Abstract
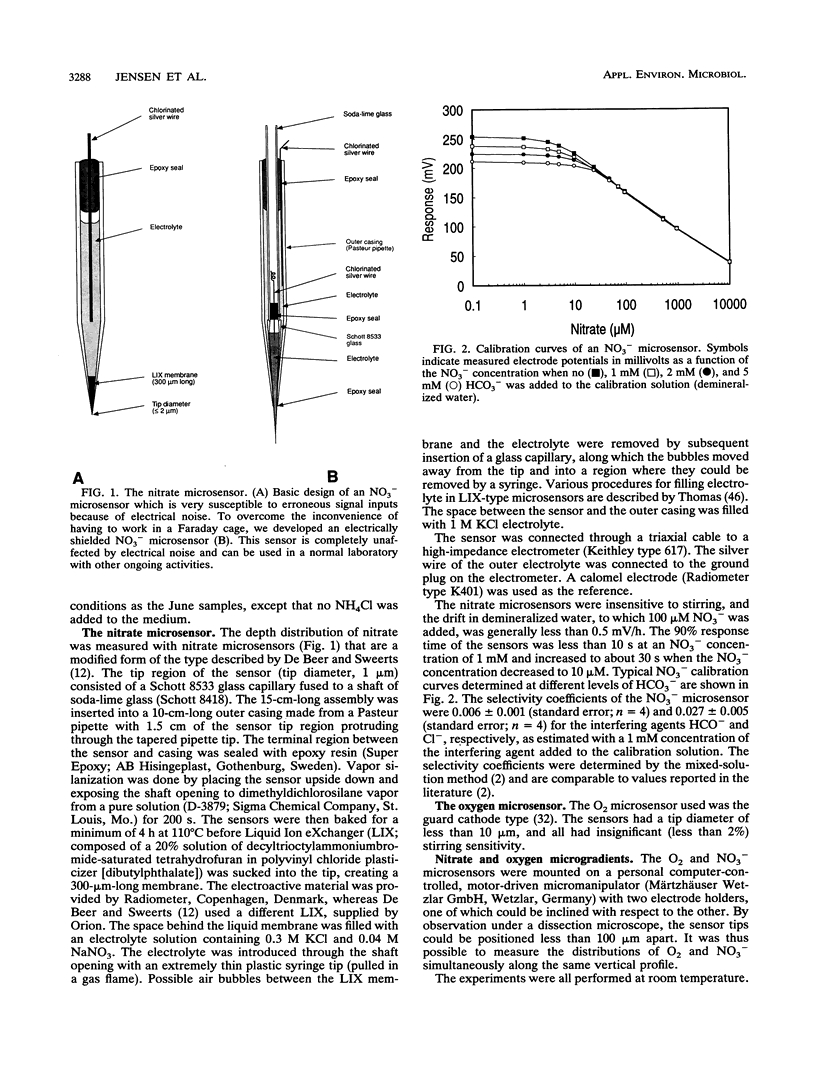
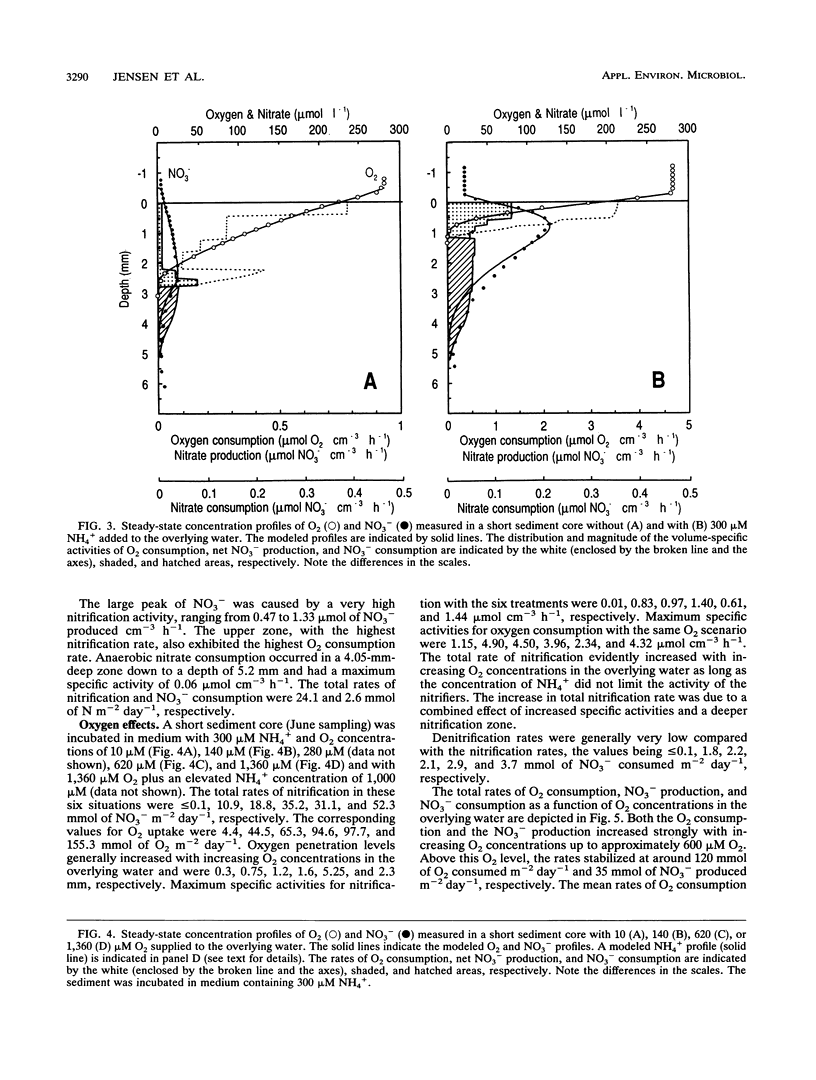
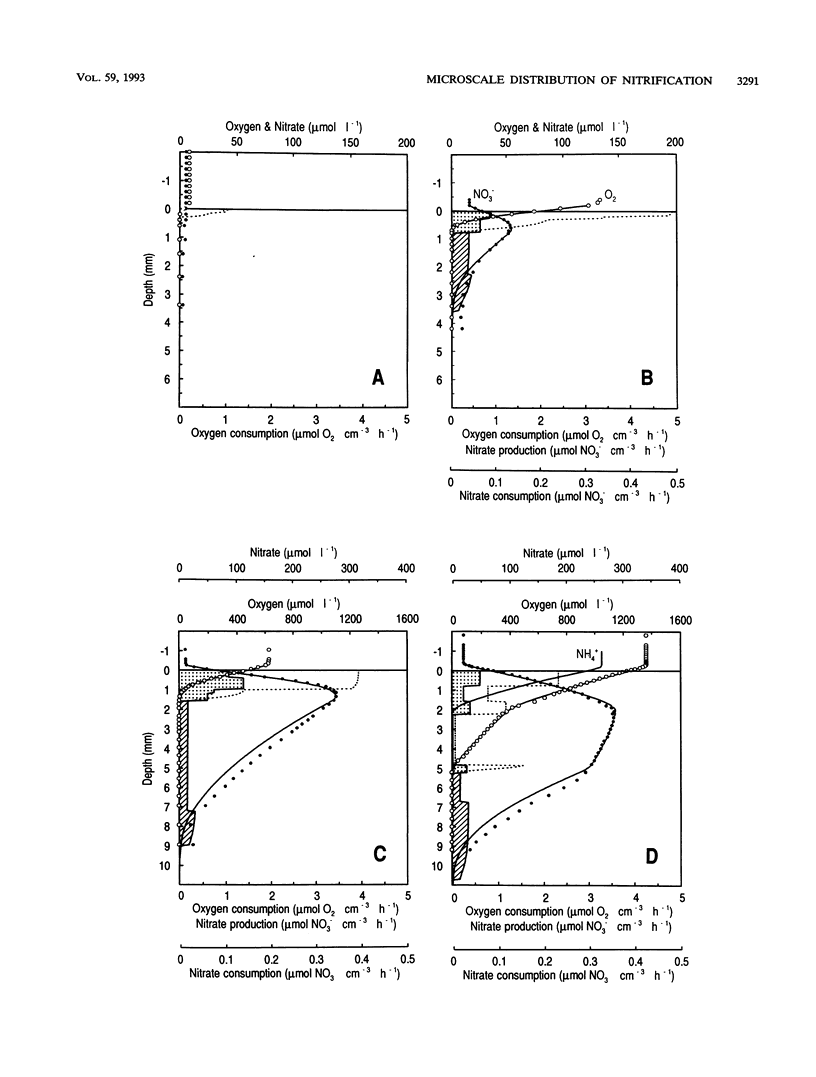
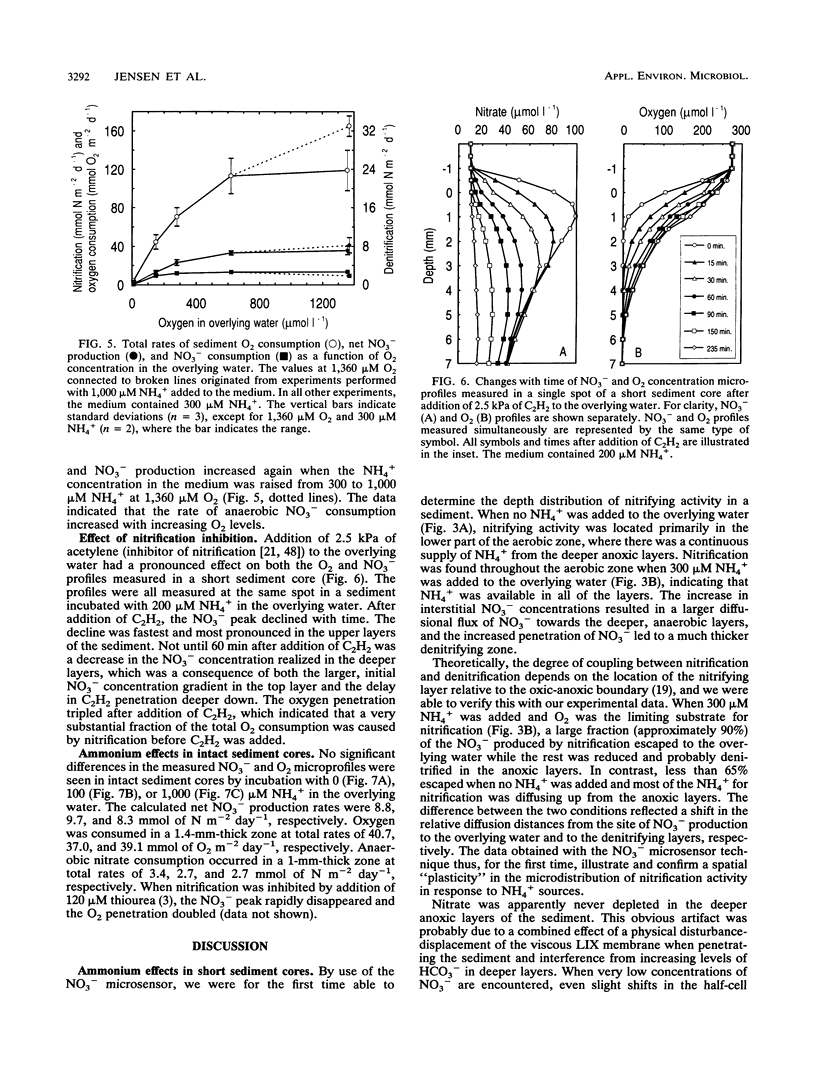
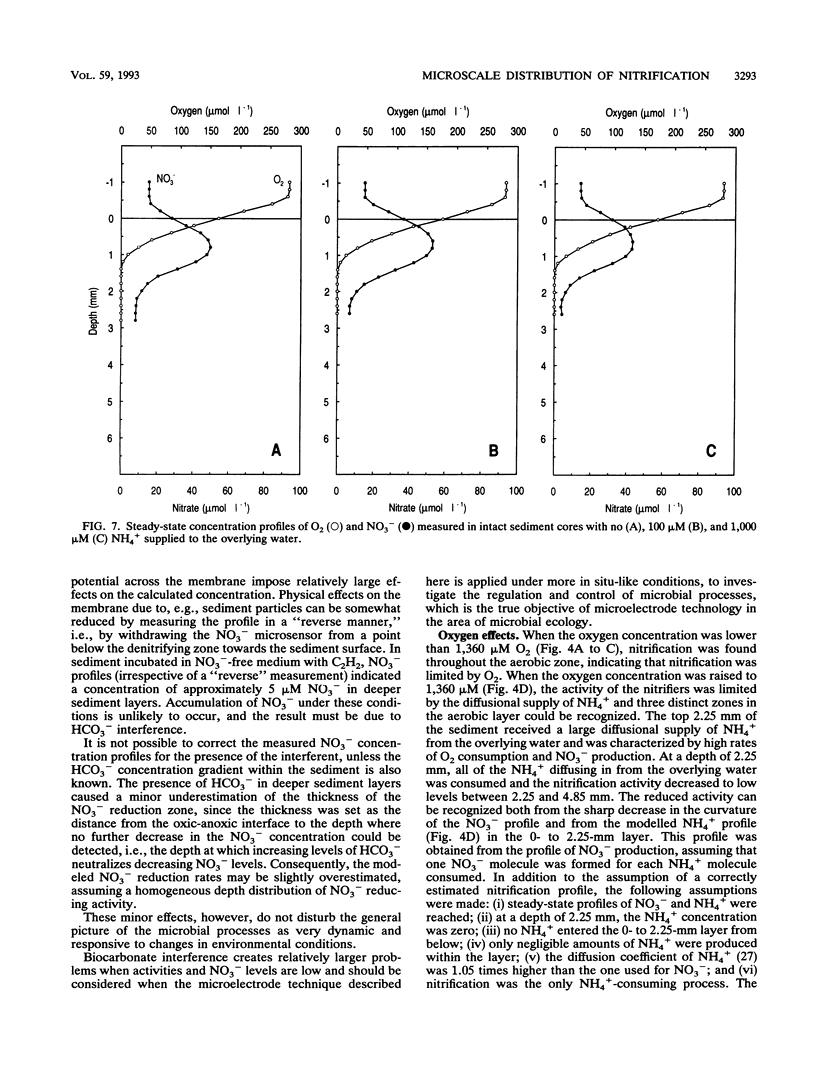
Microprofiles of O2 and NO3- were measured simultaneously in freshwater sediment with microsensors which were completely free from electrical interference because of coaxial designs. Depth profiles of nitrification (NO3- production) and denitrification (NO3- consumption) were subsequently determined by computer simulation of the measured microprofiles. The nitrifying bacterial community responded very quickly to changes in environmental conditions, and new steady-state microprofiles of O2 and NO3- were usually approached within a few hours after perturbation. Nitrification started quickly after introduction of O2 in previously anoxic layers, suggesting prolonged survival of the nitrifiers during anaerobiosis. Changes in the availability of O2 and NH4+ greatly affected the nitrification profile, and there was a high rate of coupled nitrification-denitrification under conditions in which nitrification occurred right above the oxic-anoxic interface. Addition of C2H2 rapidly removed the NO3- peaks, indicating that NO3- production was due mainly to autotrophic nitrification.