Abstract
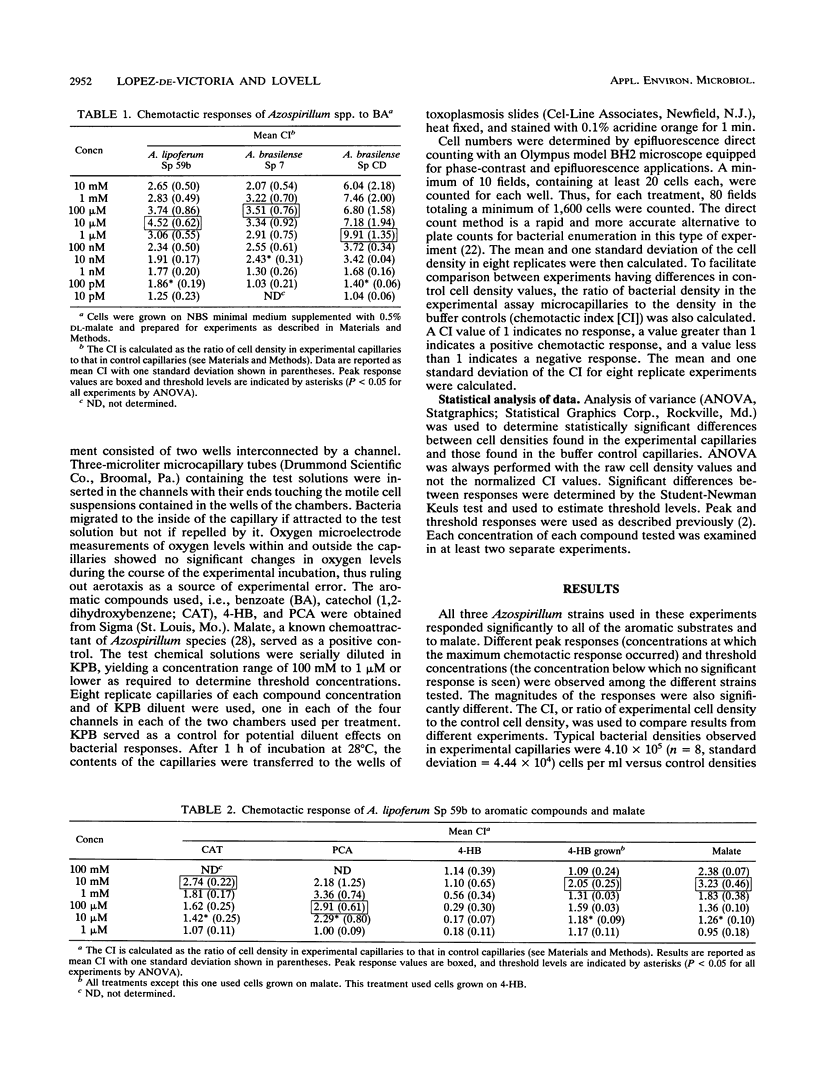
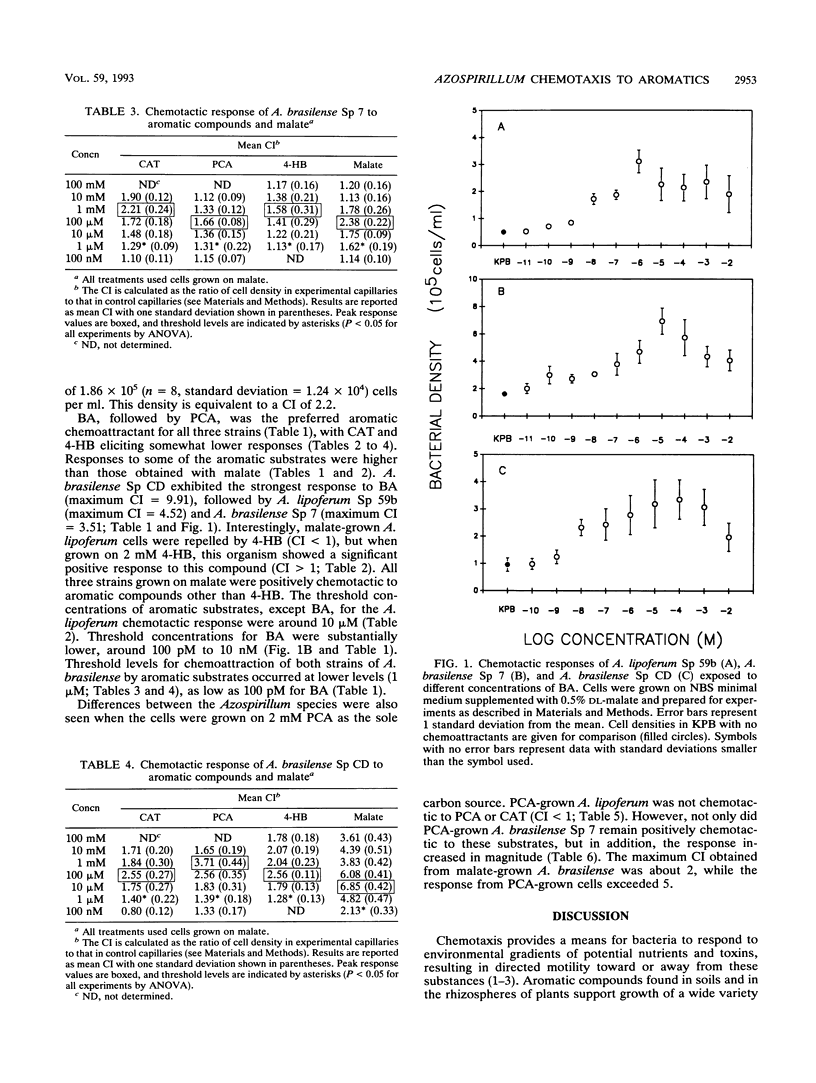
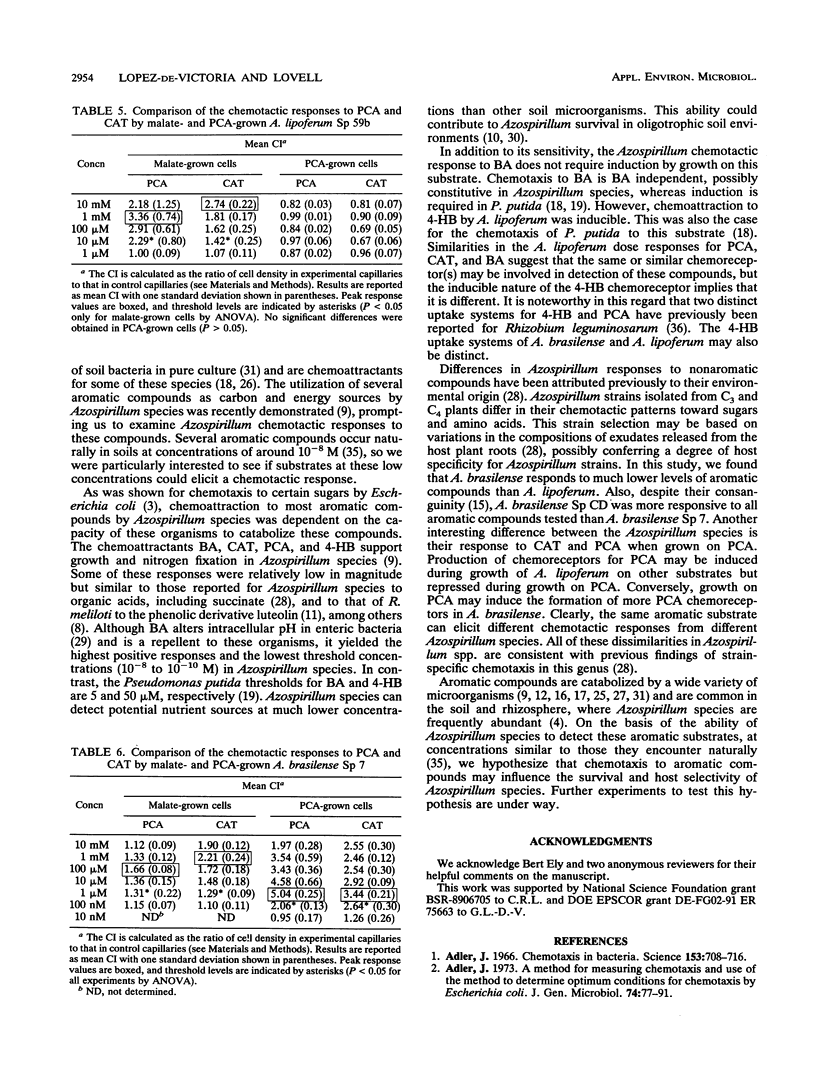
Chemotaxis of Azospirillum lipoferum Sp 59b and Azospirillum brasilense Sp 7 and Sp CD to malate and to the aromatic substrates benzoate, protocatechuate, 4-hydroxybenzoate, and catechol was assayed by the capillary method and direct cell counts. A. lipoferum required induction by growth on 4-hydroxybenzoate for positive chemotaxis to this compound. Chemotaxis of Azospirillum spp. to all other substrates did not require induction. Maximum chemotactic responses for most aromatic compounds occurred at concentrations of 1 to 10 mM for A. lipoferum and 100 μM to 1 mM for A. brasilense. Threshold levels of these chemoattractants ranged from nanomolar to micromolar, with A. brasilense Sp CD showing the lowest threshold levels for the substrates tested. Benzoate was the strongest chemoattractant tested, with threshold concentrations in the nanomolar to picomolar range for all strains. Azospirillum spp. clearly have more sensitive chemosensory mechanisms for certain aromatic substrates than previously reported in some other soil bacteria. This sensitivity allows Azospirillum spp. to detect and respond to aromatic substrates at concentrations relevant to the soil and rhizosphere environments. The ability to detect such low concentrations of aromatic compounds in soils may confer advantages in survival and colonization of the rhizosphere by Azospirillum species.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Science. 1966 Aug 12;153(3737):708–716. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3737.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:341–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caetano-Anollés G., Crist-Estes D. K., Bauer W. D. Chemotaxis of Rhizobium meliloti to the plant flavone luteolin requires functional nodulation genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3164–3169. