Abstract
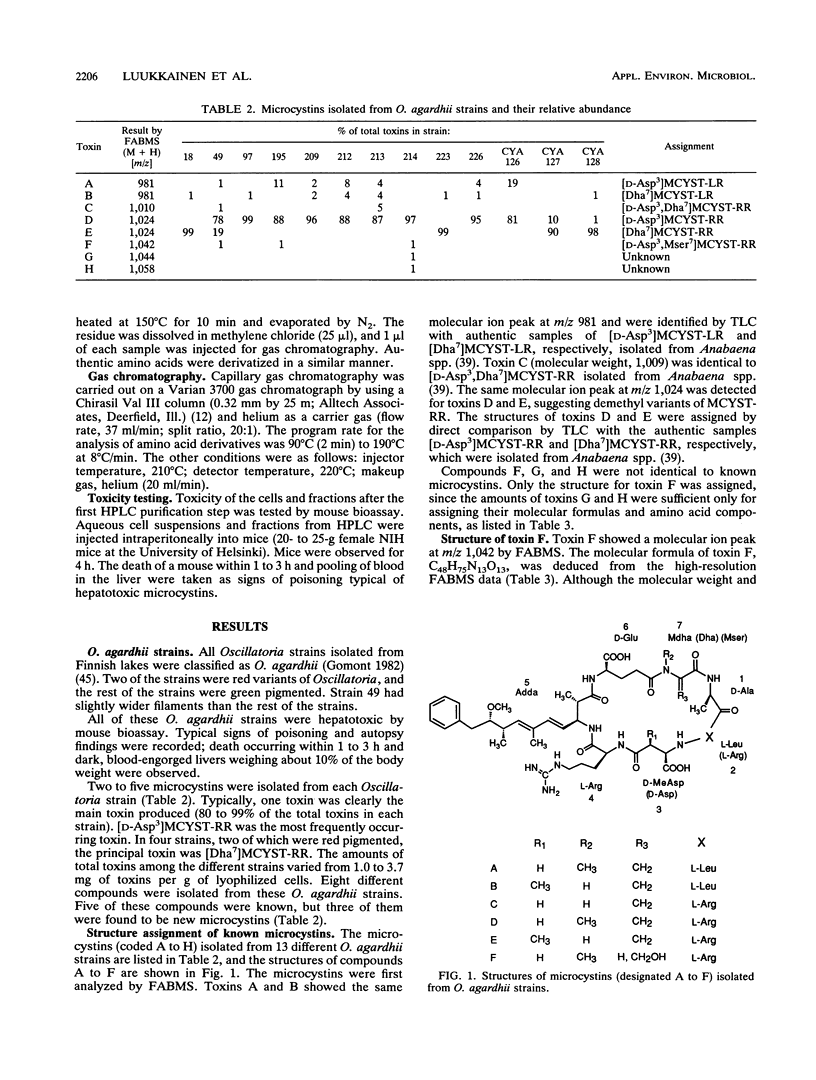
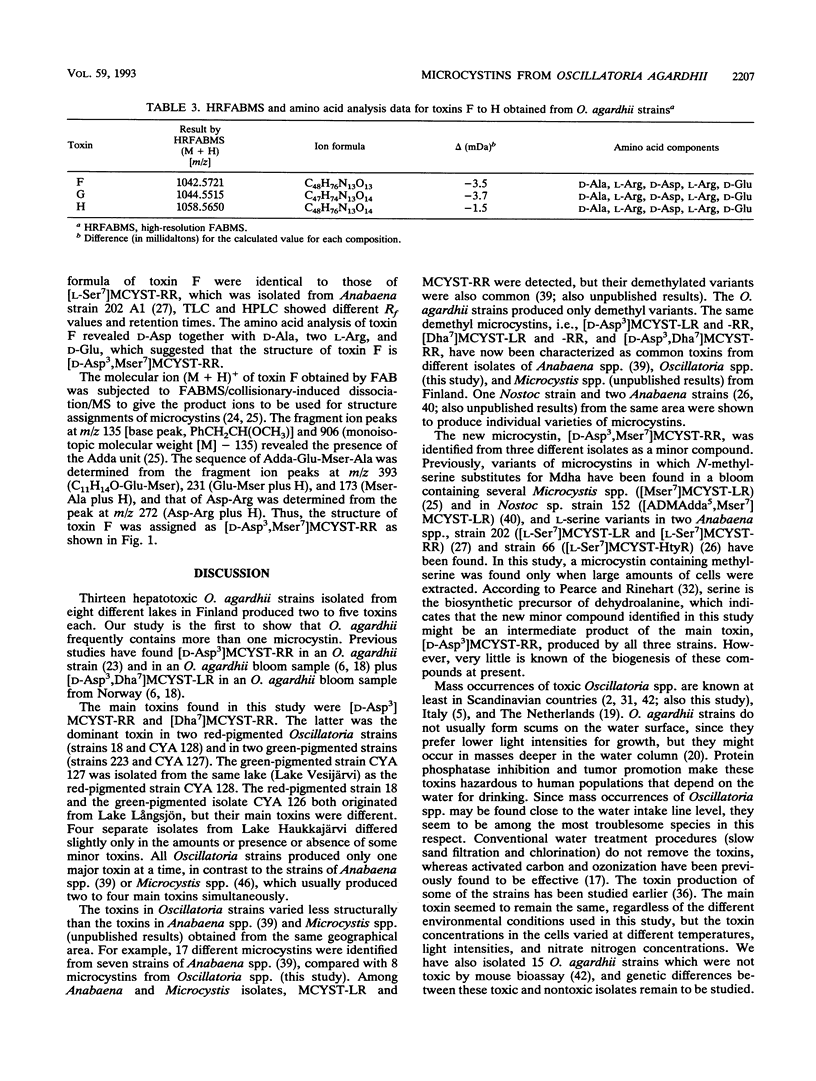
Microcystins (cyclic heptapeptide hepatotoxins), isolated from 13 freshwater Oscillatoria agardhii strains from eight different Finnish lakes by high-performance liquid chromatography, were characterized by amino acid analysis, fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry (FABMS), and tandem FABMS (FABMS/collisionary-induced dissociation/MS). All strains produced two to five different microcystins. In total, eight different compounds, of which five were known microcystins, were isolated. The known compounds identified were [D-Asp3]MCYST (microcystin)-LR, [Dha7]MCYST-LR, [D-Asp3]MCYST-RR, [Dha7]MCYST-RR, and [D-Asp3,Dha7]MCYST-RR. This is the first time that isolation of these toxins from Oscillatoria spp., with the exception of [D-Asp3]MCYST-RR, has been reported. Three of the strains produced a new microcystin, and the structure was assigned as [D-Asp3,Mser7]MCYST-RR. The structures of two new microcystins, produced as minor components by one Oscillatoria strain, could not be determined because of the small amounts isolated from the cells. Four strains produced [Dha7]MCYST-RR as the main toxin, but [D-Asp3]MCYST-RR was clearly the most abundant and most frequently occurring toxin among these isolates of O. agardhii.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beasley V. R., Dahlem A. M., Cook W. O., Valentine W. M., Lovell R. A., Hooser S. B., Harada K., Suzuki M., Carmichael W. W. Diagnostic and clinically important aspects of cyanobacterial (blue-green algae) toxicoses. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1989 Oct;1(4):359–365. doi: 10.1177/104063878900100417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg K., Skulberg O. M., Skulberg R., Underdal B., Willén T. Observations of toxic blue-green algae (Cyanobacteria) in some Scandinavian lakes. Acta Vet Scand. 1986;27(3):440–452. doi: 10.1186/BF03548157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruno M., Gucci P. M., Pierdominici E., Sestili P., Ioppolo A., Sechi N., Volterra L. Microcystin-like toxins in different freshwater species of Oscillatoria. Toxicon. 1992 Oct;30(10):1307–1311. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(92)90448-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael W. W., Beasley V., Bunner D. L., Eloff J. N., Falconer I., Gorham P., Harada K., Krishnamurthy T., Yu M. J., Moore R. E. Naming of cyclic heptapeptide toxins of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). Toxicon. 1988;26(11):971–973. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael W. W. Cyanobacteria secondary metabolites--the cyanotoxins. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;72(6):445–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb01858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconer I. R., Buckley T. H. Tumour promotion by Microcystis sp., a blue-green alga occurring in water supplies. Med J Aust. 1989 Mar 20;150(6):351–351. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1989.tb136517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank H., Nicholson G. J., Bayer E. Rapid gas chromatographic separation of amino acid enantiomers with a novel chiral stationary phase. J Chromatogr Sci. 1977 May 10;15(5):174–176. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/15.5.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gathercole P. S., Thiel P. G. Liquid chromatographic determination of the cyanoginosins, toxins produced by the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J Chromatogr. 