Abstract
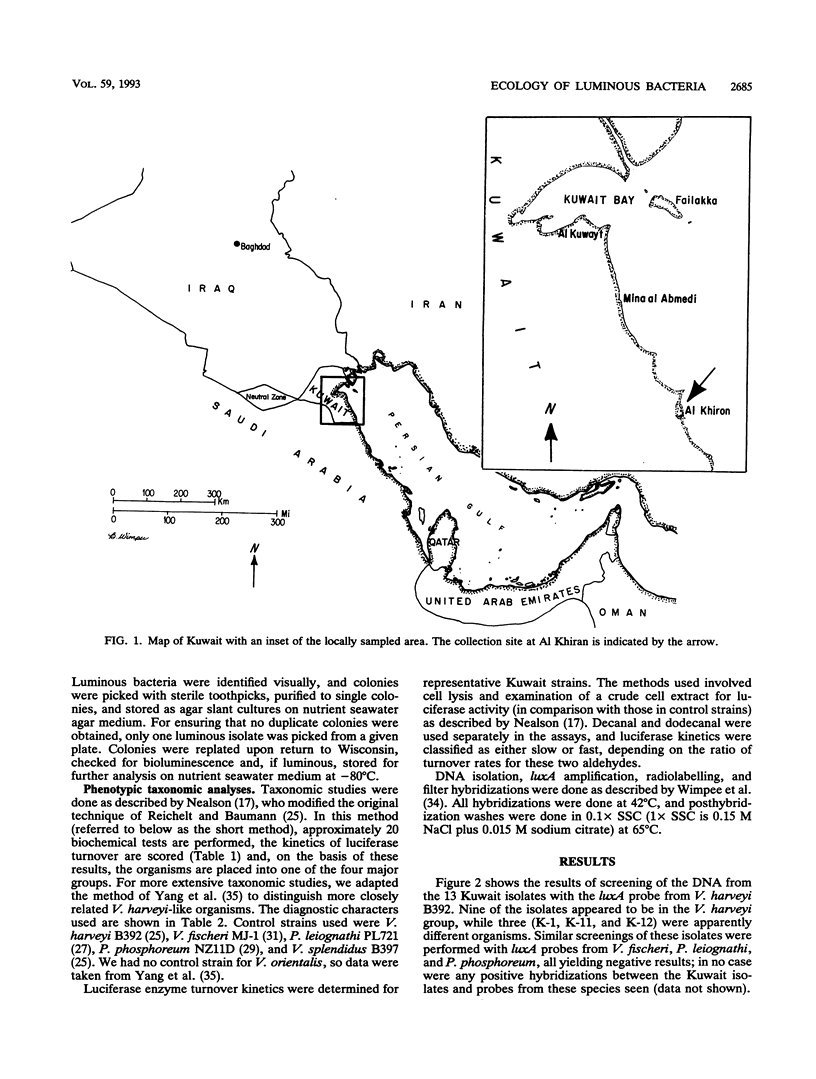
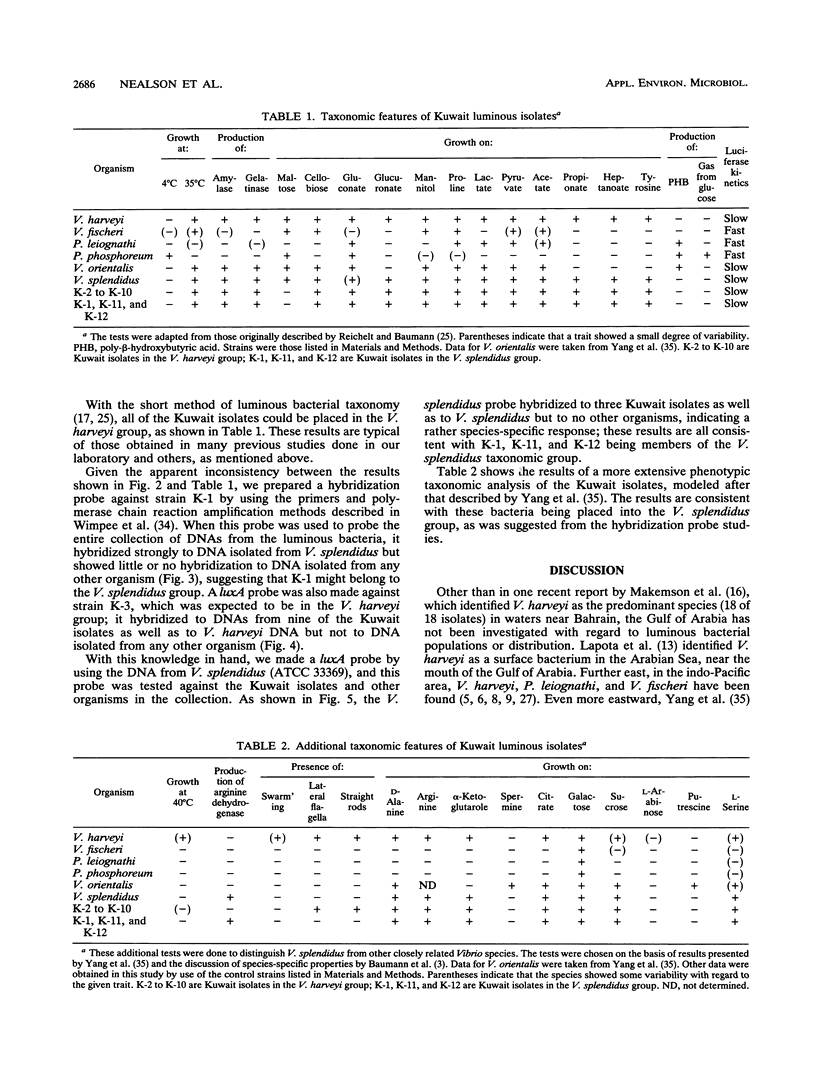
Hybridization probes specific for the luxA genes of four groups of luminous bacteria were used to screen luminous isolates obtained from the Persian Gulf, near Al Khiran, Kuwait Nine of these isolates were identified as Vibrio harveyi, a commonly encountered planktonic isolate, while three others showed no hybridization to any of the four probes (V. harveyi, Vibrio fischeri, Photobacterium phosphoreum, or Photobacterium leiognathi) under high-stringency conditions. Polymerase chain reaction amplification was used to prepare a luxA probe against one of these isolates, K-1, and this probe was screened under high-stringency conditions against a collection of DNAs from luminous bacteria; it was found to hybridize specifically to the DNA of the species Vibrio splendidus. A probe prepared against the type strain of V. splendidus (ATCC 33369) was tested against the collection of luminous bacterial DNA preparations and against the Kuwait isolates and was found to hybridize only against the type strain and the three unidentified Kuwait isolates. Extensive taxonomic analysis by standard methods confirmed the identification of the 13 isolates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Woolkalis M. J., Bang S. S. Evolutionary relationships in vibrio and Photobacterium: a basis for a natural classification. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:369–398. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap P. V., McFall-Ngai M. J. Initiation and control of the bioluminescent symbiosis between Photobacterium leiognathi and leiognathid fish. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;503:269–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb40614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leisman G., Cohn D. H., Nealson K. H. Bacterial origin of luminescence in marine animals. Science. 1980 Jun 13;208(4449):1271–1273. doi: 10.1126/science.208.4449.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makemson J. C., Fulayfil N., Basson P. Association of luminous bacteria with artificial and natural surfaces in arabian gulf seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jul;58(7):2341–2343. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2341-2343.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K., Cohn D., Leisman G., Tebo B. Co-evolution of luminous bacteria and their eukaryotic hosts. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;361:76–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb46512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'brien C. H., Sizemore R. K. Distribution of the Luminous Bacterium Beneckea harveyi in a Semitropical Estuarine Environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):928–933. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.928-933.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. D., Roberts D. M., White V. K., Dry M. A., Simpson L. M. Bioluminescence in a strain of the human pathogenic bacterium Vibrio vulnificus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1209–1211. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1209-1211.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff S. A., Colwell R. R. Distribution and identification of luminous bacteria from the sargasso sea. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):983–987. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.983-987.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. M., Colwell R. R. Detection of luciferase gene sequence in nonluminescent Vibrio cholerae by colony hybridization and polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1286–1293. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1286-1293.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt J. L., Baumann P., Baumann L. Study of genetic relationships among marine species of the genera Beneckea and Photobacterium by means of in vitro DNA/DNA hybridization. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Oct 11;110(1):101–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00416975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Greenberg E. P., Hastings J. W. Planktonic marine luminous bacteria: species distribution in the water column. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):302–306. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.302-306.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Morin J. G. Luminous enteric bacteria of marine fishes: a study of their distribution, densities, and dispersion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Sep;38(3):406–411. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.3.406-411.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Nealson K. H. Symbiotic association of Photobacterium fischeri with the marine luminous fish Monocentris japonica; a model of symbiosis based on bacterial studies. Biol Bull. 1976 Dec;151(3):574–586. doi: 10.2307/1540507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo M., Yetinson T. Physiological characteristics underlying the distribution patterns of luminous bacteria in the mediterranean sea and the gulf of elat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Oct;38(4):577–584. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.4.577-584.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimpee C. F., Nadeau T. L., Nealson K. H. Development of species-specific hybridization probes for marine luminous bacteria by using in vitro DNA amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1319–1324. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1319-1324.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yetinson T., Shilo M. Seasonal and geographic distribution of luminous bacteria in the eastern mediterranean sea and the gulf of elat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1230–1238. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1230-1238.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]