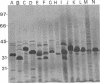
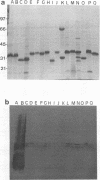
Abstract
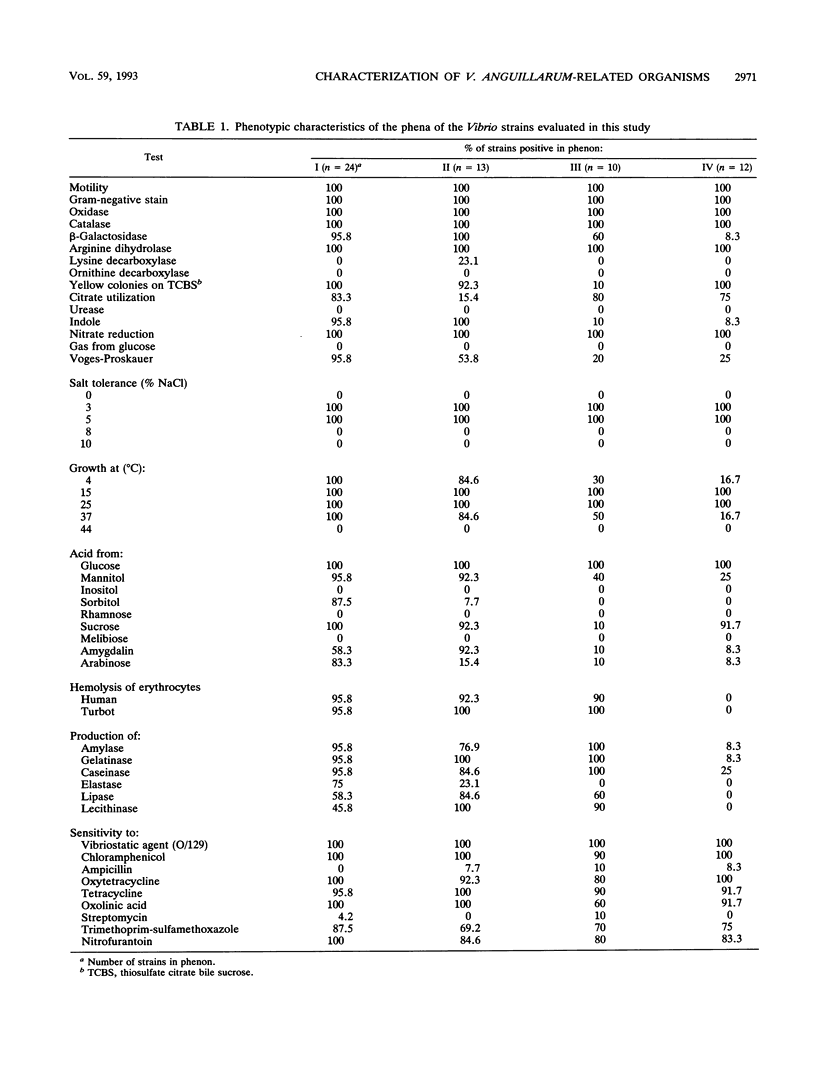
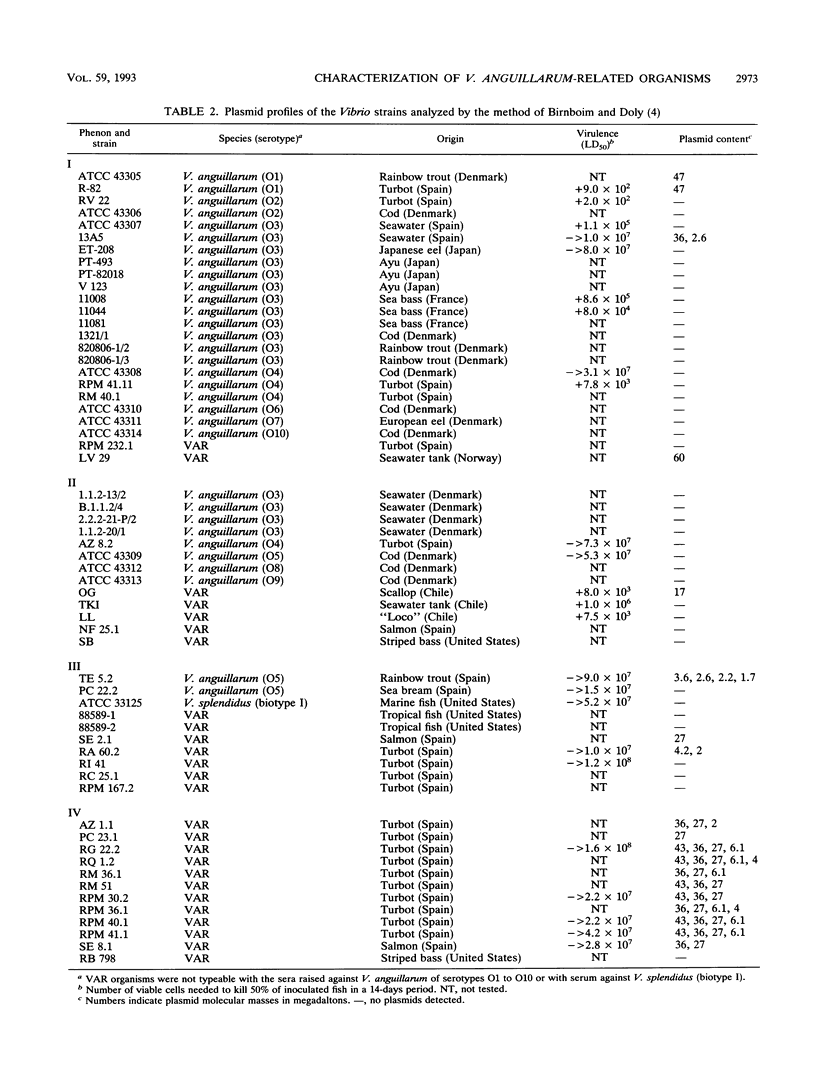
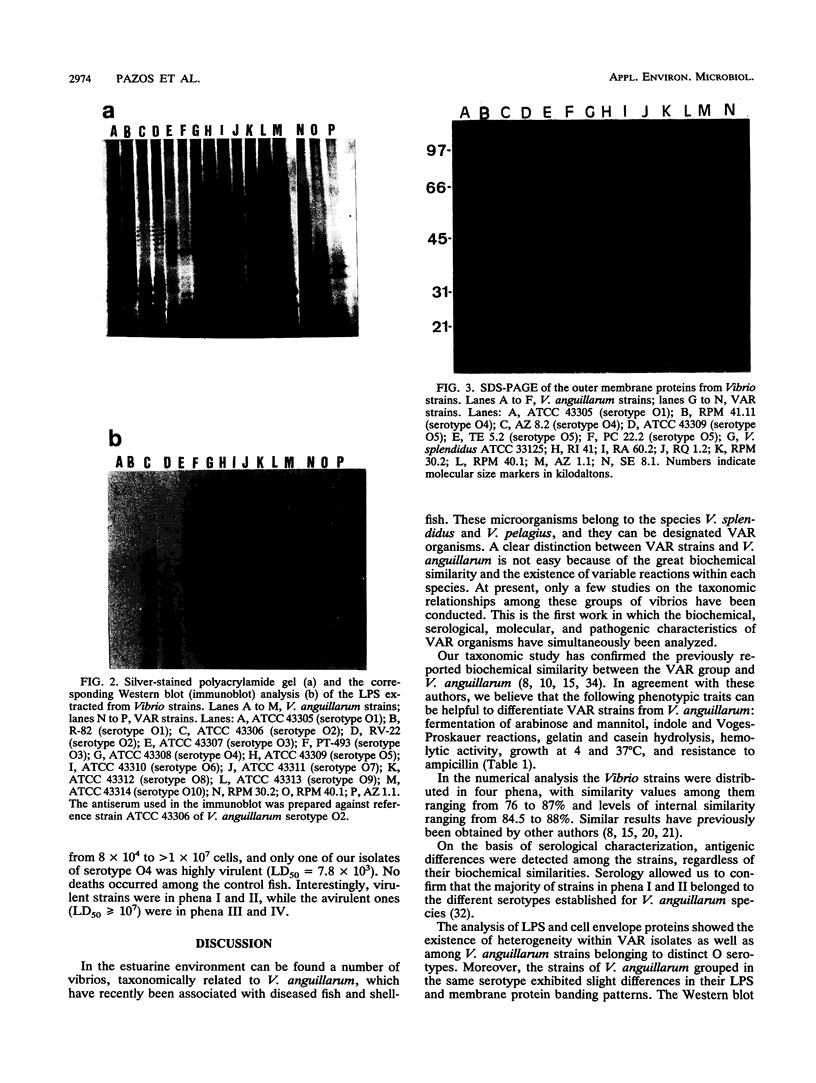
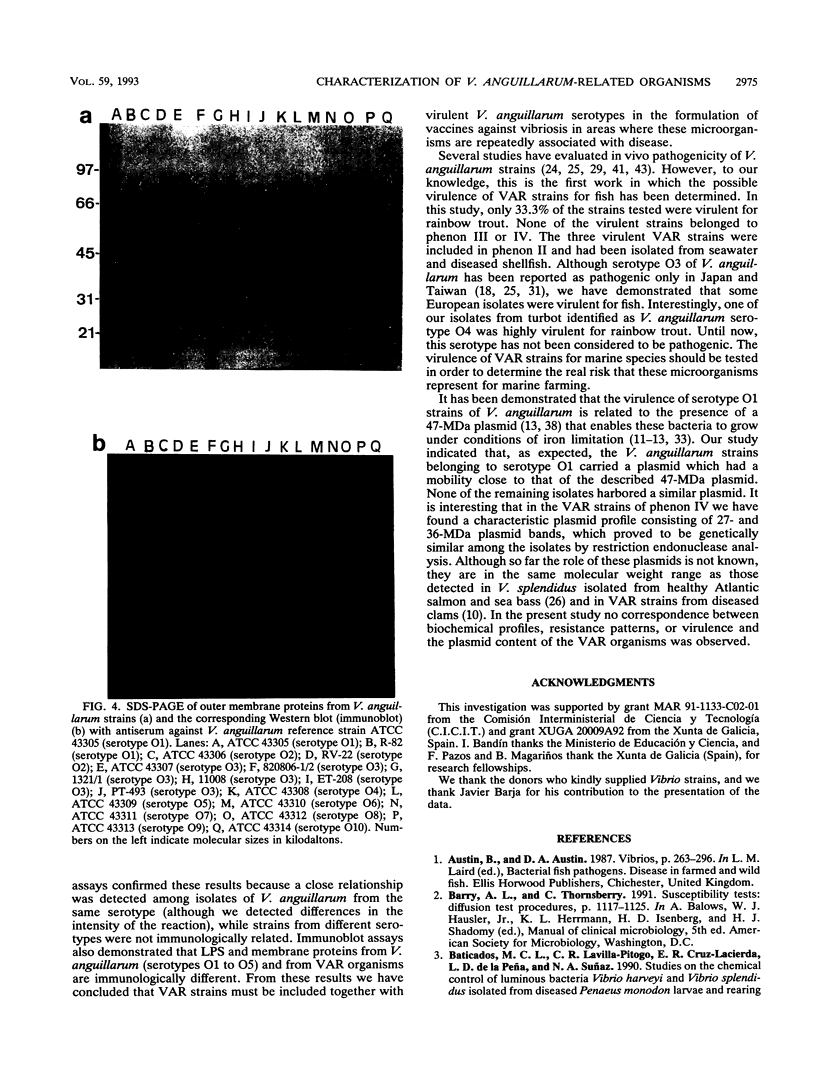
The phenotypic, molecular, and virulence properties of 46 Vibrio anguillarum-related (VAR) strains isolated from diseased fish and shellfish and from the environment were investigated. Twelve reference strains belonging to the 10 serotypes of V. anguillarum and the Vibrio splendidus type strain were included for comparison. Numerical taxonomy studies allowed us to group the isolates into four phena. The main phenotypic traits to differentiate VAR strains from V. anguillarum were fermentation of arabinose and mannitol, indole and Voges-Proskauer reactions, gelatin and casein hydrolysis, hemolytic activity, growth at 37 and 4°C, and resistance to ampicillin. Serological analysis confirmed that phena I and II were composed mainly of strains of V. anguillarum, while phena III and IV included VAR strains. Excluding the reference strains, the typeable isolates belonged to serotypes O3 (15 strains), O4 (3 strains), and O5 (2 strains) of V. anguillarum. The infectivity trials showed that only 9 of a total of 24 strains tested displayed virulence for rainbow trout. Virulent strains (50% lethal dose ranging from 102 to 106 cells) included V. anguillarum strains belonging to serotypes O1 (one strain), O2 (one strain), O3 (three isolates), and O4 (one isolate) and only three strains of the VAR group. