Abstract
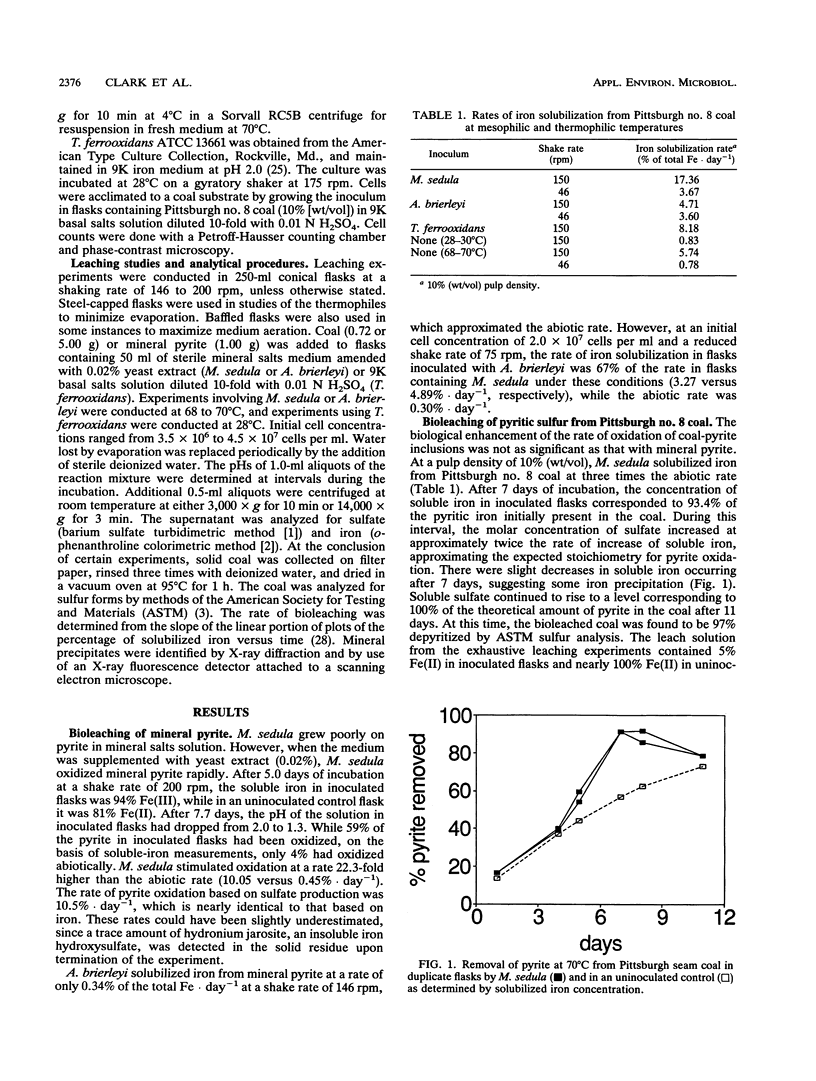
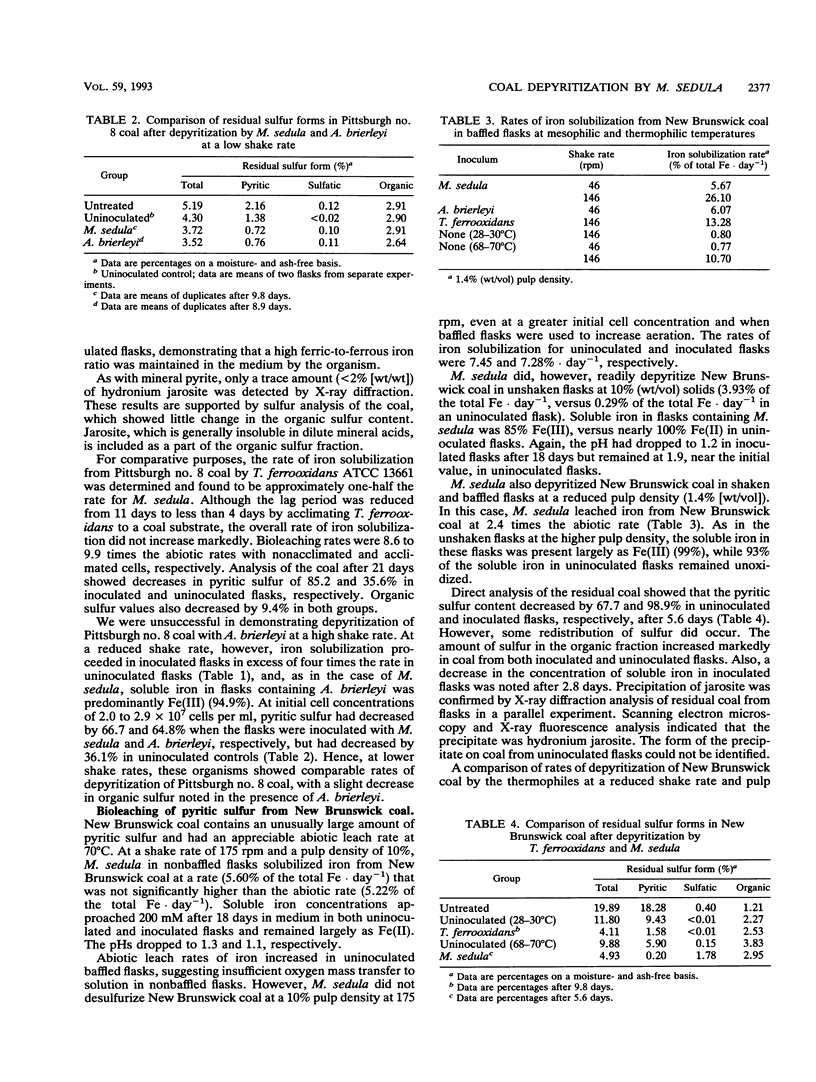
The kinetics of pyrite oxidation by Metallosphaera sedula were investigated with mineral pyrite and two coals with moderate (Pittsburgh no. 8) and high (New Brunswick, Canada) pyritic sulfur content. M. sedula oxidized mineral pyrite at a greater rate than did another thermophile, Acidianus brierleyi, or a mesophile, Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Maximum rates of coal depyritization were also greater with M. sedula, although the magnitude of biological stimulation above abiotic rates was notably less than with mineral pyrite. Coal depyritization appears to be limited by the oxidation of pyrite with ferric ions and not by the rate of biotic oxidation of ferrous iron, as evidenced by the maintenance of a high ratio of ferric to ferrous iron in solution by M. sedula. Significant precipitation of hydronium jarosite at elevated temperature occurred only with New Brunswick coal.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldi F., Clark T., Pollack S. S., Olson G. J. Leaching of Pyrites of Various Reactivities by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1853–1856. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1853-1856.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchins S. R., Davidson M. S., Brierley J. A., Brierley C. L. Microorganisms in reclamation of metals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:311–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson G. J. Rate of Pyrite Bioleaching by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: Results of an Interlaboratory Comparison. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):642–644. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.642-644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN M. P., LUNDGREN D. G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. J Bacteriol. 1959 May;77(5):642–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.5.642-647.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P. C., Stumm W. Acidic mine drainage: the rate-determining step. Science. 1970 Feb 20;167(3921):1121–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3921.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


