Abstract
A combination of polymerase chain reaction-assisted rRNA sequence retrieval and fluorescent oligonucleotide probing was used to identify in situ a hitherto unculturable, big, magnetotactic, rod-shaped organism in freshwater sediment samples collected from Lake Chiemsee. Tentatively named “Magnetobacterium bavaricum,” this bacterium is evolutionarily distant from all other phylogenetically characterized magnetotactic bacteria and contains unusually high numbers of magnetosomes (up to 1,000 magnetosomes per cell). The spatial distribution in the sediment was studied, and up to 7 × 105 active cells per cm3 were found in the microaerobic zone. Considering its average volume (25.8 ± 4.1 μm3) and relative abundance (0.64 ± 0.17%), “M. bavaricum” may account for approximately 30% of the microbial biovolume and may therefore be a dominant fraction of the microbial community in this layer. Its microhabitat and its high content of sulfur globules and magnetosomes suggest that this organism has an iron-dependent way of energy conservation which depends on balanced gradients of oxygen and sulfide.
Full text
PDF


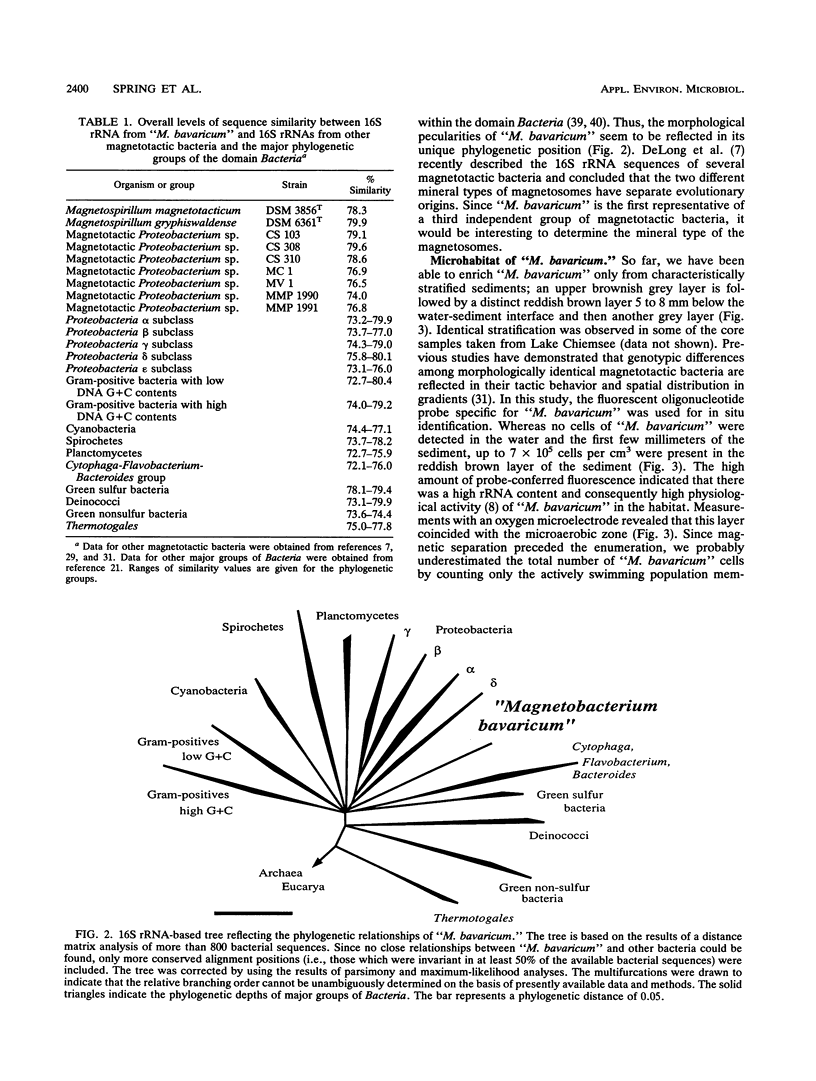
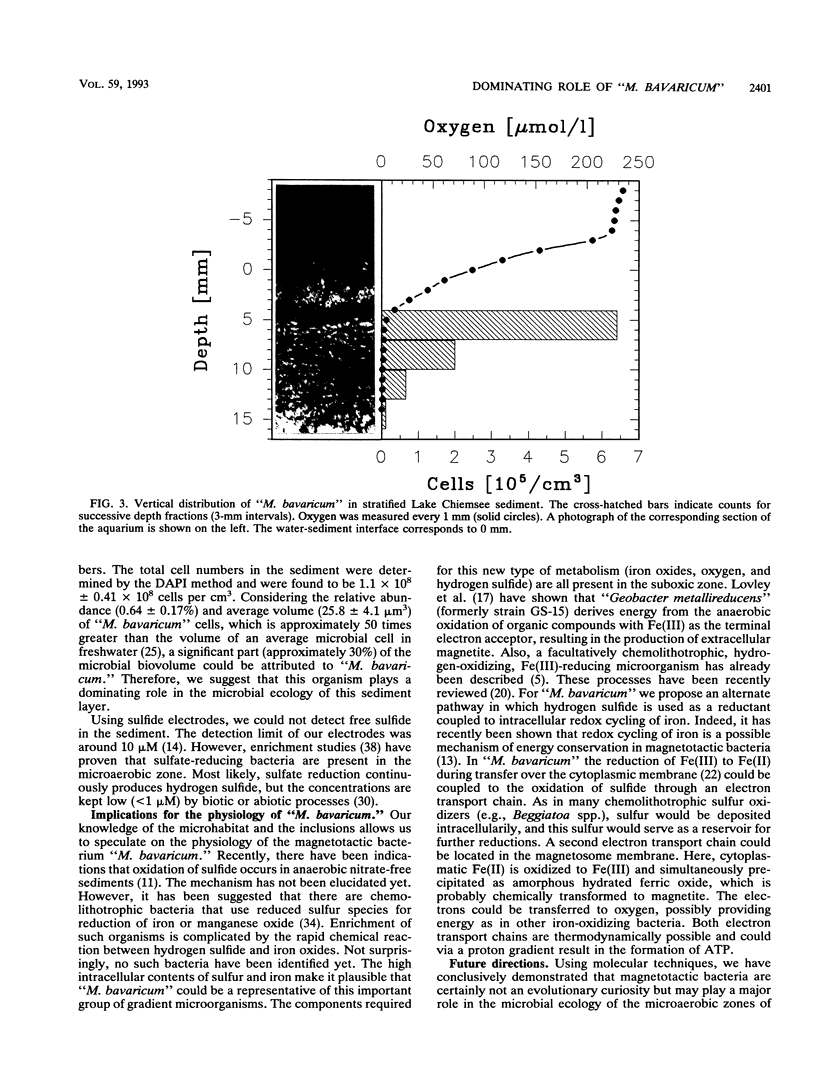


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann R. I., Binder B. J., Olson R. J., Chisholm S. W., Devereux R., Stahl D. A. Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1919–1925. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1919-1925.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann R. I., Krumholz L., Stahl D. A. Fluorescent-oligonucleotide probing of whole cells for determinative, phylogenetic, and environmental studies in microbiology. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):762–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.762-770.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann R., Springer N., Ludwig W., Görtz H. D., Schleifer K. H. Identification in situ and phylogeny of uncultured bacterial endosymbionts. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):161–164. doi: 10.1038/351161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccavo F., Blakemore R. P., Lovley D. R. A Hydrogen-Oxidizing, Fe(III)-Reducing Microorganism from the Great Bay Estuary, New Hampshire. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Oct;58(10):3211–3216. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.10.3211-3216.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delong E. F., Frankel R. B., Bazylinski D. A. Multiple evolutionary origins of magnetotaxis in bacteria. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):803–806. doi: 10.1126/science.259.5096.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden P. A., Schmidt T. M., Blakemore R. P., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic analysis of Aquaspirillum magnetotacticum using polymerase chain reaction-amplified 16S rRNA-specific DNA. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;41(2):324–325. doi: 10.1099/00207713-41-2-324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerin W. F., Blakemore R. P. Redox Cycling of Iron Supports Growth and Magnetite Synthesis by Aquaspirillum magnetotacticum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Apr;58(4):1102–1109. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.4.1102-1109.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S., Sparks N. H., Board R. G. Magnetotactic bacteria: microbiology, biomineralization, palaeomagnetism and biotechnology. Adv Microb Physiol. 1990;31:125–181. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moench T. T., Konetzka W. A. A novel method for the isolation and study of a magnetotactic bacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Nov 13;119(2):203–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00964274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Myers C. R. Microbial reduction of manganese and iron: new approaches to carbon cycling. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):439–443. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.439-443.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Overbeek R., Larsen N., Marsh T. L., McCaughey M. J., Maciukenas M. A., Kuan W. M., Macke T. J., Xing Y., Woese C. R. The Ribosomal Database Project. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2199–2200. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti L. C., Blakemore R. P. Hydroxamate production by Aquaspirillum magnetotacticum. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):73–76. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.73-76.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thamdrup B., Finster K., Hansen J. W., Bak F. Bacterial disproportionation of elemental sulfur coupled to chemical reduction of iron or manganese. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):101–108. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.101-108.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Kandler O., Wheelis M. L. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4576–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]