Abstract
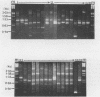
The 10-mer primer OPM-01 (5'-GTT GGT GGC T-3') was used to generate random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD) profiles by polymerase chain reaction for 91 strains of Listeria monocytogenes from raw milk, food, and veterinary, medical, and food-environmental sources. The profiles obtained contained 1 to 10 bands within the molecular size range of 0.5 to 5.0 kbp. Reproducibility was enhanced by annealing at low stringency and introducing a 1-min ramp time between annealing and extension temperatures. Thirty-three RAPD profiles were observed, with specific profiles being observed for strains from each source. RAPD profiles allowed discrimination within serogroups, although five RAPD profiles which were not confined to one serotype were found. Within food strains, one RAPD profile was more common than others, suggesting this to be a common type among strains from this source.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassam B. J., Caetano-Anollés G., Gresshoff P. M. DNA amplification fingerprinting of bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1992 Oct;38(1):70–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00169422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brousseau R., Saint-Onge A., Préfontaine G., Masson L., Cabana J. Arbitrary primer polymerase chain reaction, a powerful method to identify Bacillus thuringiensis serovars and strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):114–119. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.114-119.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caetano-Anollés G., Bassam B. J., Gresshoff P. M. DNA amplification fingerprinting using very short arbitrary oligonucleotide primers. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Jun;9(6):553–557. doi: 10.1038/nbt0691-553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czajka J., Bsat N., Piani M., Russ W., Sultana K., Wiedmann M., Whitaker R., Batt C. A. Differentiation of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua by 16S rRNA genes and intraspecies discrimination of Listeria monocytogenes strains by random amplified polymorphic DNA polymorphisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):304–308. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.304-308.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J., Gilmour A. Occurrence of Listeria species in raw milk and dairy products produced in Northern Ireland. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;72(2):119–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb01812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier S. I., Audurier A., Marquet-Van der Mee N., Notermans S., Wernars K. A comparative study of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis and conventional phage typing for epidemiological studies of Listeria monocytogenes isolates. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jun;143(5):507–512. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier S. I., Wernars K. Typing of Listeria strains by random amplification of polymorphic DNA. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jun;143(5):499–505. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier S., van de Giessen A., Heuvelman K., Wernars K. RAPD analysis of Campylobacter isolates: DNA fingerprinting without the need to purify DNA. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1992 Jun;14(6):260–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1992.tb00700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]