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of lipopolysaccharide and outer membrane proteins showed heterogeneity not only among the 10 V. anguillarum serotypes but also within the VAR group. Immunoblot assays demonstrated a close relationship among V. anguillarum strains from the same serotype, while strains from different serotypes were not antigenically related. The VAR strains did not share antigenic components with the serotypes of V. anguillarum tested (serotypes O1 to O5). Plasmids were detected in only 19 of the total of 59 strains. The majority of the strains carrying plasmids were grouped within phenon IV, in which plasmid bands of 27 and 36 MDa were found in all the isolates. No correlation between the plasmid content of VAR microorganisms and their phenotypic or virulence characteristics was observed. From these results it can be concluded that VAR strains associated with disease should be included together with V. anguillarum in the formulation of vaccines against vibriosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowser P. R., Rosemark R., Reiner C. R. A preliminary report of vibriosis in cultured American lobsters, Homarus americanus. J Invertebr Pathol. 1981 Jan;37(1):80–85. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(81)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant T. N., Lee J. V., West P. A., Colwell R. R. A probability matrix for the identification of species of Vibrio and related genera. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;61(5):469–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant T. N., Lee J. V., West P. A., Colwell R. R. Numerical classification of species of Vibrio and related genera. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;61(5):437–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conchas R. F., Lemos M. L., Barja J. L., Toranzo A. E. Distribution of plasmid- and chromosome-mediated iron uptake systems in Vibrio anguillarum strains of different origins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Oct;57(10):2956–2962. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.10.2956-2962.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Actis L. A., Mitoma Y., Perez-Casal J., Tolmasky M. E., Valvano M. A. Plasmid-mediated iron sequestering systems in pathogenic strains of Vibrio anguillarum and Escherichia coli. Basic Life Sci. 1985;30:759–774. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2447-8_52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Hodges L. L., Schiewe M. H. Curing of a plasmid is correlated with an attenuation of virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):897–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.897-902.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filip C., Fletcher G., Wulff J. L., Earhart C. F. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by the ionic detergent sodium-lauryl sarcosinate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.717-722.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. L., Rasmussen H. B., Dalsgaard I. Study of Vibrio anguillarum strains from different sources with emphasis on ecological and pathobiological properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Sep;54(9):2264–2267. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.9.2264-2267.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. L. Vibrio anguillarum: a comparative study of fish pathogenic, environmental, and reference strains. Acta Vet Scand. 1983;24(4):456–476. doi: 10.1186/BF03546718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhr E., Larsen J. L., Lillehaug A., Gudding R., Heum M., Håstein T. Characterization of Vibrio anguillarum and closely related species isolated from farmed fish in Norway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2750–2757. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2750-2757.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen U. B., Larsen J. L. Serotyping of Vibrio anguillarum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Mar;51(3):593–597. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.3.593-597.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolmasky M. E., Actis L. A., Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L., Crosa J. H. Plasmids mediating iron uptake in Vibrio anguillarum strains isolated from turbot in Spain. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):1989–1997. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-1989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L., Potter S. A., Colwell R. R., Hetrick F. M., Crosa J. H. Molecular factors associated with virulence of marine vibrios isolated from striped bass in Chesapeake Bay. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1220–1227. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1220-1227.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiik R., Andersen K., Daae F. L., Hoff K. A. Virulence studies based on plasmid profiles of the fish pathogen Vibrio salmonicida. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):819–825. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.819-825.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]