Abstract
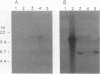
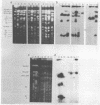
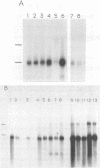
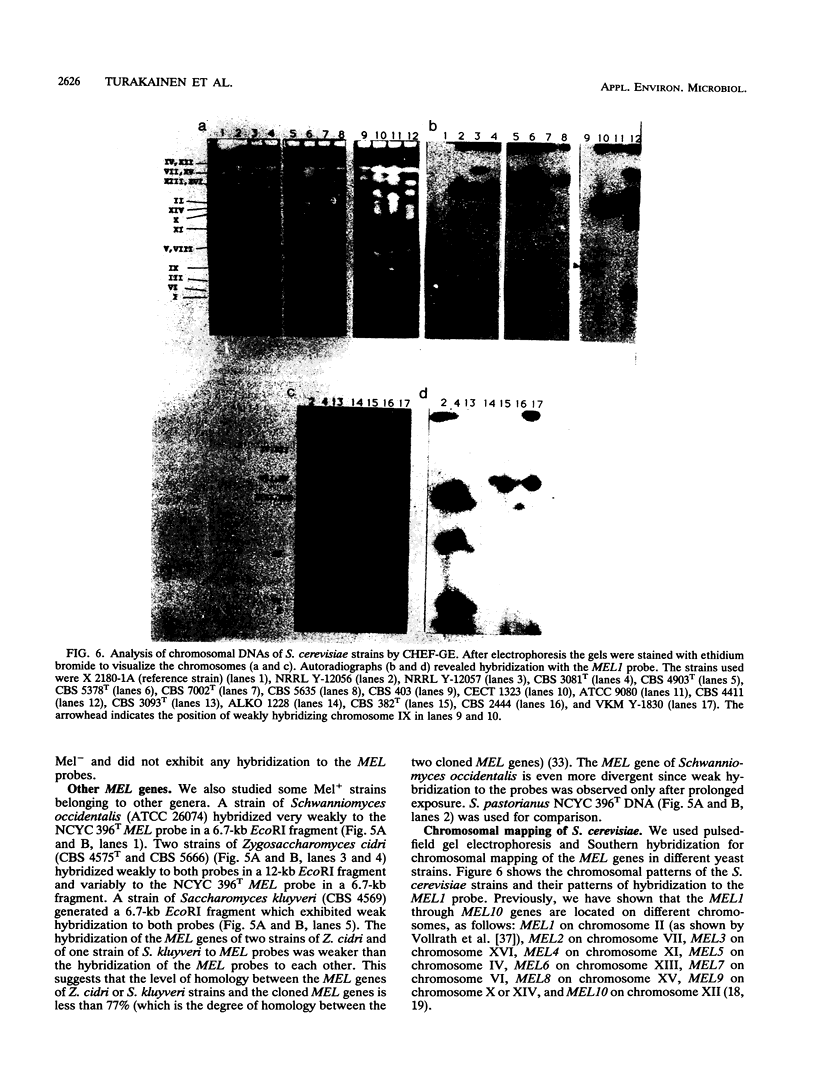
In Saccharomyces spp. the ability to use melibiose depends on the presence of a MEL gene encoding alpha-galactosidase. We used two cloned MEL genes as probes to characterize the physical structure and chromosomal location of the MEL genes in several industrial and natural Mel+ strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Saccharomyces pastorianus, and Saccharomyces bayanus. Electrokaryotyping showed that all of the S. pastorianus strains and most of the S. bayanus strains studied had one MEL locus. The MEL gene in S. bayanus strains was similar but not identical to the S. pastorianus MEL gene. Mel+ S. cerevisiae strains had one to seven loci containing MEL sequences. The MEL genes of these strains could be divided into two categories on the basis of hybridization to MEL1, one group exhibiting strong hybridization to MEL1 and the other group exhibiting weak hybridization to MEL1. In S. pastorianus and S. bayanus strains, the MEL gene was expressed as a single 1.5-kb transcript, and the expression was galactose inducible. In some S. cerevisiae strains, the MEL genes were expressed even without induction at fairly high levels. Expression was usually further induced by galactose. In two strains, CBS 5378 and CBS 4903, expression of the MEL genes was at the same level without induction as it was in most other strains with induction. In all S. cerevisiae strains, irrespective of the number of MEL genes, mRNA of only one size (1.6 kb) was observed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop D. F., Calhoun D. H., Bernstein H. S., Hantzopoulos P., Quinn M., Desnick R. J. Human alpha-galactosidase A: nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the mature enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4859–4863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIIS J., OTTOLENGHI P. Localization of melibiase in a strain of veast. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1959;31:272–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUPT W., ALPS H. [On the fermentation of melibiose by Saccaharomyces strains]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1963;45:179–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Hopper J. E. Isolation of the yeast regulatory gene GAL4 and analysis of its dosage effects on the galactose/melibiose regulon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6971–6975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew O. M., Douglas H. C. Genetic co-regulation of galactose and melibiose utilization in Saccharomyces. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.33-41.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. S., Ochoa A. G., Gascón S. alpha-Galactosidase from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Cellular localization, and purification of the external enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 15;77(2):375–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P. L. The nucleotide sequence of the yeast MEL1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7257–7268. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindegren C. C., Spiegelman S., Lindegren G. Mendelian Inheritance of Adaptive Enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1944 Nov 15;30(11):346–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.30.11.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini A. V., Martini A. Three newly delimited species of Saccharomyces sensu stricto. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1987;53(2):77–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00419503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister L., Finkelstein D. B. Alterations in translatable ribonucleic acid after heat shock of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):603–612. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.603-612.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumov G. I., Naumova E. S., Lantto R. A., Louis E. J., Korhola M. Genetic homology between Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its sibling species S. paradoxus and S. bayanus: electrophoretic karyotypes. Yeast. 1992 Aug;8(8):599–612. doi: 10.1002/yea.320080804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumov G., Naumova E., Turakainen H., Suominen P., Korhola M. Polymeric genes MEL8, MEL9 and MEL10--new members of alpha-galactosidase gene family in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1991 Sep;20(4):269–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00318514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumov G., Turakainen H., Naumova E., Aho S., Korhola M. A new family of polymorphic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: alpha-galactosidase genes MEL1-MEL7. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):119–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00259458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Fellinger A. J., Toonen M. Y., van Wassenaar D., Verrips C. T. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the alpha-galactosidase cDNA from Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (guar). Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Nov;13(5):541–550. doi: 10.1007/BF00027314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post-Beittenmiller M. A., Hamilton R. W., Hopper J. E. Regulation of basal and induced levels of the MEL1 transcript in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1238–1245. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman S., Lindegren C. C., Lindegren G. Maintenance and Increase of a Genetic Character by a Substrate-Cytoplasmic Interaction in the Absence of the Specific Gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1945 Mar;31(3):95–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.31.3.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner-Smith M., Bozzato R. P., Skipper N., Davies R. W., Hopper J. E. Analysis of the inducible MEL1 gene of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis and its secreted product, alpha-galactosidase (melibiase). Gene. 1985;36(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turakainen H., Korhola M., Aho S. Cloning, sequence and chromosomal location of a MEL gene from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis NCYC396. Gene. 1991 May 15;101(1):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90229-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W., Connelly C., Hieter P. Physical mapping of large DNA by chromosome fragmentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6027–6031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarrow D., Nakase T. DNA base composition of species of the genus Saccharomyces. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(1):81–88. doi: 10.1007/BF02565038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Herder I. F., Rosell A. M., van Zuilen C. M., Punt P. J., van den Hondel C. A. Cloning and expression of a member of the Aspergillus niger gene family encoding alpha-galactosidase. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jun;233(3):404–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00265437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]