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3164-3169.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chet I., Mitchell R. Ecological aspects of microbial chemotactic behavior. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:221–239. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.001253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobereiner J., Marriel I. E., Nery M. Ecological distribution of Spirillum lipoferum Beijerinck. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Oct;22(10):1464–1473. doi: 10.1139/m76-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardisson C., Sala-Trepat J. M., Stanier R. Y. Pathways for the oxidation of aromatic compounds by Azotobacter. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Nov;59(1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood C. S., Parales R. E., Dispensa M. Chemotaxis of Pseudomonas putida toward chlorinated benzoates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1501–1503. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1501-1503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood C. S., Rivelli M., Ornston L. N. Aromatic acids are chemoattractants for Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):622–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.622-628.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kape R., Parniske M., Werner D. Chemotaxis and nod Gene Activity of Bradyrhizobium japonicum in Response to Hydroxycinnamic Acids and Isoflavonoids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):316–319. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.316-319.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palleroni N. J. Chamber for bacterial chemotaxis experiments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Nov;32(5):729–730. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.5.729-730.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke D., Rivelli M., Ornston L. N. Chemotaxis to aromatic and hydroaromatic acids: comparison of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Rhizobium trifolii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):417–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.417-422.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold B., Hurek T., Fendrik I. Strain-specific chemotaxis of Azospirillum spp. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):190–195. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.190-195.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske D. R., Adler J. Change in intracellular pH of Escherichia coli mediates the chemotactic response to certain attractants and repellents. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1196–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1196-1208.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Colwell R. R. Survival strategies of bacteria in the natural environment. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):365–379. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.365-379.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Ornston L. N. The beta-ketoadipate pathway. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9(0):89–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarrand J. J., Krieg N. R., Döbereiner J. A taxonomic study of the Spirillum lipoferum group, with descriptions of a new genus, Azospirillum gen. nov. and two species, Azospirillum lipoferum (Beijerinck) comb. nov. and Azospirillum brasilense sp. nov. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Aug;24(8):967–980. doi: 10.1139/m78-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


