Abstract
The synthesis of an RNA probe specific for the hlyA gene of Listeria monocytogenes by in vitro transcription from a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-generated template incorporating bacteriophage T7 promoter sequences is described. This simple method produced a high yield of RNA which hybridized specifically with hlyA PCR products on a membrane, resulting in RNA-DNA hybrids which were detected by an immunoenzymatic assay with an anti-RNA-DNA hybrid antibody. The RNA probe hybridization system was more sensitive in the analysis of the PCR products than was the conventional agarose gel electrophoresis method. When applied to the analysis of PCR samples from cultures of various Listeria and non-Listeria organisms, the RNA probe was reactive in the assay of 62 different L. monocytogenes isolates but not other Listeria species. Among the non-Listeria organisms tested, only Enterococcus faecalis gave a weak positive reaction with more than 10(9) cells per ml. This reactivity disappeared at lower cell densities. This strategy for the synthesis and application of RNA probes should facilitate the analysis of PCR products in the detection of L. monocytogenes and possibly other food pathogens.
Full text
PDF


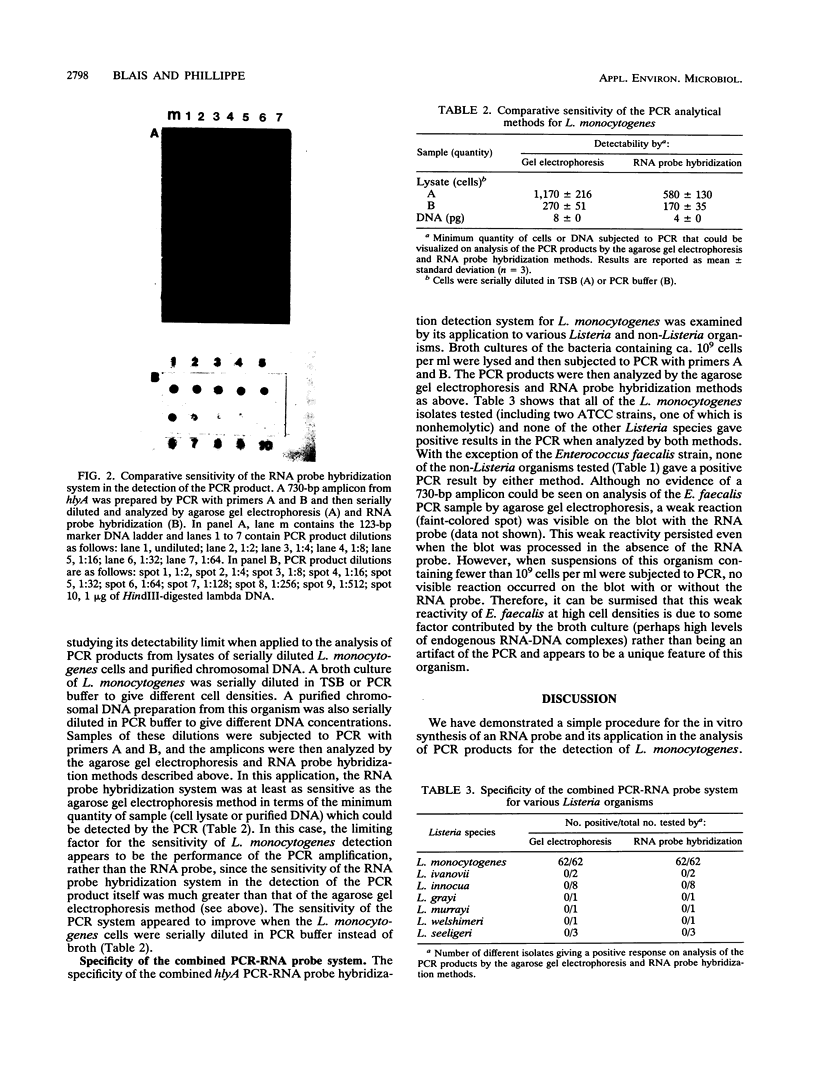


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhunia A. K., Johnson M. G. Monoclonal antibody specific for Listeria monocytogenes associated with a 66-kilodalton cell surface antigen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1924–1929. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1924-1929.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. L., Moore A. S., Patchett R. A., Collins M. D., Kroll R. G. Use of the polymerase chain reaction and oligonucleotide probes for the rapid detection and identification of Carnobacterium species from meat. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;72(4):294–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenevert J., Mengaud J., Gormley E., Cossart P. A DNA probe specific for L. monocytogenes in the genus Listeria. Int J Food Microbiol. 1989 Jul;8(4):317–319. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(89)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digweed M., Günthert U. Recombinant selection by microinjection: a simple cDNA cloning procedure for production of exclusively sense RNA transcripts. Gene. 1989 Nov 15;83(1):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90412-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Peterkin P. I. Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):476–511. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.476-511.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitter S., Heuzenroeder M., Thomas C. J. A combined PCR and selective enrichment method for rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;73(1):53–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb04968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furrer B., Candrian U., Hoefelein C., Luethy J. Detection and identification of Listeria monocytogenes in cooked sausage products and in milk by in vitro amplification of haemolysin gene fragments. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991 May;70(5):372–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1991.tb02951.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guatelli J. C., Whitfield K. M., Kwoh D. Y., Barringer K. J., Richman D. D., Gingeras T. R. Isothermal, in vitro amplification of nucleic acids by a multienzyme reaction modeled after retroviral replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1874–1878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Raposa S., Warshaw J., Johnson A., Halbert D., Klinger J. D. A new colorimetric nucleic acid hybridization assay for Listeria in foods. Int J Food Microbiol. 1989 Jun;8(3):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(89)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler S., Leimeister-Wächter M., Chakraborty T., Lottspeich F., Goebel W. The gene coding for protein p60 of Listeria monocytogenes and its use as a specific probe for Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1943–1950. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1943-1950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Chenevert J., Pereira J. M., Geoffroy C., Gicquel-Sanzey B., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Cossart P. Expression in Escherichia coli and sequence analysis of the listeriolysin O determinant of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):766–772. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.766-772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederhauser C., Candrian U., Höfelein C., Jermini M., Bühler H. P., Lüthy J. Use of polymerase chain reaction for detection of Listeria monocytogenes in food. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1564–1568. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1564-1568.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossen L., Holmstrøm K., Olsen J. E., Rasmussen O. F. A rapid polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based assay for the identification of Listeria monocytogenes in food samples. Int J Food Microbiol. 1991 Nov;14(2):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(91)90101-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoflet E. S., Koeberl D. D., Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. Genomic amplification with transcript sequencing. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.3340835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D., Rashtchian A. Immunochemical approaches to gene probe assays. Anal Biochem. 1987 Mar;161(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90467-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. The experimental induction of antibodies to nucleic acids. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):70–85. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. F., Cao W. W., Johnson M. G. 16S rRNA-based probes and polymerase chain reaction method to detect Listeria monocytogenes cells added to foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Sep;58(9):2827–2831. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.9.2827-2831.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernars K., Heuvelman C. J., Chakraborty T., Notermans S. H. Use of the polymerase chain reaction for direct detection of Listeria monocytogenes in soft cheese. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;70(2):121–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1991.tb04437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatcroft R., Watson R. J. A Positive Strain Identification Method for Rhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):574–576. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.574-576.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




