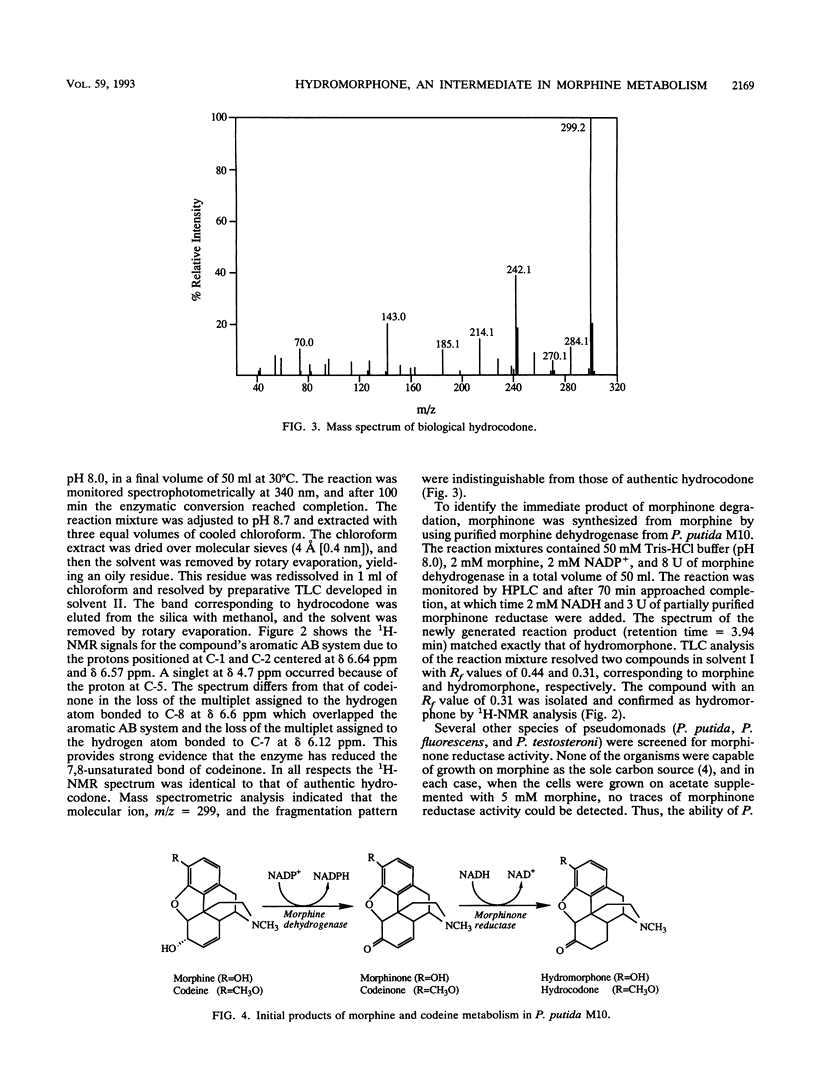
The morphine alkaloid hydromorphone (dihydromorphinone) was identified as an intermediary metabolite in the degradation of morphine by Pseudomonas putida M10. A constitutive NADH-dependent morphinone reductase capable of catalyzing the reduction of the 7,8-unsaturated bond of morphinone and codeinone, yielding hydromorphone and hydrocodone, respectively, was shown to be present in cell extracts. The structures have been identified by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry. Morphinone reductase has been partially purified by anion-exchange and gel filtration chromatography. This enzyme has potential applications as a biocatalyst for the synthesis of the highly potent analgesic hydromorphone and the antitussive hydrocodone.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce N. C., Wilmot C. J., Jordan K. N., Stephens L. D., Lowe C. R. Microbial degradation of the morphine alkaloids. Purification and characterization of morphine dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida M10. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 15;274(Pt 3):875–880. doi: 10.1042/bj2740875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce N. C., Wilmot C. J., Jordan K. N., Trebilcock A. E., Gray Stephens L. D., Lowe C. R. Microbial degradation of the morphine alkaloids: identification of morphine as an intermediate in the metabolism of morphine by Pseudomonas putida M10. Arch Microbiol. 1990;154(5):465–470. doi: 10.1007/BF00245229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IIZUKA K., YAMADA M., SUZUKI J., SEKI I., AIDA K., OKUDA S., ASAI T., TSUDA K. [Studies in the field of microbiological decomposition. XVI. Decomposition of alkaloids of the morphine group by Trametes sanguinea]. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1962 Jan;10:67–70. doi: 10.1248/cpb.10.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz D. A., Reddy G. S., Vatvars A. Identification of transformation products arising from bacterial oxidation of codeine by Streptomyces griseus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):831–836. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.831-836.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liras P., Kasparian S. S., Umbreit W. W. Enzymatic transformation of morphine by hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas testosteroni. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):650–656. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.650-656.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liras P., Umbreit W. W. Transformation of morphine by resting cells and cell-free systems of Arthrobacter sp. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):262–266. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.262-266.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poochikian G. K., Cradock J. C. Simple high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the separation of 3,6-diacetylmorphine hydrochloride (heroin) and hydrolysis products. J Chromatogr. 1979 Apr 1;171:371–376. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)95317-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMADA M., IIZUKA K., OKUDA S., ASAI T., TSUDA K. [Studies in the field of microbiological decomposition. XVII. Transformation of alkaloids in the morphine series by Trametes sanguinea. (2)]. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1962 Oct;10:981–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



