Abstract
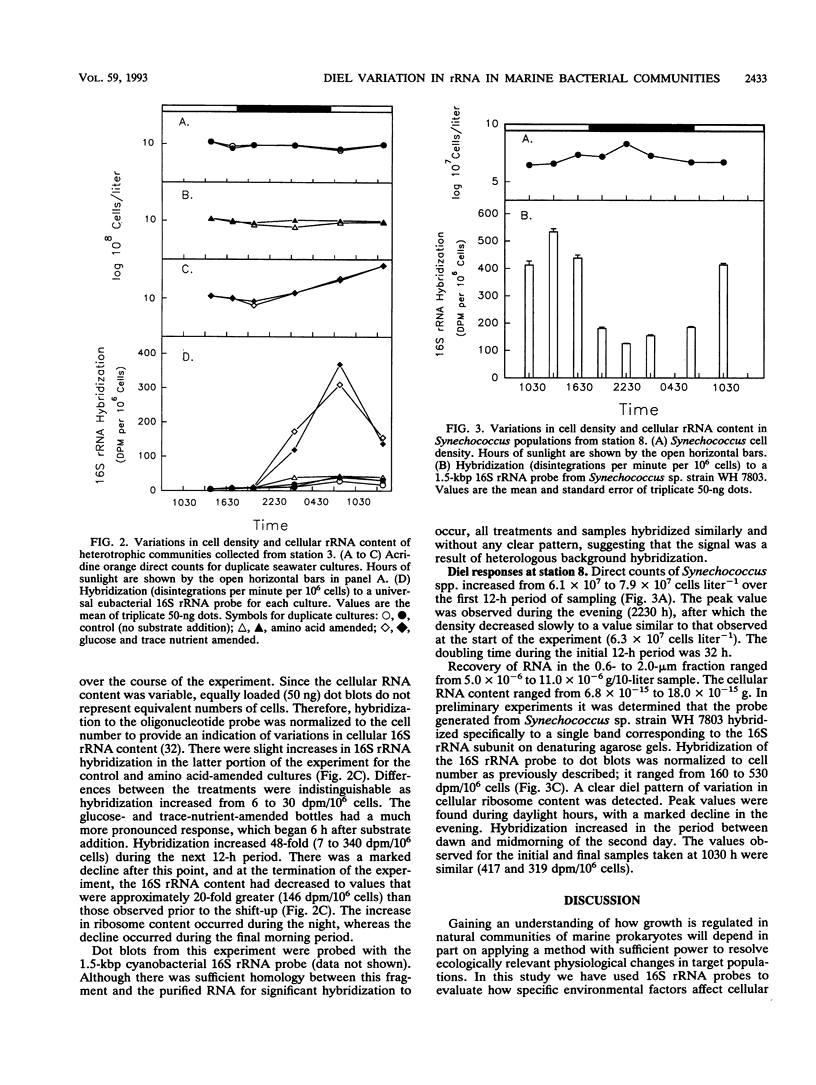
The development of a clear understanding of the physiology of marine prokaryotes is complicated by the difficulties inherent in resolving the activity of various components of natural microbial communities. Application of appropriate molecular biological techniques offers a means of overcoming some of these problems. In this regard, we have used direct probing of bulk RNA purified from selective size fractions to examine variations in the rRNA content of heterotrophic communities and Synechococcus populations on the southeastern U.S. continental shelf. Heterotrophic communities in natural seawater cultures amended with selected substrates were examined. Synechococcus populations were isolated from the water column by differential filtration. The total cellular rRNA content of the target populations was assayed by probing RNA purified from these samples with an oligonucleotide complementing a universally conserved region in the eubacterial 16S rRNA (heterotrophs) or with a 1.5-kbp fragment encoding the Synechococcus sp. strain WH 7803 16S rRNA (cyanobacteria). The analyses revealed that heterotrophic bacteria responded to the addition of glucose and trace nutrients after a 6-h lag period. However, no response was detected after amino acids were added. The cellular rRNA content increased 48-fold before dropping to a value 20 times that detected before nutrients were added. Variations in the rRNA content from Synechococcus spp. followed a distinct diel pattern imposed by the phasing of cell division within the irradiance cycle. The results indicate that careful application of these appropriate molecular biological techniques can be of great use in discerning basic physiological characteristics of selected natural populations and the mechanisms which regulate growth at the subcellular level.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann R. I., Binder B. J., Olson R. J., Chisholm S. W., Devereux R., Stahl D. A. Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1919–1925. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1919-1925.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittain A. M., Karl D. M. Catabolism of tritiated thymidine by aquatic microbial communities and incorporation of tritium into RNA and protein. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1245–1254. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1245-1254.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian R. R., Hanson R. B., Newell S. Y. Comparison of methods for measurement of bacterial growth rates in mixed batch cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1160–1165. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1160-1165.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards U., Rogall T., Blöcker H., Emde M., Böttger E. C. Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7843–7853. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson R. L., Buckley E. N., Palumbo A. V. Response of marine bacterioplankton to differential filtration and confinement. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):49–55. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.49-55.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., McCallum K., Davis A. A. Novel major archaebacterial group from marine plankton. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):148–149. doi: 10.1038/356148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Britschgi T. B., Moyer C. L., Field K. G. Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):60–63. doi: 10.1038/345060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., DeLong E. F., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic group-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for identification of single microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.720-726.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey W. H., Paul J. H. Thymidine uptake, thymidine incorporation, and thymidine kinase activity in marine bacterium isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1367–1372. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1367-1372.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchman D., K'nees E., Hodson R. Leucine incorporation and its potential as a measure of protein synthesis by bacteria in natural aquatic systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):599–607. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.599-607.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. G., Singleton F. L. Variations in rRNA content of marine Vibrio spp. during starvation-survival and recovery. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):201–207. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.201-207.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Macleod R. A. Observations on the distinction between oligotrophic and eutrophic marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1017–1022. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1017-1022.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Lane D. J., Giovannoni S. J., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A. Microbial ecology and evolution: a ribosomal RNA approach. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:337–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichard Scott L., Paul John H. Detection of Gene Expression in Genetically Engineered Microorganisms and Natural Phytoplankton Populations in the Marine Environment by mRNA Analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1721–1727. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1721-1727.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy K. J., Webb R., Sherman L. A. Bacterial RNA isolation with one hour centrifugation in a table-top ultracentrifuge. Biotechniques. 1990 Mar;8(3):250–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M., Weller R., Bateson M. M. 16S rRNA sequences reveal numerous uncultured microorganisms in a natural community. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):63–65. doi: 10.1038/345063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman M., Gregory R. P., Carr N. G. Novel Role for Phycoerythrin in a Marine Cyanobacterium, Synechococcus Strain DC2. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):818–820. doi: 10.1126/science.230.4727.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]