Abstract
Borrelia hermsii, Borrelia parkeri, Borrelia anserina, and Borrelia coriaceae produced several lipoproteins identified by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and fluorography of bacteria grown in [3H]palmitate. Five major acylated proteins were demonstrated by sequential alkaline and acid hydrolysis. High-pressure liquid chromatography of isolated proteins confirmed that covalently bound radioactivity was represented by fatty acids.
Full text
PDF
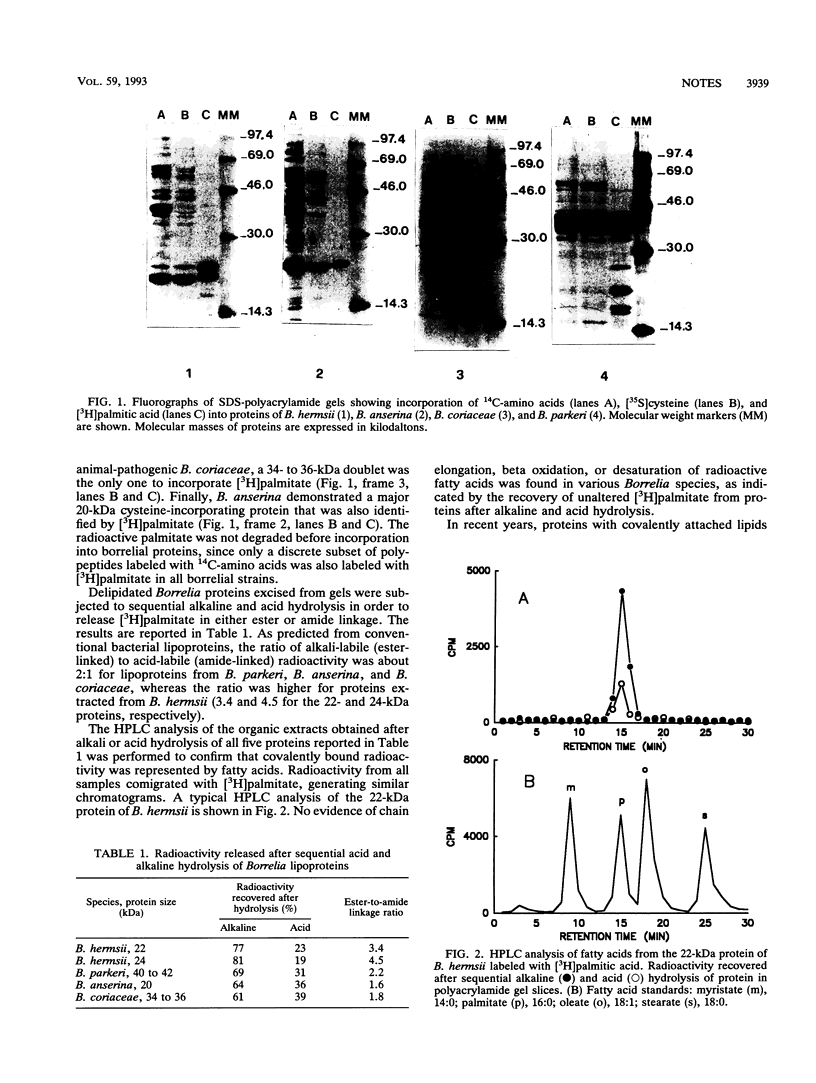

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandt M. E., Riley B. S., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Immunogenic integral membrane proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi are lipoproteins. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):983–991. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.983-991.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Brandt M. E., Erwin A. L., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Major integral membrane protein immunogens of Treponema pallidum are proteolipids. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2872–2877. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2872-2877.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DaMassa A. J., Adler H. E. Avian spirochetosis: natural transmission by Argas (Persicargas) sanchezi (Ixodoidea: argasidae) and existence of different serologic and immunologic types of Borrelia anserina in the United States. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Jan;40(1):154–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deich R. A., Metcalf B. J., Finn C. W., Farley J. E., Green B. A. Cloning of genes encoding a 15,000-dalton peptidoglycan-associated outer membrane lipoprotein and an antigenically related 15,000-dalton protein from Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):489–498. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.489-498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdile L. F., Brandt M. A., Warakomski D. J., Westrack G. J., Sadziene A., Barbour A. G., Mays J. P. Role of attached lipid in immunogenicity of Borrelia burgdorferi OspA. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):81–90. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.81-90.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C. Anatomy and chemistry of spirochetes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):114–160. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.114-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. A., Johnson R. C. Methylated DNA in Borrelia species. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6602–6604. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6602-6604.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona L. I., Beck G., Habicht G. S. Purification and immunological characterization of a major low-molecular-weight lipoprotein from Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):4995–5003. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.4995-5003.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehl K. S., Farmer S. G., Komorowski R. A., Knox K. K. Antigenic variation among Borrelia spp. in relapsing fever. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):899–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.899-902.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Burgdorfer W., Hayes S. F., Barbour A. G. Isolation of a spirochete from the soft tick, Ornithodoros coriaceus: a possible agent of epizootic bovine abortion. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.3898367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S. Post-translational modification and processing of outer membrane prolipoproteins in Escherichia coli. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;60(1):5–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00226297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. B., Lampen J. O. Glyceride-cysteine lipoproteins and secretion by Gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):315–322. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.315-322.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley B. S., Oppenheimer-Marks N., Hansen E. J., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Virulent Treponema pallidum activates human vascular endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):484–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambri V., Cevenini R. Incorporation of cysteine by Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia hermsii. Can J Microbiol. 1992 Oct;38(10):1016–1021. doi: 10.1139/m92-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambri V., Moroni A., Massaria F., Brocchi E., De Simone F., Cevenini R. Immunological characterization of a low molecular mass polypeptidic antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1991 Nov;3(6):345–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1991.tb04260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoenner H. G. Biology of Borrelia hermsii in Kelly medium. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):540–543. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.540-543.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel L. M., Brandt M. E., Norgard M. V. Analysis of the N-terminal region of the 47-kilodalton integral membrane lipoprotein of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1568–1576. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1568-1576.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg G. A., Towler D. A., Munson R. S., Jr Lipoproteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4161–4164. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4161-4164.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Kim M. F. Major membrane surface proteins of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae selectively modified by covalently bound lipid. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5546–5555. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5546-5555.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Tokunaga M. Biogenesis of lipoproteins in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:127–157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



