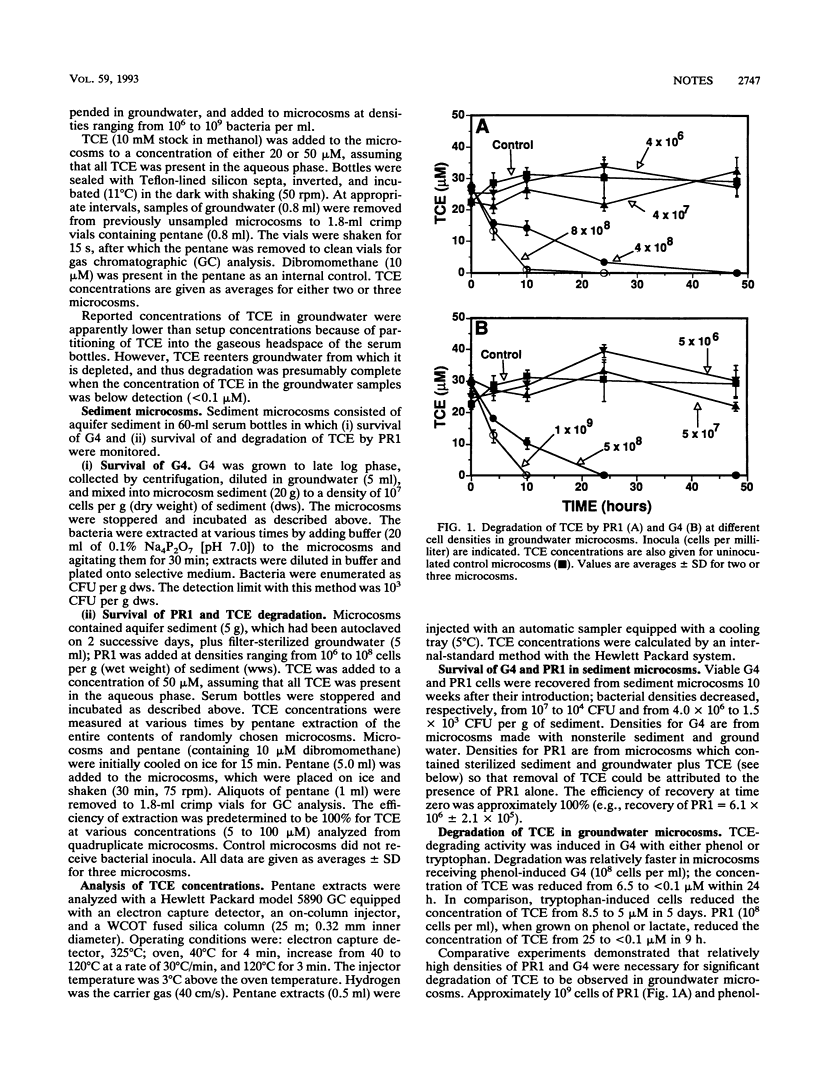
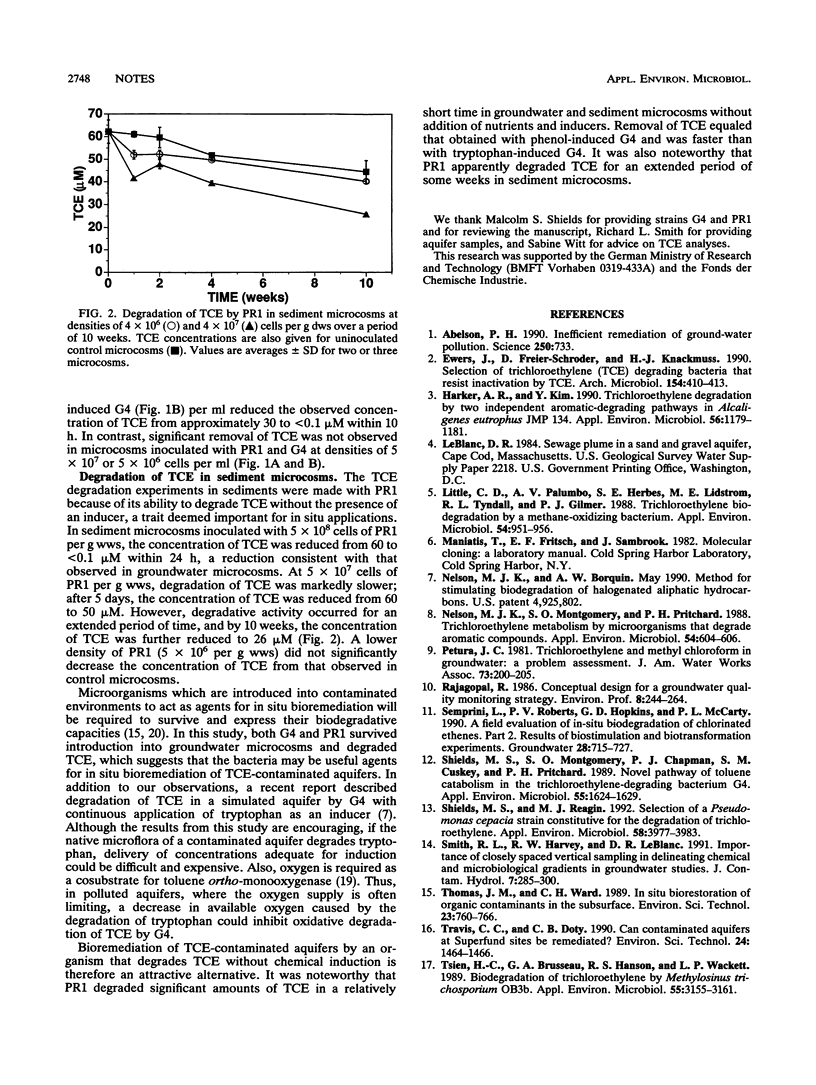
Abstract
Pseudomonas cepacia G4 degrades trichloroethylene (TCE) via a degradation pathway for aromatic compounds which is induced by substrates such as phenol and tryptophan. P. cepacia G4 5223 PR1 (PR1) is a Tn5 insertion mutant which constitutively expresses the toluene ortho-monooxygenase responsible for TCE degradation. In groundwater microcosms, phenol-induced strain G4 and noninduced strain PR1 degraded TCE (20 and 50 microM) to nondetectable levels (< 0.1 microM) within 24 h at densities of 10(8) cells per ml; at lower densities, degradation of TCE was not observed after 48 h. In aquifer sediment microcosms, TCE was reduced from 60 to < 0.1 microM within 24 h at 5 x 10(8) PR1 organisms per g (wet weight) of sediment and from 60 to 26 microM over a period of 10 weeks at 5 x 10(7) PR1 organisms per g. Viable G4 and PR1 cells decreased from approximately 10(7) to 10(4) per g over the 10-week period.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson P. H. Inefficient remediation of ground-water pollution. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):733–733. doi: 10.1126/science.2237418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewers J., Freier-Schröder D., Knackmuss H. J. Selection of trichloroethene (TCE) degrading bacteria that resist inactivation by TCE. Arch Microbiol. 1990;154(4):410–413. doi: 10.1007/BF00276540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Kim Y. Trichloroethylene degradation by two independent aromatic-degrading pathways in Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1179–1181. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1179-1181.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C. D., Palumbo A. V., Herbes S. E., Lidstrom M. E., Tyndall R. L., Gilmer P. J. Trichloroethylene biodegradation by a methane-oxidizing bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):951–956. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.951-956.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Montgomery S. O., Pritchard P. H. Trichloroethylene metabolism by microorganisms that degrade aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):604–606. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.604-606.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. S., Montgomery S. O., Chapman P. J., Cuskey S. M., Pritchard P. H. Novel pathway of toluene catabolism in the trichloroethylene-degrading bacterium g4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1624–1629. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1624-1629.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. S., Reagin M. J. Selection of a Pseudomonas cepacia strain constitutive for the degradation of trichloroethylene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Dec;58(12):3977–3983. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.3977-3983.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay R. E., Loeber R., Gagnon C., Charlebois P., Larivée S., LeBlanc M. Disruptive boys with stable and unstable high fighting behavior patterns during junior elementary school. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1991 Jun;19(3):285–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00911232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Brusseau G. A., Hanson R. S., Waclett L. P. Biodegradation of trichloroethylene by Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3155–3161. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3155-3161.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Brusseau G. A., Householder S. R., Hanson R. S. Survey of microbial oxygenases: trichloroethylene degradation by propane-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2960–2964. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2960-2964.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Degradation of trichloroethylene by toluene dioxygenase in whole-cell studies with Pseudomonas putida F1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1703–1708. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1703-1708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., Wilson B. H. Biotransformation of trichloroethylene in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):242–243. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.242-243.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


