Abstract
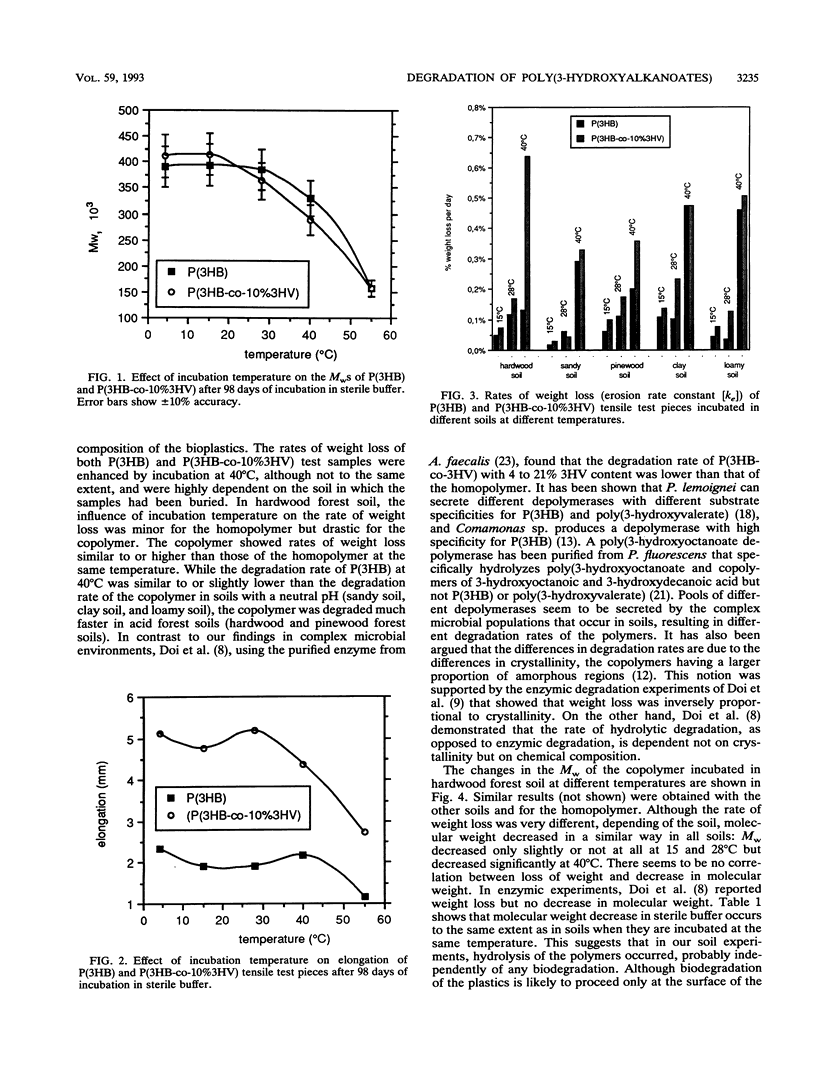
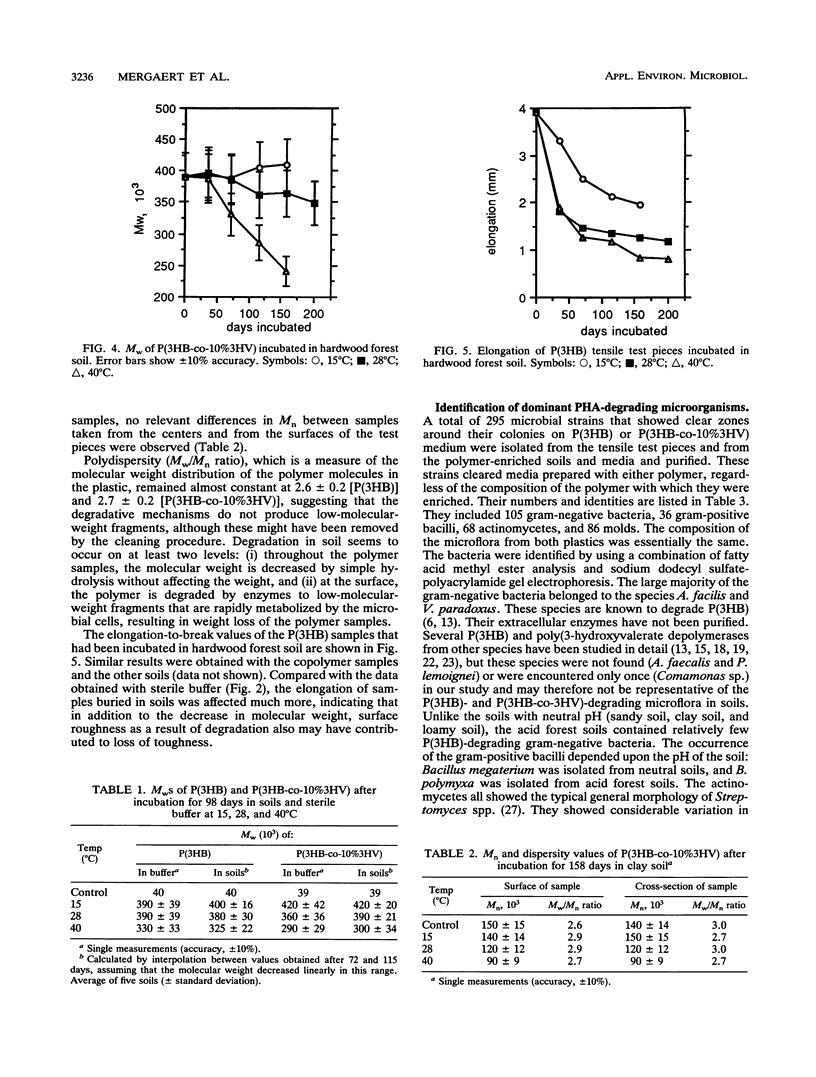
The microbial degradation of tensile test pieces made of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) [P(3HB)] or a copolymer of 90% 3-hydroxybutyric acid and 10% 3-hydroxyvaleric acid was studied in soils incubated at a constant temperature of 15, 28, or 40 degrees C for up to 200 days. In addition, hydrolytic degradation in sterile buffer at temperatures ranging from 4 to 55 degrees C was monitored for 98 days. Degradation was measured through loss of weight (surface erosion), molecular weight, and mechanical strength. While no weight loss was recorded in sterile buffer, samples incubated in soils were degraded at an erosion rate of 0.03 to 0.64% weight loss per day, depending on the polymer, the soil, and the incubation temperature. The erosion rate was enhanced by incubation at higher temperatures, and in most cases the copolymer lost weight at a higher rate than the homopolymer. The molecular weights of samples incubated at 40 degrees C in soils and those incubated at 40 degrees C in sterile buffer decreased at similar rates, while the molecular weights of samples incubated at lower temperatures remained almost unaffected, indicating that molecular weight decrease is due to simple hydrolysis and not to the action of biodegrading microorganisms. The degradation resulted in loss of mechanical properties. From the samples used in the biodegradation studies, 295 dominant microbial strains capable of degrading P (3HB) and the poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) copolymer in vitro were isolated and identified.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson A. J., Dawes E. A. Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):450–472. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.450-472.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson A. J., Haywood G. W., Dawes E. A. Biosynthesis and composition of bacterial poly(hydroxyalkanoates). Int J Biol Macromol. 1990 Apr;12(2):102–105. doi: 10.1016/0141-8130(90)90060-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budwill K., Fedorak P. M., Page W. J. Methanogenic degradation of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Apr;58(4):1398–1401. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.4.1398-1401.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHOWDHURY A. A. POLY-BETA-HYDROXYBUTTERSAEURE ABBAUENDE BAKTERIEN UND EXOENZYM. Arch Mikrobiol. 