Abstract
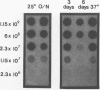
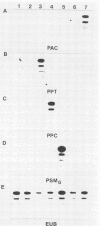
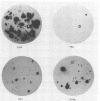
A simple technique in which rRNA-targeted oligodeoxynucleotide probes are used to identify bacteria immobilized on membranes is described. By using colony lifts, bacteria are directly transferred from plates to untreated nitrocellulose membranes. Alternatively, cells resuspended from colonies can be applied to membranes by using a vacuum manifold under high-salt conditions. Blotted cells are baked and hybridized under stringent conditions by using standard protocols. Treatment of blotted cells with sodium dodecyl sulfate, urea, formaldehyde, or protease had no apparent effect on hybridization signals. Hybridization to rRNA from cells that had been stored refrigerated for 6 days was readily detected; however, fivefold more cells (approximately 10(7) cells) were required to obtain hybridization signals comparable to those generated by cells not subjected to storage. The sequences of oligonucleotide probes specific for Pseudomonas cepacia, Comamonas testosteroni, and Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and a group probe identifying Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas mendocina, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Comamonas acidovorans, and "Flavobacterium" lutescens are presented. In conjunction with the colony lift hybridization procedure, bacteria isolated from river water were identified by using these probes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann R. I., Krumholz L., Stahl D. A. Fluorescent-oligonucleotide probing of whole cells for determinative, phylogenetic, and environmental studies in microbiology. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):762–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.762-770.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann R. I., Zarda B., Stahl D. A., Schleifer K. H. Identification of individual prokaryotic cells by using enzyme-labeled, rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Sep;58(9):3007–3011. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.9.3007-3011.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amy P. S., Haldeman D. L., Ringelberg D., Hall D. H., Russell C. Comparison of Identification Systems for Classification of Bacteria Isolated from Water and Endolithic Habitats within the Deep Subsurface. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Oct;58(10):3367–3373. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.10.3367-3373.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill D. L., Fredrickson J. K., Thomas J. M. Vertical and horizontal variations in the physiological diversity of the aerobic chemoheterotrophic bacterial microflora in deep southeast coastal plain subsurface sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1058–1065. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1058-1065.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill D. L., Ghiorse W. C. Characterization of subsurface bacteria associated with two shallow aquifers in oklahoma. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):580–588. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.580-588.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betzl D., Ludwig W., Schleifer K. H. Identification of lactococci and enterococci by colony hybridization with 23S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2927–2929. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2927-2929.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun-Howland E. B., Danielsen S. A., Nierzwicki-Bauer S. A. Development of a rapid method for detecting bacterial cells in situ using 16S rRNA-targeted probes. Biotechniques. 1992 Dec;13(6):928–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rijk P., Neefs J. M., Van de Peer Y., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2075–2089. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., DeLong E. F., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic group-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for identification of single microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.720-726.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand R. G., Martin G. L., Furer P., Hazen A. A recruitment-of-praise package to increase productivity levels of developmentally handicapped workers. Behav Modif. 1990 Jan;14(1):97–113. doi: 10.1177/01454455900141007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurtshuk R. J., Blick M., Bresser J., Fox G. E., Jurtshuk P., Jr Rapid in situ hybridization technique using 16S rRNA segments for detecting and differentiating the closely related gram-positive organisms Bacillus polymyxa and Bacillus macerans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Aug;58(8):2571–2578. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.8.2571-2578.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Larsen N., Woese C. R. The ribosomal RNA database project. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):2017–2021. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterhout G. J., Shull V. H., Dick J. D. Identification of clinical isolates of gram-negative nonfermentative bacteria by an automated cellular fatty acid identification system. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):1822–1830. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.1822-1830.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayler G. S., Layton A. C. Environmental application of nucleic acid hybridization. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:625–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Bratina B. J., Tsuji K., Hanson R. S. Use of oligodeoxynucleotide signature probes for identification of physiological groups of methylotrophic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2858–2865. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2858-2865.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarda B., Amann R., Wallner G., Schleifer K. H. Identification of single bacterial cells using digoxigenin-labelled, rRNA-targeted oligonucleotides. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Dec;137(12):2823–2830. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-12-2823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]