Abstract
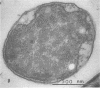
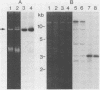
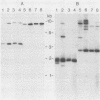
A gram-negative bacterium which hydrolyzed aryl N-methylcarbamate insecticides was isolated from an agricultural soil which quickly degraded these pesticides. This organism, designated strain ER2, grew on carbofuran as a sole source of carbon and nitrogen with a doubling time of 3 h in a mineral salts medium. The aromatic nucleus of the molecule was not metabolized, and carbofuran 7-phenol accumulated as the end product of metabolism. The insecticides carbaryl, bendiocarb, and propoxur were similarly hydrolyzed, with each yielding the corresponding phenol. Strain ER2 contained two plasmids (120 and 130 kb). A probe cloned from the pDL11 plasmid of Achromobacter sp. strain WM111, which encodes the carbofuran hydrolase (mcd) gene (P. H. Tomasek and J. S. Karns, J. Bacteriol. 171:4038-4044, 1989), hybridized to the 120-kb plasmid. Restriction fragment profiles of pDL11 and strain ER2 plasmid DNAs suggested that the 120-kb plasmid of strain ER2 is very similar to pDL11. On the basis of the results of biochemical tests, 16S rRNA sequence analysis, and membrane lipid analyses, strain ER2 was found to be a phylogenetically unique type II methylotroph. The constitutive carbofuran hydrolase activity in glucose-grown cells increased sevenfold when strain ER2 was grown in the presence of 100 mg of carbofuran per liter as the sole source of carbon and nitrogen or as the sole nitrogen source in the presence of glucose. Growth on carbofuran resulted in the induction of enzymes required for methylamine-dependent respiration and the serine pathway of formaldehyde assimilation. These results indicate that the carbofuran hydrolase mcd gene is conserved on a plasmid found in organisms from different geographic areas and that the specific activity of carbofuran degradation may increase in response to carbofuran treatment.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackmore M. A., Quayle J. R. Microbial growth on oxalate by a route not involving glyoxylate carboligase. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):53–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1180053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratina B. J., Brusseau G. A., Hanson R. S. Use of 16S rRNA analysis to investigate phylogeny of methylotrophic bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;42(4):645–648. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-4-645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapalamadugu S., Chaudhry G. R. Microbiological and biotechnological aspects of metabolism of carbamates and organophosphates. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 1992;12(5-6):357–389. doi: 10.3109/07388559209114232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry G. R., Ali A. N. Bacterial metabolism of carbofuran. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1414–1419. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1414-1419.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrastil J., Wilson J. T. A sensitive colorimeter method for formaldehyde. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jan;63(1):202–207. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Strom T., Quayle J. R. Purification and properties of 3-hexulose phosphate synthase and phospho-3-hexuloisomerase from Methylococcus capsulatus. Biochem J. 1974 Dec;144(3):477–486. doi: 10.1042/bj1440477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guckert J. B., Ringelberg D. B., White D. C., Hanson R. S., Bratina B. J. Membrane fatty acids as phenotypic markers in the polyphasic taxonomy of methylotrophs within the Proteobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Nov;137(11):2631–2641. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-11-2631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclennan D. G., Ousby J. C., Vasey R. B., Cotton N. T. The influence of dissolved oxygen on Pseudomonas AM1 grown on methanol in continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(3):395–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. H., Smith G. A., Fredrickson H. L., Vestal J. R., White D. C. Sensitive assay, based on hydroxy fatty acids from lipopolysaccharide lipid A, for Gram-negative bacteria in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Nov;44(5):1170–1177. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.5.1170-1177.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramanand K., Sharmila M., Singh N., Sethunathan N. Metabolism of carbamate insecticides by resting cells and cell-free preparations of a soil bacterium, Arthrobacter sp. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1991 Mar;46(3):380–386. doi: 10.1007/BF01688935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiert J. G., Crawford R. L. Catabolism of pentachlorophenol by a Flavobacterium sp. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):825–830. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasek P. H., Karns J. S. Cloning of a carbofuran hydrolase gene from Achromobacter sp. strain WM111 and its expression in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4038–4044. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4038-4044.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp E., Akhtar M. H. Identification and characterization of a pseudomonas strain capable of metabolizing phenoxybenzoates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1294–1300. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1294-1300.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp E., Knowles R. Effects of Nitrapyrin [2-Chloro-6-(Trichloromethyl) Pyridine] on the Obligate Methanotroph Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):258–262. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.258-262.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Bratina B. J., Tsuji K., Hanson R. S. Use of oligodeoxynucleotide signature probes for identification of physiological groups of methylotrophic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2858–2865. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2858-2865.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji K., Tsien H. C., Hanson R. S., DePalma S. R., Scholtz R., LaRoche S. 16S ribosomal RNA sequence analysis for determination of phylogenetic relationship among methylotrophs. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jan;136(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatcroft R., Watson R. J. A Positive Strain Identification Method for Rhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):574–576. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.574-576.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatcroft R., Watson R. J. Distribution of insertion sequence ISRm1 in Rhizobium meliloti and other gram-negative bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jan;134(1):113–121. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatcroft R., Williams P. A. Rapid methods for the study of both stable and unstable plasmids in Pseudomonas. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jun;124(2):433–437. doi: 10.1099/00221287-124-2-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]