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binnerup S. J., Jensen K., Revsbech N. P., Jensen M. H., Sørensen J. Denitrification, dissimilatory reduction of nitrate to ammonium, and nitrification in a bioturbated estuarine sediment as measured with N and microsensor techniques. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):303–313. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.303-313.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bédard C., Knowles R. Physiology, biochemistry, and specific inhibitors of CH4, NH4+, and CO oxidation by methanotrophs and nitrifiers. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):68–84. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.68-84.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P. B., Nielsen L. P., Revsbech N. P., Sørensen J. Microzonation of denitrification activity in stream sediments as studied with a combined oxygen and nitrous oxide microsensor. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1234–1241. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1234-1241.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman M. R., Wood P. M. Suicidal inactivation and labelling of ammonia mono-oxygenase by acetylene. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):719–725. doi: 10.1042/bj2270719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen B. B., Revsbech N. P. Colorless Sulfur Bacteria, Beggiatoa spp. and Thiovulum spp., in O(2) and H(2)S Microgradients. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1261–1270. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1261-1270.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike I., Hattori A. Simultaneous determinations of nitrification and nitrate reduction in coastal sediments by a 15N dilution technique. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):853–857. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.853-857.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühl M., Jørgensen B. B. Microsensor measurements of sulfate reduction and sulfide oxidation in compact microbial communities of aerobic biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Apr;58(4):1164–1174. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.4.1164-1174.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishio T., Koike I., Hattori A. Denitrification, nitrate reduction, and oxygen consumption in coastal and estuarine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):648–653. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.648-653.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimel J. P., Firestone M. K., Killham K. S. Identification of heterotrophic nitrification in a sierran forest soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):802–806. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.802-806.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweerts J. P., de Beer D. Microelectrode measurements of nitrate gradients in the littoral and profundal sediments of a meso-eutrophic lake (lake vechten, the Netherlands). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Mar;55(3):754–757. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.3.754-757.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen J. Denitrification rates in a marine sediment as measured by the acetylene inhibition technique. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):139–143. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.139-143.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


