Abstract
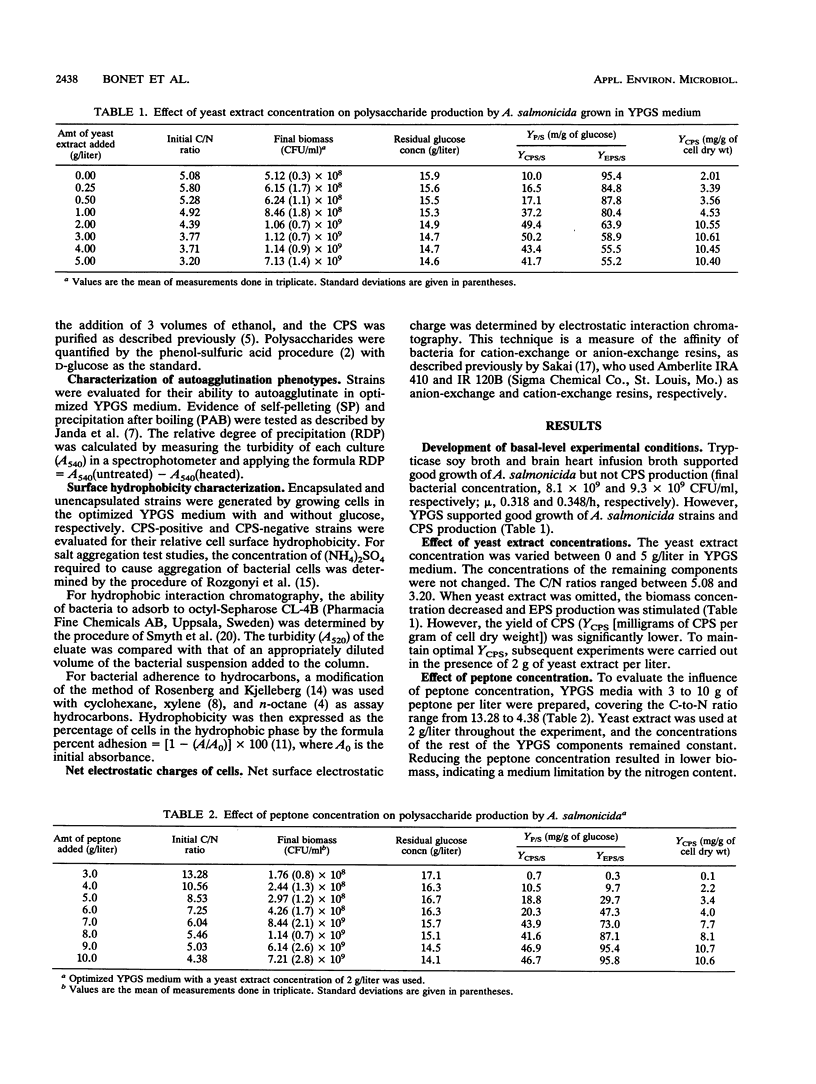
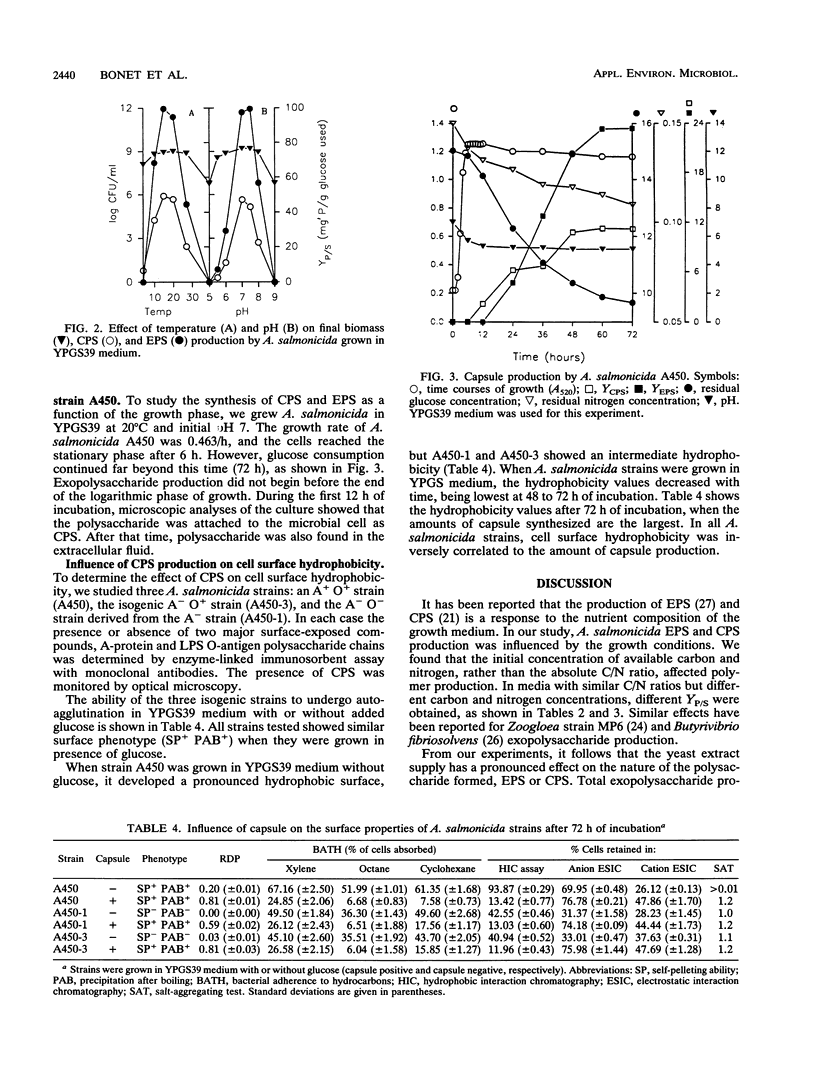
Extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) and capsular polysaccharide (CPS) production by Aeromonas salmonicida A450 and the influence of the capsule on cell surface properties were studied. A. salmonicida did not produce CPS or EPS when glucose, phosphate, magnesium chloride, or trace mineral components were absent from the medium. The addition of yeast extract improved capsule production. Neither EPS nor CPS formation depended on the C/N ratio, although it appeared to be influenced by the level of carbon and nitrogen in the culture. Both EPS and CPS production started at the end of the logarithmic growth phase. The amounts of EPS and CPS produced were not influenced by temperature changes between 15 and 20 degrees C and was maximal from pH 7 to 7.5. Cell surface properties were strongly influenced by capsule production; high CPS production was associated with enhanced cell hydrophilicity and autoagglutination. The effect of CPS on cell surface properties was independent of the presence of the surface protein array (A-layer).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gannon J. T., Manilal V. B., Alexander M. Relationship between Cell Surface Properties and Transport of Bacteria through Soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):190–193. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.190-193.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrote A., Bonet R., Merino S., Simon-Pujol M. D., Congregado F. Occurrence of a capsule in Aeromonas salmonicida. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Aug 15;74(2-3):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90417-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W., Ainsworth T., Chamberlain J. B., Austen R. A., Buckley J. T., Trust T. J. Loss of virulence during culture of Aeromonas salmonicida at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.333-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Oshiro L. S., Abbott S. L., Duffey P. S. Virulence markers of mesophilic aeromonads: association of the autoagglutination phenomenon with mouse pathogenicity and the presence of a peripheral cell-associated layer. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3070–3077. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3070-3077.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. S., Gorman S. P., McCafferty D. F., Woolfson A. D. The effects of three non-antibiotic, antimicrobial agents on the surface hydrophobicity of certain micro-organisms evaluated by different methods. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;71(3):218–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1991.tb04451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Buckley J. T., Ishiguro E. E., Phipps B. M., Monette J. P., Trust T. J. Purification and disposition of a surface protein associated with virulence of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):1077–1084. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.1077-1084.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Hermansson M., Mårdén P., Jones G. W. The transient phase between growth and nongrowth of heterotrophic bacteria, with emphasis on the marine environment. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:25–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G., Cuperus P. L., Bruce A. W., van der Mei H. C., Tomeczek L., Khoury A. H., Busscher H. J. Comparison of contact angles and adhesion to hexadecane of urogenital, dairy, and poultry lactobacilli: effect of serial culture passages. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1549–1553. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1549-1553.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. Bacterial adherence to polystyrene: a replica method of screening for bacterial hydrophobicity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):375–377. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.375-377.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Bayer E. A., Delarea J., Rosenberg E. Role of Thin Fimbriae in Adherence and Growth of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1 on Hexadecane. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):929–937. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.929-937.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai D. K. Adhesion of Aeromonas salmonicida strains associated with net electrostatic charges of host tissue cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):704–710. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.704-710.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai D. K. Electrostatic mechanism of survival of virulent Aeromonas salmonicida strains in river water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1343–1349. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1343-1349.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai D. K. Loss of virulence in a protease-deficient mutant of Aeromonas salmonicida. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):146–152. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.146-152.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Jonsson P., Olsson E., Soderlind O., Rosengren J., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Differences in hydrophobic surface characteristics of porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with or without K88 antigen as revealed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):462–472. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.462-472.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow W. T., Dassy B., Lieb M., Fournier J. M. Staphylococcus aureus growth and type 5 capsular polysaccharide production in synthetic media. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):618–621. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.618-621.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unz R. F., Farrah S. R. Exopolymer production and flocculation by zoogloea mp6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):623–626. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.623-626.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Alstine J. M., Trust T. J., Brooks D. E. Differential partition of virulent Aeromonas salmonicida and attenuated derivatives possessing specific cell surface alterations in polymer aqueous-phase systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1309–1313. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1309-1313.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachenheim D. E., Patterson J. A. Anaerobic Production of Extracellular Polysaccharide by Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens nyx. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):385–391. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.385-391.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrangstadh M., Szewzyk U., Ostling J., Kjelleberg S. Starvation-specific formation of a peripheral exopolysaccharide by a marine Pseudomonas sp., strain S9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2065–2072. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2065-2072.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


