Abstract
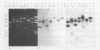
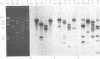
Transcription maps of the Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis prolate phage c2 and small isometric phage sk1 were constructed. Early and late transcripts were demonstrated in phage c2. Early transcription was localized to within a 7.5-kb EcoRV fragment, and late transcription included the region which encodes the phage structural proteins and a lysin gene. Early, middle, and late transcripts were demonstrated in phage sk1. Transcription was confined to an 11.3-kb region defined by the three EcoRV restriction fragments of 6.2, 4.7, and 0.46 kb during the early part of the sk1 life cycle. Middle gene transcripts extended from the EcoRV site (defining the left-hand limit of early gene expression) through the cos site and included the 4.3-kb PvuII-cos fragment. Late transcription was detected over the remainder of the phage genome. These results indicated that gene expression was temporally regulated at the level of transcription in these two lactococcal phages and that two regions of time-dependent transcription exist in phage c2 and three in phage sk1.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chung D. K., Chung S. K., Batt C. A. Antisense RNA directed against the major capsid protein of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris bacteriophage 4-1 confers partial resistance to the host. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1992 Apr;37(1):79–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00174207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Sinsheimer R. L. Process of infection with bacteriophage phiX174. XXXVII. RNA metabolism in phiX174-infected cells. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):151–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.151-160.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J. Plasmid complements of Streptococcus lactis NCDO 712 and other lactic streptococci after protoplast-induced curing. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Shub D. A. Transcriptional regulation of bacteriophage SPO1 protein synthesis in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):951–962. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.951-962.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C., Miller L. A., Klaenhammer T. R. Cloning, expression, and sequence determination of a bacteriophage fragment encoding bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6419–6426. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6419-6426.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C., Pierce K., Klaenhammer T. R. The conjugative plasmid pTR2030 encodes two bacteriophage defense mechanisms in lactococci, restriction modification (R+/M+) and abortive infection (Hsp+). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2416–2419. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2416-2419.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W. Differentiation of lactic streptococcal phages into phage species by DNA-DNA homology. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):343–349. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.343-349.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis Audrey W. Conjugal Transfer in Lactic Streptococci of Plasmid-Encoded Insensitivity to Prolate- and Small Isometric-Headed Bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):777–783. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.777-783.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. G., Batt C. A. Antisense mRNA-Mediated Bacteriophage Resistance in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1109–1113. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1109-1113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Farina M., Model P. Transcription in bacteriophage f1-infected Escherichia coli. Messenger populations in the infected cell. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 5;164(3):377–393. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A. Conjugative 40-megadalton plasmid in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis DRC3 is associated with resistance to nisin and bacteriophage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):68–74. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.68-74.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Phage lambda and the regulation of transcription termination. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90523-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sizemore C., Buchner E., Rygus T., Witke C., Götz F., Hillen W. Organization, promoter analysis and transcriptional regulation of the Staphylococcus xylosus xylose utilization operon. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jul;227(3):377–384. doi: 10.1007/BF00273926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A. Regional and temporal control of genetic transcription in phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1190–1195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. The genetics and physiology of bacteriophage T7. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):562–574. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C., Siegel R. B. Control of template specificity of E. coli RNA polymerase by a phage-coded protein. Nature. 1969 Sep 13;223(5211):1111–1113. doi: 10.1038/2231111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]