1963 Dec 10;47:167–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delafield F. P., Doudoroff M., Palleroni N. J., Lusty C. J., Contopoulos R. Decomposition of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate by pseudomonads. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1455–1466. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1455-1466.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland S. J., Jolly A. M., Yasin M., Tighe B. J. Polymers for biodegradable medical devices. II. Hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate copolymers: hydrolytic degradation studies. Biomaterials. 1987 Jul;8(4):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(87)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusty C. J., Doudoroff M. Poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate depolymerases of Pseudomonas lemoignei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):960–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Saito T., Fukui T., Shirakura Y., Tomita K. Purification and properties of extracellular poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerases from Pseudomonas lemoignei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 21;827(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer A., Jendrossek D., Schlegel H. G. Degradation of poly(3-hydroxyoctanoic acid) [P(3HO)] by bacteria: purification and properties of a P(3HO) depolymerase from Pseudomonas fluorescens GK13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Apr;59(4):1220–1227. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.4.1220-1227.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakura Y., Fukui T., Tanio T., Nakayama K., Matsuno R., Tomita K. An extracellular D(-)-3-hydroxybutyrate oligomer hydrolase from Alcaligenes faecalis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 28;748(2):331–339. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90310-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanio T., Fukui T., Shirakura Y., Saito T., Tomita K., Kaiho T., Masamune S. An extracellular poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase from Alcaligenes faecalis. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):71–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timm A., Steinbüchel A. Formation of polyesters consisting of medium-chain-length 3-hydroxyalkanoic acids from gluconate by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other fluorescent pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3360–3367. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3360-3367.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


