Abstract
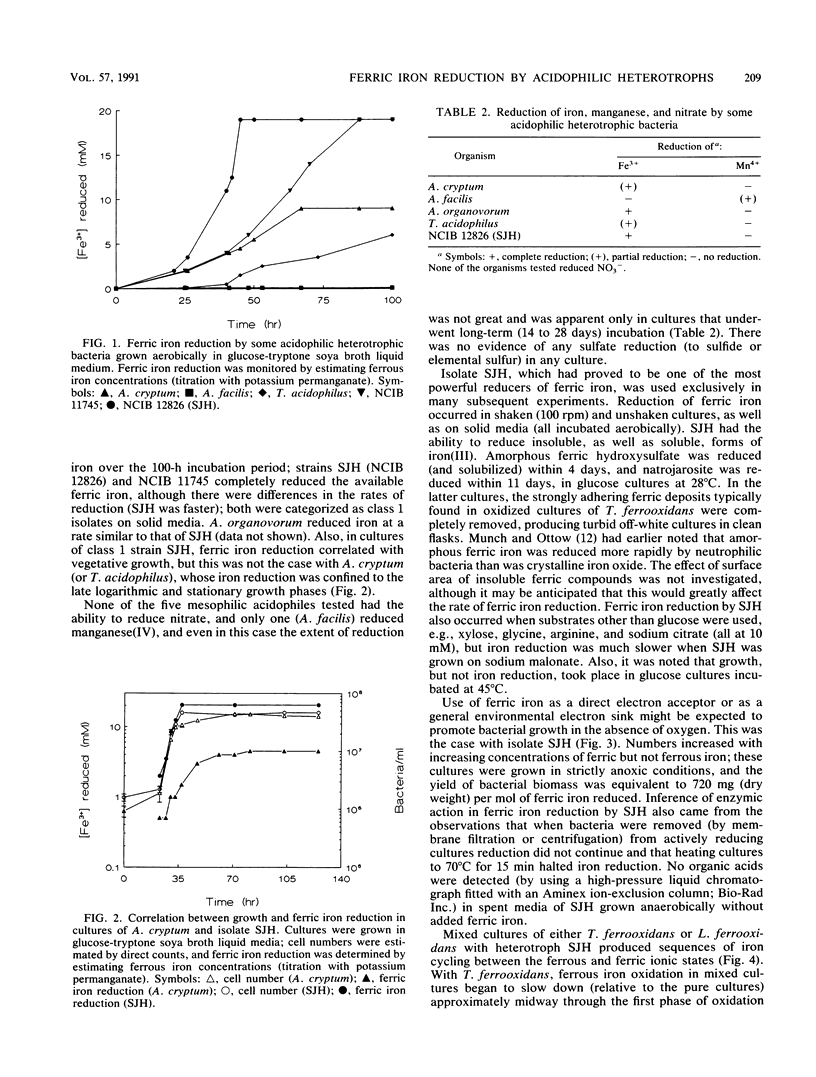
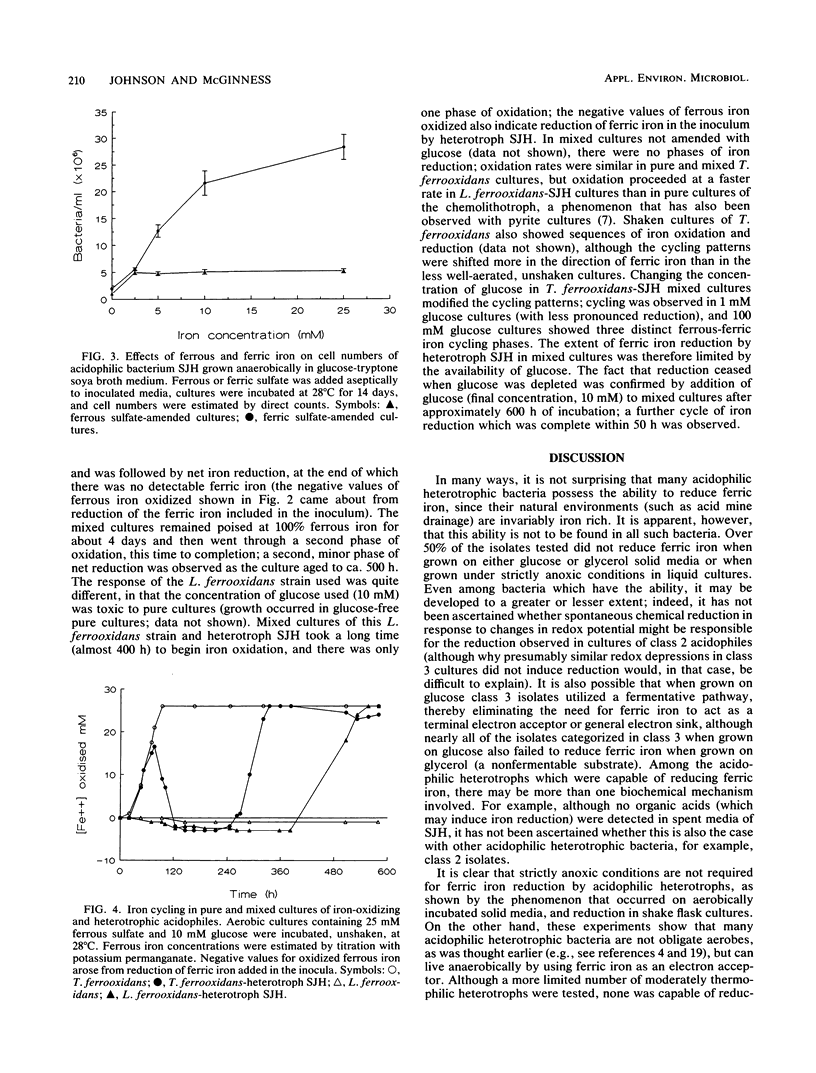
Fifty mesophilic and five moderately thermophilic strains of acidophilic heterotrophic bacteria were tested for the ability to reduce ferric iron in liquid and solid media under aerobic conditions; about 40% of the mesophiles (but none of the moderate thermophiles) displayed at least some capacity to reduce iron. Both rates and extents of ferric iron reduction were highly strain dependent. No acidophilic heterotroph reduced nitrate or sulfate, and (limited) reduction of manganese(IV) was noted in only one strain (Acidiphilium facilis), an acidophile which did not reduce iron. Insoluble forms of ferric iron, both amorphous and crystalline, were reduced, as well as soluble iron. There was evidence that, in at least some acidophilic heterotrophs, iron reduction was enzymically mediated and that ferric iron could act as a terminal electron acceptor. In anaerobically incubated cultures, bacterial biomass increased with increasing concentrations of ferric but not ferrous iron. Mixed cultures of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans or Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and an acidophilic heterotroph (SJH) produced sequences of iron cycling in ferrous iron-glucose media.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brock T. D., Gustafson J. Ferric iron reduction by sulfur- and iron-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):567–571. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.567-571.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazaroff N., Sigal W., Wasserman A. Iron Oxidation and Precipitation of Ferric Hydroxysulfates by Resting Thiobacillus ferrooxidans Cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):924–938. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.924-938.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C., Von Klopotek A. Enzymatic reduction of iron oxide by fungi. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jul;18(1):41–43. doi: 10.1128/am.18.1.41-43.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugio T., Tsujita Y., Inagaki K., Tano T. Reduction of Cupric Ions with Elemental Sulfur by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Mar;56(3):693–696. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.3.693-696.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wichlacz P. L., Unz R. F. Acidophilic, heterotrophic bacteria of acidic mine waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1254–1261. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1254-1261.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