1987 Nov 6;408:435–440. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)81837-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada K., Matsuura K., Suzuki M., Watanabe M. F., Oishi S., Dahlem A. M., Beasley V. R., Carmichael W. W. Isolation and characterization of the minor components associated with microcystins LR and RR in the cyanobacterium (blue-green algae). Toxicon. 1990;28(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(90)90006-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada K., Ogawa K., Kimura Y., Murata H., Suzuki M., Thorn P. M., Evans W. R., Carmichael W. W. Microcystins from Anabaena flos-aquae NRC 525-17. Chem Res Toxicol. 1991 Sep-Oct;4(5):535–540. doi: 10.1021/tx00023a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada K., Ogawa K., Matsuura K., Nagai H., Murata H., Suzuki M., Itezono Y., Nakayama N., Shirai M., Nakano M. Isolation of two toxic heptapeptide microcystins from an axenic strain of Microcystis aeruginosa, K-139. Toxicon. 1991;29(4-5):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(91)90022-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy T., Szafraniec L., Hunt D. F., Shabanowitz J., Yates J. R., 3rd, Hauer C. R., Carmichael W. W., Skulberg O., Codd G. A., Missler S. Structural characterization of toxic cyclic peptides from blue-green algae by tandem mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):770–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKintosh C., Beattie K. A., Klumpp S., Cohen P., Codd G. A. Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 21;264(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80245-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima R., Yoshizawa S., Watanabe M. F., Harada K., Furusawa M., Carmichael W. W., Fujiki H. In vitro and in vivo effects of protein phosphatase inhibitors, microcystins and nodularin, on mouse skin and fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):867–874. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91226-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meriluoto J. A., Sandström A., Eriksson J. E., Remaud G., Craig A. G., Chattopadhyaya J. Structure and toxicity of a peptide hepatotoxin from the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria agardhii. Toxicon. 1989;27(9):1021–1034. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(89)90153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namikoshi M., Sivonen K., Evans W. R., Carmichael W. W., Rouhiainen L., Luukkainen R., Rinehart K. L. Structures of three new homotyrosine-containing microcystins and a new homophenylalanine variant from Anabaena sp. strain 66. Chem Res Toxicol. 1992 Sep-Oct;5(5):661–666. doi: 10.1021/tx00029a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namikoshi M., Sivonen K., Evans W. R., Carmichael W. W., Sun F., Rouhiainen L., Luukkainen R., Rinehart K. L. Two new L-serine variants of microcystins-LR and -RR from Anabaena sp. strains 202 A1 and 202 A2. Toxicon. 1992 Nov;30(11):1457–1464. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(92)90521-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namikoshi M., Sivonen K., Evans W. R., Sun F., Carmichael W. W., Rinehart K. L. Isolation and structures of microcystins from a cyanobacterial water bloom (Finland). Toxicon. 1992 Nov;30(11):1473–1479. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(92)90523-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiwaki-Matsushima R., Ohta T., Nishiwaki S., Suganuma M., Kohyama K., Ishikawa T., Carmichael W. W., Fujiki H. Liver tumor promotion by the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin-LR. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1992;118(6):420–424. doi: 10.1007/BF01629424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen K., Carmichael W. W., Namikoshi M., Rinehart K. L., Dahlem A. M., Niemelä S. I. Isolation and characterization of hepatotoxic microcystin homologs from the filamentous freshwater cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. strain 152. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2650–2657. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2650-2657.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen K. Effects of light, temperature, nitrate, orthophosphate, and bacteria on growth of and hepatotoxin production by Oscillatoria agardhii strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2658–2666. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2658-2666.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen K., Kononen K., Carmichael W. W., Dahlem A. M., Rinehart K. L., Kiviranta J., Niemela S. I. Occurrence of the hepatotoxic cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena in the Baltic Sea and structure of the toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):1990–1995. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.1990-1995.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen K., Namikoshi M., Evans W. R., Carmichael W. W., Sun F., Rouhiainen L., Luukkainen R., Rinehart K. L. Isolation and characterization of a variety of microcystins from seven strains of the cyanobacterial genus Anabaena. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Aug;58(8):2495–2500. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.8.2495-2500.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen K., Namikoshi M., Evans W. R., Färdig M., Carmichael W. W., Rinehart K. L. Three new microcystins, cyclic heptapeptide hepatotoxins, from Nostoc sp. strain 152. Chem Res Toxicol. 1992 Jul-Aug;5(4):464–469. doi: 10.1021/tx00028a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen K., Namikoshi M., Evans W. R., Gromov B. V., Carmichael W. W., Rinehart K. L. Isolation and structures of five microcystins from a Russian Microcystis aeruginosa strain CALU 972. Toxicon. 1992 Nov;30(11):1481–1485. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(92)90524-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivonen K., Skulberg O. M., Namikoshi M., Evans W. R., Carmichael W. W., Rinehart K. L. Two methyl ester derivatives of microcystins, cyclic heptapeptide hepatotoxins, isolated from Anabaena flos-aquae strain CYA 83/1. Toxicon. 1992 Nov;30(11):1465–1471. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(92)90522-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M. F., Oishi S., Harda K., Matsuura K., Kawai H., Suzuki M. Toxins contained in Microcystis species of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). Toxicon. 1988;26(11):1017–1025. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witten J. L., Schaffer M. H., O'Shea M., Cook J. C., Hemling M. E., Rinehart K. L., Jr Structures of two cockroach neuropeptides assigned by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):350–358. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91560-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa S., Matsushima R., Watanabe M. F., Harada K., Ichihara A., Carmichael W. W., Fujiki H. Inhibition of protein phosphatases by microcystins and nodularin associated with hepatotoxicity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1990;116(6):609–614. doi: 10.1007/BF01637082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


