Abstract
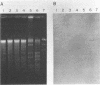
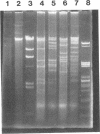
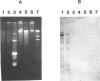
Pseudomonas putida P111 is able to utilize a broad range of monochlorinated, dichlorinated, and trichlorinated benzoates. The involvement of two separate dioxygenases was noted from data on plasmid profiles and DNA hybridization. The benzoate dioxygenase, which converts 3-chlorobenzoate (3-CB), 4-CB, and benzoate to the corresponding catechols via reduction of a dihydrodiol, was shown to be chromosomally coded. The chlorobenzoate-1,2-dioxygenase that converts ortho-chlorobenzoates to the corresponding catechols without the need of a functional dioldehydrogenase was shown to be encoded on plasmid pPB111 (75 kb). Cured strains were unable to utilize ortho-chlorobenzoates for growth. DNA hybridization data indicated that catabolism of the corresponding chlorocatechols was coded on chromosomal genes. Maintenance of plasmid pPB111 was dependent on the presence of ortho-chlorobenzoates in the growth media. A unique variant of P111 (P111D), able to grow on 3,5-dichlorobenzoate (3,5-DCB), was obtained by continuous subculturing from media containing progressively lower and higher concentrations of 3-CB and 3,5-DCB, respectively. The low frequency of segregants able to grow on 2,5-DCB, 2,3-DCB, and 2,3, 5-trichlorobenzoate was evident by lag periods greater than 200 h. Continued subculture on 3,5-DCB resulted in the formation of new plasmid pPH111 (120 kb), which was homologous to pPB111. A probe from the clc operon, which encodes for the chlorocatechol pathway, hybridized to plasmid pPH111 and to the chromosome of the wild-type strain P111 but not to its plasmid pPB111 nor to the chromosome of strain P111A, which had lost the ability to utilize chlorobenzoates.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. H., Huang C. M., Higson F. K., Brenner V., Focht D. D. Construction of a 3-chlorobiphenyl-utilizing recombinant from an intergeneric mating. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):647–654. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.647-654.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adriaens P., Kohler H. P., Kohler-Staub D., Focht D. D. Bacterial dehalogenation of chlorobenzoates and coculture biodegradation of 4,4'-dichlorobiphenyl. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):887–892. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.887-892.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Restriction mapping of a chlorobenzoate degradative plasmid and molecular cloning of the degradative genes. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D. K., Kellogg S. T., Hamada S., Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmid specifying total degradation of 3-chlorobenzoate by a modified ortho pathway. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):639–646. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.639-646.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Weightman A. J., Knackmuss H. J., Timmis K. N. Transposon mutagenesis and cloning analysis of the pathways for degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 3-chlorobenzoate in Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134(pJP4). J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):85–90. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.85-90.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Hellwig M., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Isolation and characterization of a 3-chlorobenzoate degrading pseudomonad. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00696222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engesser K. H., Schulte P. Degradation of 2-bromo-, 2-chloro- and 2-fluorobenzoate by Pseudomonas putida CLB 250. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 15;51(1):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetzner S., Müller R., Lingens F. Degradation of 2-chlorobenzoate by Pseudomonas cepacia 2CBS. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1989 Nov;370(11):1173–1182. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1989.370.2.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetzner S., Müller R., Lingens F. Purification and some properties of 2-halobenzoate 1,2-dioxygenase, a two-component enzyme system from Pseudomonas cepacia 2CBS. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):279–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.279-290.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht D. D., Shelton D. Growth kinetics of Pseudomonas alcaligenes C-0 relative to inoculation and 3-chlorobenzoate metabolism in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1846–1849. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1846-1849.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz B., Chakrabarty A. M. Organization and nucleotide sequence determination of a gene cluster involved in 3-chlorocatechol degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4460–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann J., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Metabolism of 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 3,5-dichlorobenzoate by a pseudomonad. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):421–428. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.421-428.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez B. S., Higson F. K., Kondrat R., Focht D. D. Metabolism of and inhibition by chlorobenzoates in Pseudomonas putida P111. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3361–3366. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3361-3366.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey W. J., Focht D. D. Degradation of mono-, di-, and trihalogenated benzoic acids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa JB2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Dec;56(12):3842–3850. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.12.3842-3850.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks T. S., Smith A. R., Quirk A. V. Degradation of 4-Chlorobenzoic Acid by Arthrobacter sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):1020–1025. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.1020-1025.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Molin S., Aagaard-Hansen H. Partitioning of plasmid R1 in Escherichia coli. I. Kinetics of loss of plasmid derivatives deleted of the par region. Plasmid. 1980 Sep;4(2):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins E. J., Gordon M. P., Caceres O., Lurquin P. F. Organization and sequence analysis of the 2,4-dichlorophenol hydroxylase and dichlorocatechol oxidative operons of plasmid pJP4. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2351–2359. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2351-2359.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertsova R. N., Kunc F., Golovleva L. A. Degradation of 3-chlorobenzoate in soil by pseudomonads carrying biodegradative plasmids. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1984;29(3):242–247. doi: 10.1007/BF02877315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Microbial degradation of haloaromatics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:263–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvestre M., Mailhiot K., Ahmad D., Massé R. Isolation and preliminary characterization of a 2-chlorobenzoate degrading Pseudomonas. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Apr;35(4):439–443. doi: 10.1139/m89-067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyndham R. C., Straus N. A. Chlorobenzoate catabolism and interactions between Alcaligenes and Pseudomonas species from Bloody Run Creek. Arch Microbiol. 1988;150(3):230–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00407785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Tweel W. J., Kok J. B., de Bont J. A. Reductive dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorobenzoate to 4-chlorobenzoate and hydrolytic dehalogenation of 4-chloro-, 4-bromo-, and 4-iodobenzoate by Alcaligenes denitrificans NTB-1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):810–815. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.810-815.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. R., van Neerven A. R., de Vries E. J., de Vos W. M., Zehnder A. J. Cloning and characterization of plasmid-encoded genes for the degradation of 1,2-dichloro-, 1,4-dichloro-, and 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene of Pseudomonas sp. strain P51. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):6–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.6-15.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]